


生物技术进展 ›› 2023, Vol. 13 ›› Issue (2): 181-194.DOI: 10.19586/j.2095-2341.2022.0141
• 进展评述 • 上一篇
收稿日期:2022-08-09
接受日期:2022-09-09
出版日期:2023-03-25
发布日期:2023-04-07
通讯作者:
徐玉泉
作者简介:宋开南 E-mail: S15850653283@126.com;
基金资助:
Kainan SONG( ), Linan XIE, Yuquan XU(
), Linan XIE, Yuquan XU( )
)
Received:2022-08-09
Accepted:2022-09-09
Online:2023-03-25
Published:2023-04-07
Contact:
Yuquan XU
摘要:
在农业生产中,化学除草剂的广泛使用虽然能确保作物产量,但也引发了许多环境问题,同时杂草对除草剂的抗性也会随之进化。因此,亟需开发安全性更强、作用机制更新颖的除草剂。真菌可以合成多种结构复杂的次级代谢产物,其中一些具有良好的除草活性。按照结构类型,综述了近十年国内外从真菌中分离的具有除草活性的次级代谢产物,并对真菌除草活性化合物的发展方向及应用前景进行了展望,以期为新型除草剂的研究与开发提供参考。
中图分类号:
宋开南, 谢李楠, 徐玉泉. 真菌除草活性次级代谢产物研究进展[J]. 生物技术进展, 2023, 13(2): 181-194.
Kainan SONG, Linan XIE, Yuquan XU. Progress of Fungal Secondary Metabolites with Potential Herbicidal Activity[J]. Current Biotechnology, 2023, 13(2): 181-194.
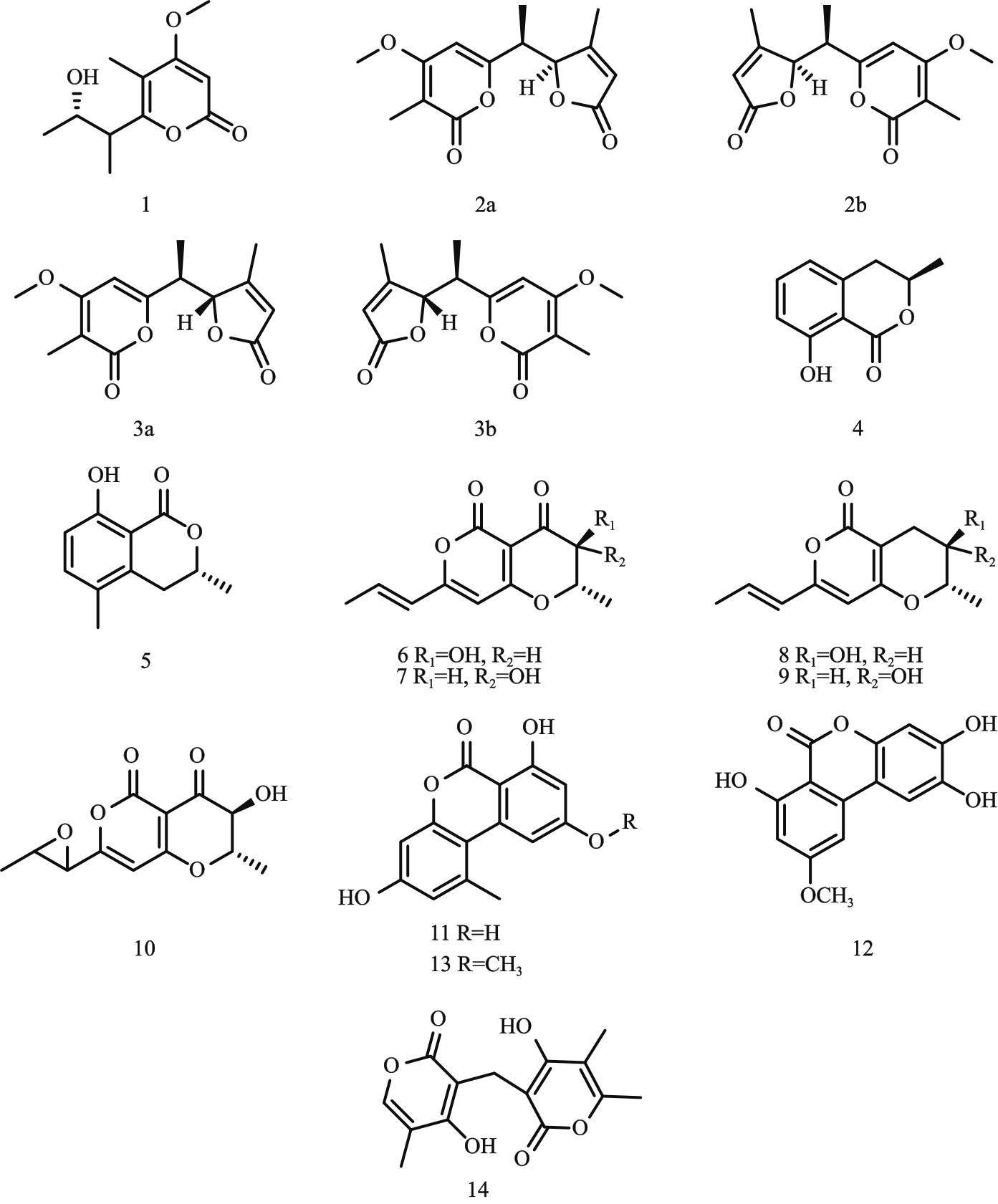
图1 α-吡喃酮类化合物结构式注:1—gulypyrones A;2—alterpyrones A;3—alterpyrones B;4—6-hydroxymellein;5—5-methylmellein;6—radicinin;7—3-epi-radicinin;
Fig. 1 Structural formula of α-pyrone compounds8—radicinol;9—3-epi-radicinol;10—cochliotoxin;11—alternariol;12—altenuisol;13—alternariol-9-methyl ether;14—colletopyrone。
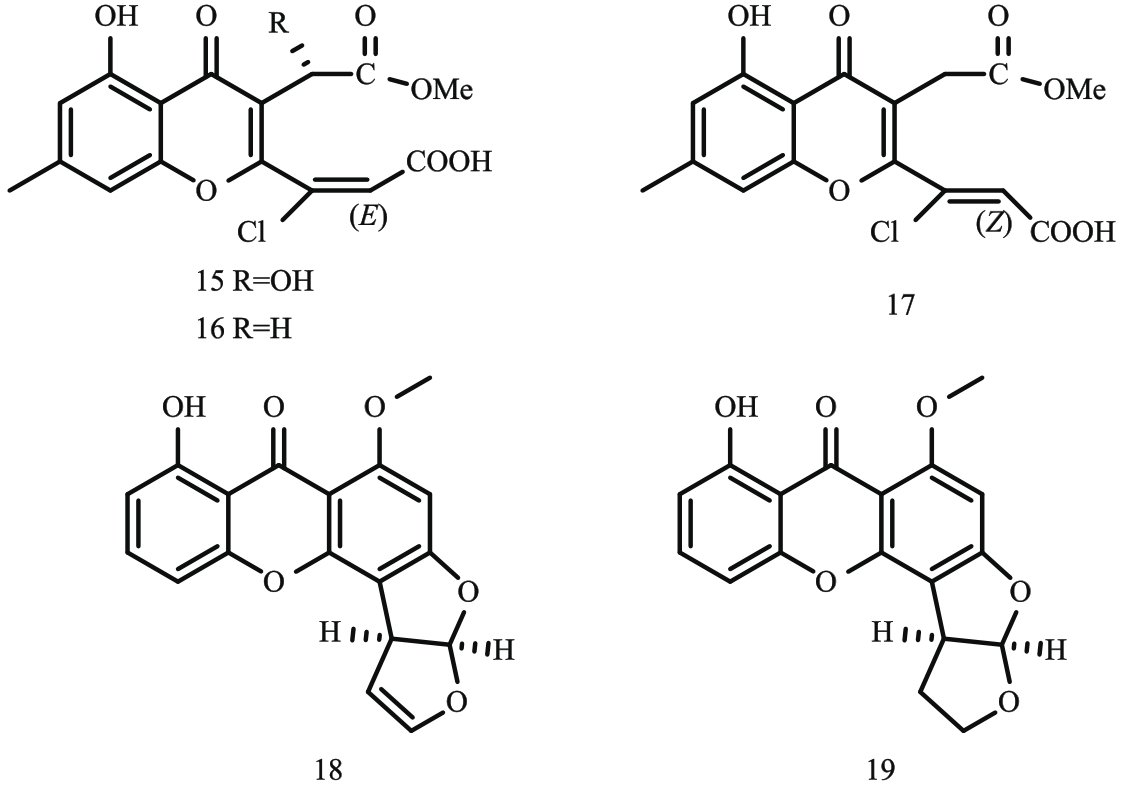
图2 γ-吡喃酮类化合物结构式注:15—chloromonilinic acid C;16—chloromonilinic acid D;17—chloromonilinic acid B;18—sterigmatocystin;19—dihydrosterigmatocystin。
Fig. 2 Structural formula οf γ-pyrone compounds
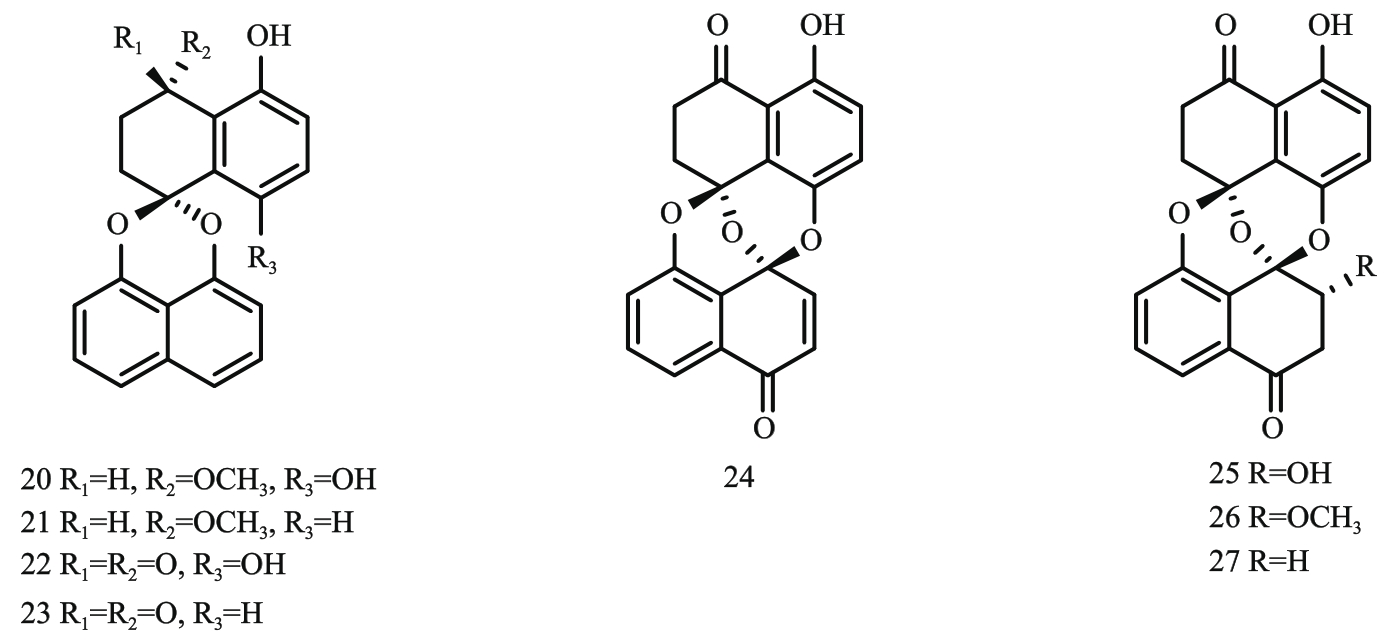
图3 螺二萘类化合物结构式注:20—palmarumycin EG1;21—palmarumycin CP19;22—palmarumycin CP17;23—palmarumycin CP2;24—preussomerin EG1;25—preussomerin EG2;26—preussomerin EG3;27—preussomerin EG4。
Fig. 3 Structural formula οf spirodinaphthalene compounds
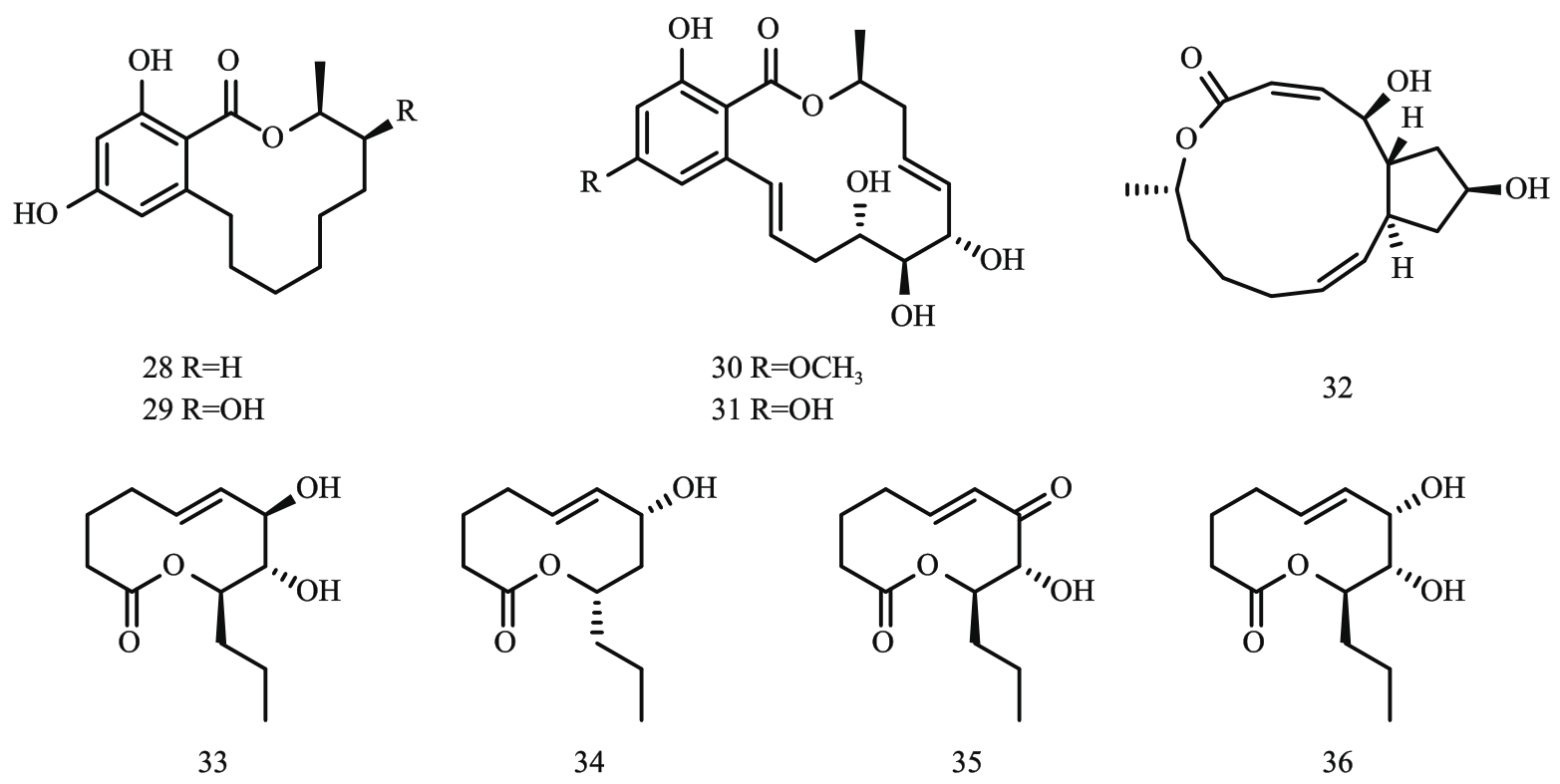
图4 大环内酯类化合物结构式注:28—(15S)-de-O-methyllasiodiplodin;29—(14S,15S)-14-hydroxy-de-O-methyllasiodiplodin;30—zeaenol;31—O-demethylated-zeaenol;
Fig. 4 Structural formula οf macrolide compounds32—ascotoxin;33—stagonolide J;34—stagonolide K;35—stagonolide A;36—herbarumin I。
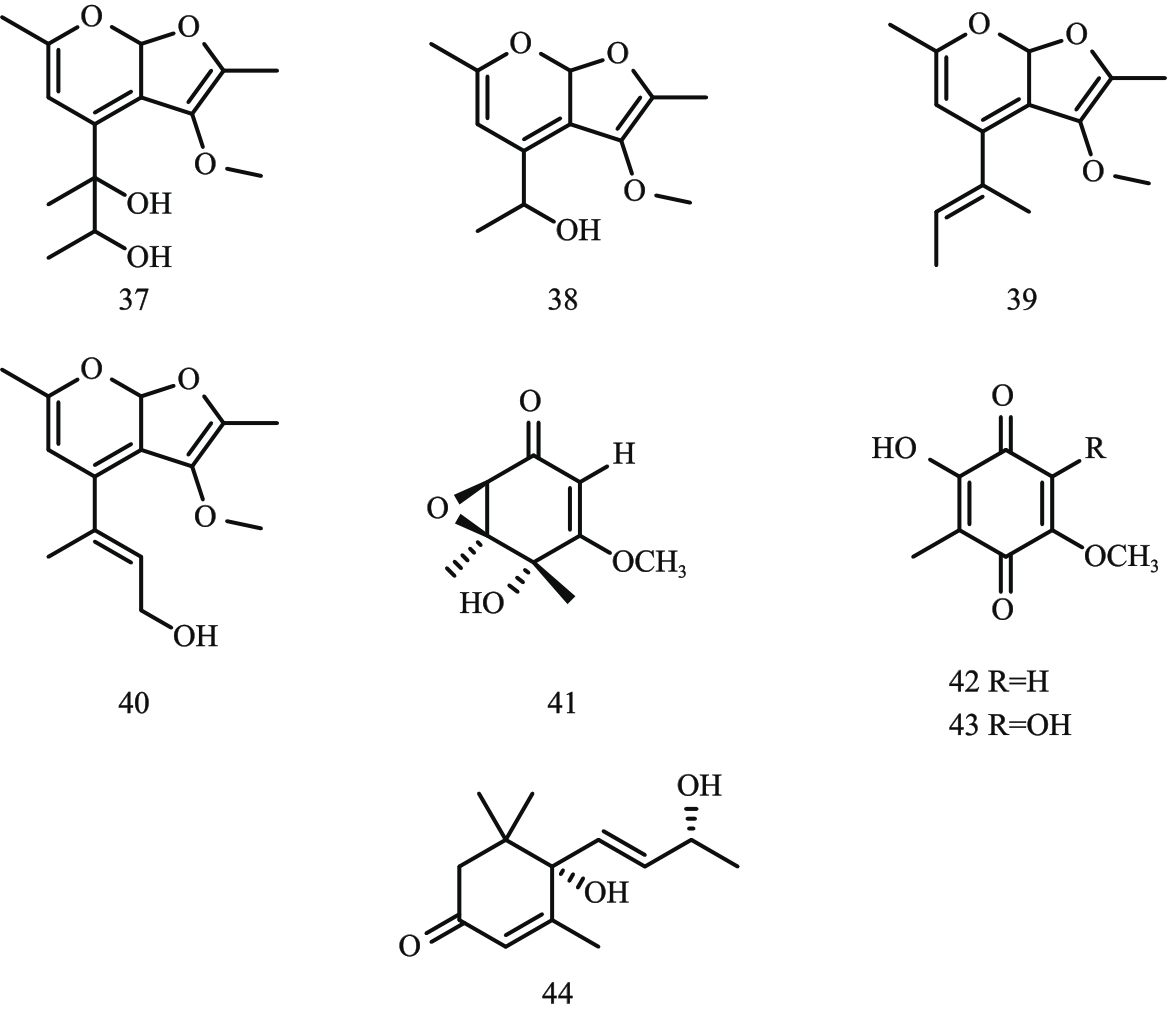
图5 呋喃并吡喃类与环己酮类化合物结构式注:37—chenopodolan A;38—chenopodolan B;39—chenopodolan C;40—chenopodolan D;41—coriloxine;42—2-hydroxy-5-methoxy-3-methylcyclohexa-2,5-diene-1,4-dione;43—fumiquinone B;44—blumenol A。
Fig. 5 Structural formula of furopyran and cyclohexanone compounds
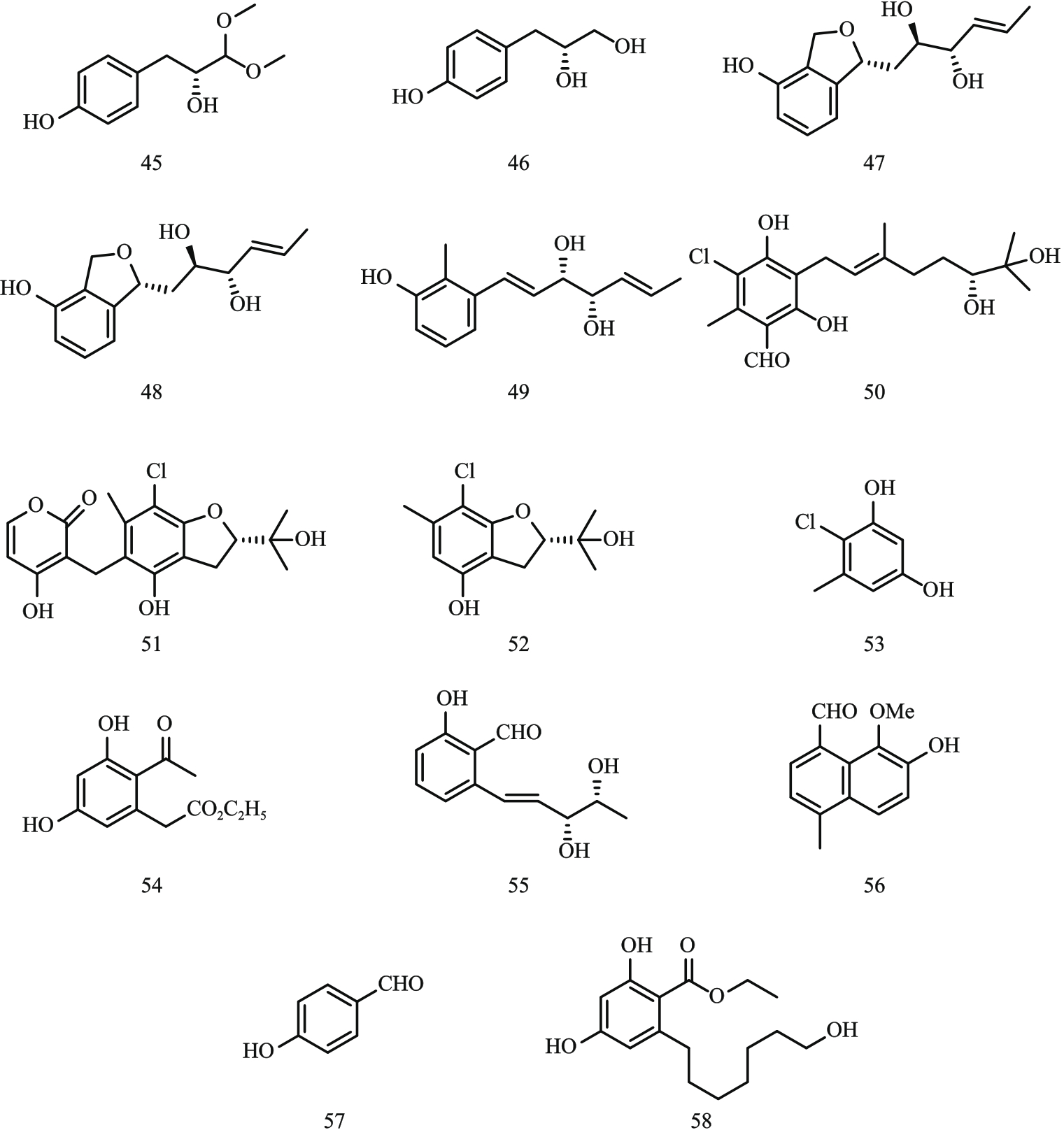
图6 酚类化合物结构式注:45—lathyroxin A;46—lathyroxin B;47—pyriculin A;48—pyriculin B;49—(10S,11S)‐(-)‐epi-pyriculol;50—colletochlorin A;51—colletochlorin E;52—colletochlorin F;53—4-chloroorcinol;54—curvulin;55—agropyrenol;56—agropyrenal;57—4-hydroxybenzaldehyde;58—ethyl 2,4-dihydroxy-6-(8-hydroxyheptyl)benzoate。
Fig. 6 Structural formula of phenol compounds

图7 萜类化合物结构式注:59—phomentrioloxin;60—phomentrioloxins B;61—phomentrioloxins C;62—ophiobolin A;63—drophiobiolin A;64—drophiobiolin B;
Fig. 7 Structural formula of terpenoid compounds65—chenopodolin;66—chenopodolin B;67—harzianelactone A;68—harzianelactone B;69—harzianone A;70—harzianone B;71—harzianone C;72—harziane。
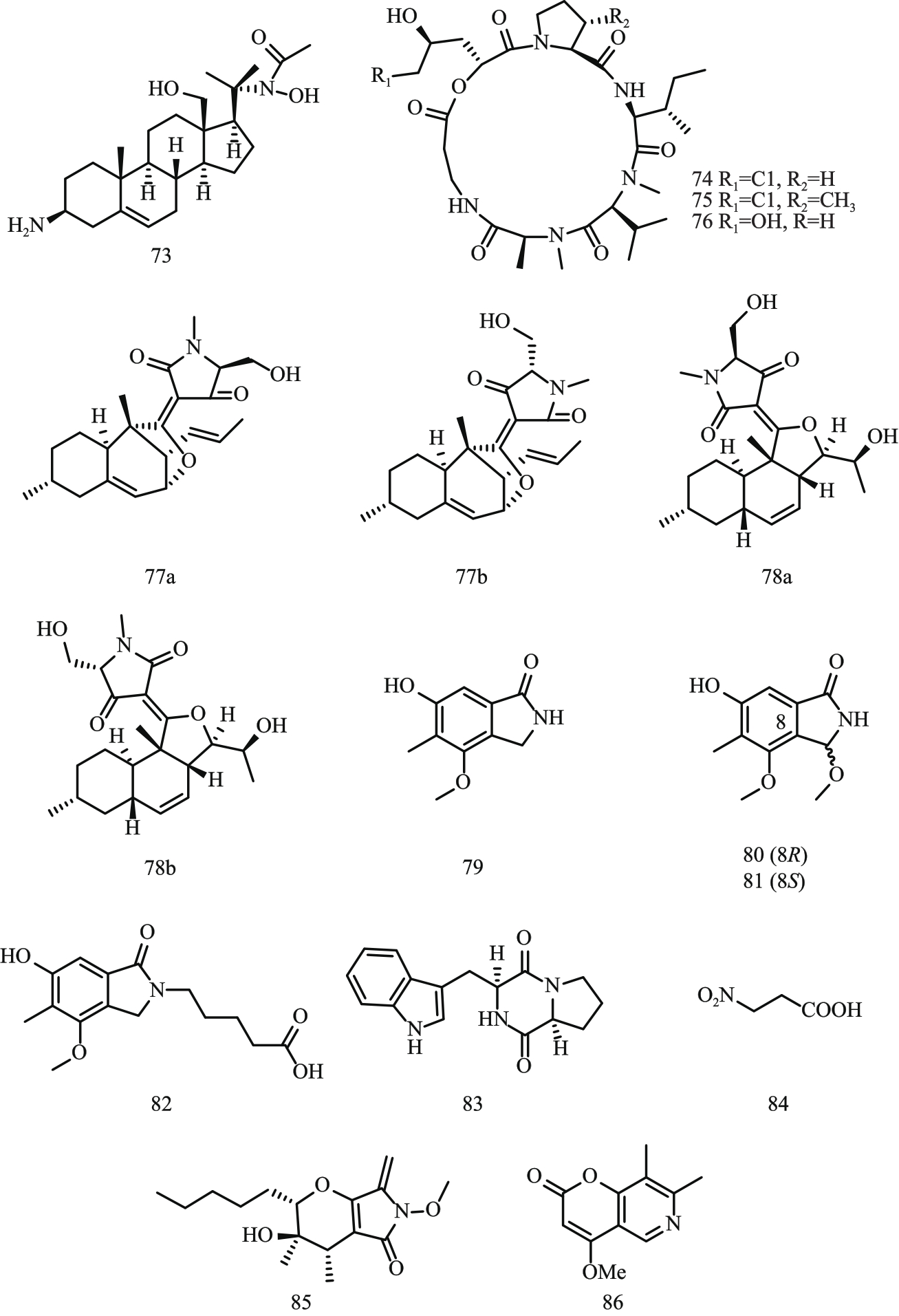
图8 含氮类化合物结构式注:73—holadysenterine;74—destruxin A;75—destruxin B;76—destruxin C;77—decalintetracid A;78—decalintetracid B;79—cichorine;
Fig. 8 Structural formula of nitrogen-containing compounds80—8-methoxycichorine;81—8-epi-methoxycichorine;82—N-(4-carboxybutyl)cichorine;83—brevianamide F;84—3-nitropropionic; 85—phaeosphaeride A;86—acuminatopyrone。
| 菌株种属 | 化合物在文中的编号 | 靶向杂草 | 参考文献 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 间座壳属D. gulyae | 1, 60~61, 84 | 向日葵H.annuus 虞美人P. rhoeas 异株荨麻U. dioica | [ |
| 甘蓝链格孢A. brassicicola | 2~3 | 稗草E. crusgalli 狗尾草S. viridis | [ |
| 藜茎点霉P. chenopodiicola | 4, 37~39 | 苦苣菜S. oleraceus L. 法国山靛M. annua | [ |
| 甜樱间座壳D. eres | 5 | 西伯利亚剪股颖A. stolonifera 浮萍L. pausicostata | [ |
| 澳大利亚平脐蠕孢C. australiensis | 5~10 | 绿毛蒺藜草C. ciliaris 加利福尼亚马唐D. californica | [ |
| 链格孢属Alternaria sp. | 11~12 | 狼尾草P. alopecuroides 紫花苜蓿M. sativa | [ |
| 希金斯刺盘孢C. higginsianum | 14, 50~53 | 浮萍L. minor 小苞列当属P. ramose | [ |
| 澳大利亚平脐蠕孢C. australiensis | 15~17 | 绿毛蒺藜草C. ciliaris | [ |
| 杂色曲霉菌A. versicolor | 18~19 | 反枝苋A. retroflexus L. 刺苋A. spinosus 绿穗苋A. hybrid | [ |
| E. gomezpompae | 20~27 | 千穗谷A. hypochondriacus 稗草E. crusgalli | [ |
| 龙眼焦腐病菌L. theobromae GC~22 | 28~29, 58 | 升马唐D. ciliaris | [ |
| C. crepinii | 30~31 | 稗草E. crusgalli | [ |
| Paraconiothyrium sp. | 32 | 稗草E. crusgalli | [ |
| 壳多胞属S. cirsii | 33~36 | 苣荬菜S. arvensis | [ |
| 藜茎点霉P. chenopodiicola | 40, 66 | 繁缕S. media 大荨麻U. dioica 苣荬菜S.arvensis 墙草P. officinalis | [ |
| 炭角菌属X. feejeensis | 41~43 | 红车轴草T. pratense 紫花苜蓿M. sativa 黍P. miliaceum 千穗谷A. hypochondriacus | [ |
| 镰刀菌属Fusarium sp. | 44, 57, 86 | 旱雀麦B. tectorum | |
| 壳二孢属A. lentis var. lathyri | 45~46 | 列当属P. ramosa | [ |
| 梨孢属P.grisea | 47~49 | 绿毛蒺藜草C. ciliaris | [ |
| 胶胞炭疽菌C. gloeosporioides | 50 | 豚草A. artemisiifolia 浮萍 | [ |
| 异茎点霉属Paraphoma sp. VIZR 1.46 | 54, 85 | 田蓟C. arvense 偃麦草E. repens | [ |
| 壳二孢叶斑病菌A. agropyrina var. nana | 55~56 | 偃麦草E. repens 法国山靛M. annua 狗尾草S. viridis 黍P. miliaceum | [ |
| 拟茎点霉属Phomopsis sp. | 59 | 毛红花C. lanatus | [ |
| 内脐蠕孢属D. gigantea | 62~64 | 马唐D. sanguinalis 藜C. album | [ |
| 藜茎点霉P. chenopodiicola | 65 | 山靛M. annua 田蓟C. arvense 狗尾草S. viridis | [ |
| 哈茨木霉T. harzianum XS~20090075 | 67~72 | 反枝苋A. retroflexus | [ |
| 澳大利亚德氏霉D. australiensis | 73 | 齿果酸模R. dentatus | [ |
| 白僵菌B. felina | 74~76 | 反枝苋A. retroflexus | [ |
| 木贼镰刀菌F. equiseti D39 | 77~78 | 反枝苋A. retroflexus A. hybrid | [ |
| 构巢曲霉A. nidulans | 79~82 | 南苜蓿M. polymorpha | [ |
| 烟曲霉A. fumigatus | 83 | 反枝苋A. mangostanus | [ |
表1 具有除草活性的真菌次级代谢产物(2012—2022)
Table 1 Herbicidal secondary metabolites from fungi (2012—2022)
| 菌株种属 | 化合物在文中的编号 | 靶向杂草 | 参考文献 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 间座壳属D. gulyae | 1, 60~61, 84 | 向日葵H.annuus 虞美人P. rhoeas 异株荨麻U. dioica | [ |
| 甘蓝链格孢A. brassicicola | 2~3 | 稗草E. crusgalli 狗尾草S. viridis | [ |
| 藜茎点霉P. chenopodiicola | 4, 37~39 | 苦苣菜S. oleraceus L. 法国山靛M. annua | [ |
| 甜樱间座壳D. eres | 5 | 西伯利亚剪股颖A. stolonifera 浮萍L. pausicostata | [ |
| 澳大利亚平脐蠕孢C. australiensis | 5~10 | 绿毛蒺藜草C. ciliaris 加利福尼亚马唐D. californica | [ |
| 链格孢属Alternaria sp. | 11~12 | 狼尾草P. alopecuroides 紫花苜蓿M. sativa | [ |
| 希金斯刺盘孢C. higginsianum | 14, 50~53 | 浮萍L. minor 小苞列当属P. ramose | [ |
| 澳大利亚平脐蠕孢C. australiensis | 15~17 | 绿毛蒺藜草C. ciliaris | [ |
| 杂色曲霉菌A. versicolor | 18~19 | 反枝苋A. retroflexus L. 刺苋A. spinosus 绿穗苋A. hybrid | [ |
| E. gomezpompae | 20~27 | 千穗谷A. hypochondriacus 稗草E. crusgalli | [ |
| 龙眼焦腐病菌L. theobromae GC~22 | 28~29, 58 | 升马唐D. ciliaris | [ |
| C. crepinii | 30~31 | 稗草E. crusgalli | [ |
| Paraconiothyrium sp. | 32 | 稗草E. crusgalli | [ |
| 壳多胞属S. cirsii | 33~36 | 苣荬菜S. arvensis | [ |
| 藜茎点霉P. chenopodiicola | 40, 66 | 繁缕S. media 大荨麻U. dioica 苣荬菜S.arvensis 墙草P. officinalis | [ |
| 炭角菌属X. feejeensis | 41~43 | 红车轴草T. pratense 紫花苜蓿M. sativa 黍P. miliaceum 千穗谷A. hypochondriacus | [ |
| 镰刀菌属Fusarium sp. | 44, 57, 86 | 旱雀麦B. tectorum | |
| 壳二孢属A. lentis var. lathyri | 45~46 | 列当属P. ramosa | [ |
| 梨孢属P.grisea | 47~49 | 绿毛蒺藜草C. ciliaris | [ |
| 胶胞炭疽菌C. gloeosporioides | 50 | 豚草A. artemisiifolia 浮萍 | [ |
| 异茎点霉属Paraphoma sp. VIZR 1.46 | 54, 85 | 田蓟C. arvense 偃麦草E. repens | [ |
| 壳二孢叶斑病菌A. agropyrina var. nana | 55~56 | 偃麦草E. repens 法国山靛M. annua 狗尾草S. viridis 黍P. miliaceum | [ |
| 拟茎点霉属Phomopsis sp. | 59 | 毛红花C. lanatus | [ |
| 内脐蠕孢属D. gigantea | 62~64 | 马唐D. sanguinalis 藜C. album | [ |
| 藜茎点霉P. chenopodiicola | 65 | 山靛M. annua 田蓟C. arvense 狗尾草S. viridis | [ |
| 哈茨木霉T. harzianum XS~20090075 | 67~72 | 反枝苋A. retroflexus | [ |
| 澳大利亚德氏霉D. australiensis | 73 | 齿果酸模R. dentatus | [ |
| 白僵菌B. felina | 74~76 | 反枝苋A. retroflexus | [ |
| 木贼镰刀菌F. equiseti D39 | 77~78 | 反枝苋A. retroflexus A. hybrid | [ |
| 构巢曲霉A. nidulans | 79~82 | 南苜蓿M. polymorpha | [ |
| 烟曲霉A. fumigatus | 83 | 反枝苋A. mangostanus | [ |
| 1 | 费云燕, 杨军, 景德道, 等. CRISPR/Cas技术在抗除草剂作物育种中的研究与应用进展[J]. 生物技术进展, 2022, 12(2): 189-197. |
| 2 | 李永祥, 冯春刚, 童德云. 草甘膦使用中存在的问题及正确使用方法[J]. 植物医生, 2014, 27(6): 44-46. |
| 3 | 杨洪李, 黄红娟, 王兆振, 等. 草甘膦对七种作物的安全性[J]. 植物保护, 2022, 48(2): 220-226+272. |
| 4 | 张翼翾. 全球抗草甘膦杂草的概况[J]. 世界农药, 2018, 40(3): 38-45. |
| 5 | 陈仕红, 冉海燕, 兰献敏, 等. 马唐和反枝苋对草甘膦的抗药性[J]. 农学学报, 2022, 12(2): 20-25. |
| 6 | XU D, XUE M, SHEN Z, et al.. Phytotoxic secondary metabolites from fungi[J/OL]. Toxins, 2021 13(4), 261[2022-12-20]. . |
| 7 | CIMMINO A, MASI M, EVIDENTE M, et al.. Fungal phytotoxins with potential herbicidal activity: chemical and biological characterization[J]. Natl. Prod. Rep., 2015,32(12):1629-1653. |
| 8 | ANDOLFI A, BOARI A, EVIDENTE M, et al.. Gulypyrones A and B and phomentrioloxins B and C produced by diaporthe gulyae, a potential mycoherbicide for saffron thistle (Carthamus lanatus)[J]. J. Natl. Prod., 2015, 78(4):623-629. |
| 9 | LI F, YE Z, HUANG Z, et al.. New α-pyrone derivatives with herbicidal activity from the endophytic fungus Alternaria brassicicola [J/OL]. Bioorg. Chem., 2021,117: 105452[2022-12-20]. |
| 10 | CIMMINO A, ANDOLFI A, ZONNO M C, et al.. Chenopodolans A-C: phytotoxic furopyrans produced by Phoma chenopodiicola, a fungal pathogen of Chenopodium album [J]. Phytochemistry, 2013,96:208-213. |
| 11 | MEEPAGALA K M, BRISCOE W E, TECHEN N, et al.. Isolation of a phytotoxic isocoumarin from Diaportheeres-infected Hedera helix (English ivy) and synthesis of its phytotoxic analogs[J]. Pest Manag. Sci., 2017,74:37-45. |
| 12 | MASI M, MEYER S, CLEMENT S, et al.. Cochliotoxin, a dihydropyranopyran-4,5-dione, and its analogues produced by cochliobolus australiensis display phytotoxic activity against buffelgrass (Cenchrus ciliaris)[J]. J. Nat. Prod., 2017, 80:1241-1247. |
| 13 | TANG J, HUANG L, LIU Y, et al.. Two phytotoxins isolated from the pathogenic fungus of the invasive weed Xanthium italicum [J/OL]. Chem. Biodivers, 2020, 17:e2000043[2022-12-20]. . |
| 14 | DEMUNER A J, BARBOSA L C A, MIRANDA A C M, et al.. The fungal phytotoxin alternariol 9-methyl ether and some of its synthetic analogues inhibit the photosynthetic electron transport chain[J]. J. Nat. Prod., 2013, 76:2234-2245. |
| 15 | MASI M, CIMMINO A, BOARI A, et al.. Colletochlorins E and F, new phytotoxic tetrasubstituted pyran-2-one and dihydrobenzofuran, isolated from Colletotrichum higginsianum with potential herbicidal activity[J]. J. Agric. Food Chem., 2017, 65:1124-1130. |
| 16 | MASI M, MEYER S, CLEMENT S, et al.. Chloromonilinic acids C and D, phytotoxic tetrasubstituted 3-chromanonacrylic acids isolated from Cochliobolus australiensis with potential herbicidal activity against buffelgrass (Cenchrus ciliaris)[J]. J. Nat. Prod., 2017, 80(10): 2771-2777. |
| 17 | ZHAO D L, HAN X B, WANG M, et al.. Herbicidal and antifungal xanthone derivatives from the alga-derived fungus Aspergillus versicolor D5[J]. J. Agric. Food Chem., 2020, 68(40): 11207-11214. |
| 18 | 刘鑫磊, 赵宇, 王卫伟, 等. 螺二萘类天然产物化学研究的新进展[J]. 有机化学, 2017, 37(11): 2883-2894. |
| 19 | MACÍAS-RUBALCAVA M L, RUIZ-VELASCO S M E, MELéNDEZ-GONZáLEZ C, et al.. Naphthoquinone spiroketals and organic extracts from the endophytic fungus Edenia gomezpompae as potential herbicides[J]. J. Agric. Food Chem., 2014, 62(16): 3553-3562. |
| 20 | 陈雪红, 苗嫄昕, 牛兆山, 等. 以细胞骨架为靶点的海洋抗肿瘤大环内酯类化合物的研究进展[J]. 中国海洋药物, 2010, 29(4): 59-65. |
| 21 | SHIONO Y, SATO S, SOFIAN F F, et al.. Phytotoxic β-resorcylic acid derivatives from the endophytic fungus Lasiodiplodia theobromae in the mangrove plant[J]. Phytochem. Lett., 2021, 44: 1-6. |
| 22 | YIN C, JIN L, SUN F, et al.. Phytotoxic and antifungal metabolites from Curvularia crepinii QTYC-1 isolated from the gut of Pantala flavescens [J]. Molecules, 2018, 23(4): 951. |
| 23 | KHAN A L, HAMAYUN M, HUSSAIN J, et al.. The newly isolated endophytic fungus Paraconiothyrium sp. LK1 produces ascotoxin[J]. Molecules, 2012, 17(1): 1103-1112. |
| 24 | DALINOVA A, DUBOVIK V, CHISTY L, et al.. Stagonolides J and K and stagochromene A, two new natural substituted nonenolides and a new disubstituted chromene-4,5-dione isolated from Stagonospora cirsii S-47 proposed for the biocontrol of Sonchus arvensis [J]. J. Agric. Food Chem., 2019, 67(47): 13040-13050. |
| 25 | EVIDENTE M, CIMMINO A, ZONNO M C, et al.. Phytotoxins produced by Phoma chenopodiicola, a fungal pathogen of Chenopodium album [J]. Phytochemistry, 2015, 117: 482-488. |
| 26 | GARCíA-MéNDEZ M C, MACíAS-RUVALCABA N A, LAPPE-OLIVERAS P, et al.. Phytotoxic potential of secondary metabolites and semisynthetic compounds from endophytic fungus Xylaria feejeensis strain SM3e-1b isolated from Sapium macrocarpum [J]. J. Agric. Food Chem., 2016, 64(21): 4255-4263. |
| 27 | MASI M, MEYER S, PESCITELLI G, et al.. Phytotoxic activity against Bromus tectorum for secondary metabolites of a seed-pathogenic Fusarium strain belonging to the F. tricinctum species complex[J]. Nat. Prod. Res., 2017, 31(23): 2768-2777. |
| 28 | KISIRIKO M, ANASTASIADI M, TERRY L A, et al.. Phenolics from medicinal and aromatic plants: characterisation and potential as biostimulants and bioprotectants[J/OL]. Molecules, 2021, 26(21): 6343[2022-12-20]. . |
| 29 | KIM W, PEEVER T L, PARK J J, et al.. Use of metabolomics for the chemotaxonomy of legume-associated Ascochyta and allied genera[J/OL]. Sci. Rep., 2016, 6:20192[2022-12-20]. . |
| 30 | MASI M, NOCERA P, BOARI A, et al.. Lathyroxins A and B, phytotoxic monosubstituted phenols isolated from Ascochyta lentis var. lathyri, a fungal pathogen of grass pea (Lathyrus sativus) [J]. J. Nat. Prod., 2018, 81(4): 1093-1097. |
| 31 | MASI M, MEYER S, GóRECKI M, et al.. Pyriculins A and B, two monosubstituted hex-4-ene-2,3-diols and other phytotoxic metabolites produced by Pyricularia grisea isolated from buffelgrass (Cenchrus ciliaris) [J]. Chirality, 2017, 29(11): 726-736. |
| 32 | MASI M, SANTORO E, CLEMENT S, et al.. Further secondary metabolites produced by the fungus Pyricularia grisea isolated from buffelgrass (Cenchrus ciliaris) [J]. Chirality, 2020, 32(10): 1234-1242. |
| 33 | MASI M, FREDA F, SANGERMANO F, et al.. Radicinin, a fungal phytotoxin as a target-specific bioherbicide for invasive buffelgrass (Cenchrus ciliaris) control[J/OL]. Molecules, 2019, 24(6): 1086[2022-12-20]. . |
| 34 | MASI M, ZONNO M C, CIMMINO A, et al.. On the metabolites produced by Colletotrichum gloeosporioides a fungus proposed for the Ambrosia artemisiifolia biocontrol; spectroscopic data and absolute configuration assignment of colletochlorin A[J]. Nat. Prod. Res., 2017, 32(13):1537-1547. |
| 35 | POLUEKTOVA E, TOKAREV Y, SOKORNOVA S, et al.. Curvulin and phaeosphaeride A from Paraphoma sp. VIZR 1.46 isolated from Cirsium arvense as potential herbicides[J/OL]. Molecules, 2018, 23(11): 2795[2022-12-20]. . |
| 36 | ANDOLFI A, CIMMINO A, VURRO M, et al.. Agropyrenol and agropyrenal, phytotoxins from Ascochyta agropyrina var. nana, a fungal pathogen of Elitrigia repens [J]. Phytochemistry, 2012, 79: 102-108. |
| 37 | CIMMINO A, ANDOLFI A, ZONNO M C, et al.. Phomentrioloxin: a phytotoxic pentasubstituted geranylcyclohexentriol produced by Phomopsis sp., a potential mycoherbicide for Carthamus lanatus biocontrol[J]. J. Nat. Prod., 2012, 79: 102-108. |
| 38 | CIMMINO A, ANDOLFI A, ZONNO M C, et al.. Phomentrioloxin, a fungal phytotoxin with potential herbicidal activity, and its derivatives: a structure-activity relationship study[J]. J. Agric. Food Chem., 2013, 61(40): 9645-9649. |
| 39 | EVIDENTE A, ANDOLFI A, CIMMINO A, et al.. Herbicidal potential of ophiobolins produced by Drechslera gigantea [J]. J. Agric. Food Chem., 2006, 54(5): 1779-1783. |
| 40 | ZATOUT R, MASI M, SANGERMANO F, et al.. Drophiobiolins A and B, bioactive ophiobolan sestertepenoids produced by Dreschslera gigantea [J]. J. Nat. Prod., 2020, 83(11): 3387-3396. |
| 41 | CIMMINO A, ANDOLFI A, ZONNO M C, et al.. Chenopodolin: a phytotoxic unrearranged ent-pimaradiene diterpene produced by Phoma chenopodicola, a fungal pathogen for Chenopodium album biocontrol[J]. J. Nat. Prod., 2013, 76(7): 1291-1297. |
| 42 | ZHAO D L, YANG L J, SHI T, et al.. Potent phytotoxic harziane diterpenes from a soft coral-derived strain of the fungus Trichoderma harzianum XS-20090075[J/OL]. Sci. Rep., 2019, 9(1): 13345[2022-12-20]. . |
| 43 | AKBAR M, JAVAID A, AHMED E, et al.. Holadysenterine, a natural herbicidal constituent from Drechslera australiensis for management of Rumex dentatus [J]. J. Agric. Food Chem., 2014, 62(2): 368-372. |
| 44 | DU F Y, LI X M, SUN Z C, et al.. Secondary metabolites with agricultural antagonistic potentials from Beauveria felina, a marine-derived entomopathogenic fungus[J]. J. Agric. Food Chem., 2020, 68(50): 14824-14831. |
| 45 | ZHAO D L, LIU J, HAN X B, et al.. Decalintetracids A and B, two pairs of unusual 3-decalinoyltetramic acid derivatives with phytotoxicity from Fusarium equiseti D39[J/OL]. Phytochemistry, 2022, 197: 113125[2022-2-11]. . |
| 46 | LIAO L, ZHANG X, LOU Y, et al.. Discovery of three new phytotoxins from the fungus Aspergillus nidulans by pathway inactivation[J/OL]. Molecules, 2019, 24(3): 515[2022-12-20]. . |
| 47 | ZHANG Q, WANG S Q, TANG H Y, et al.. Potential allelopathic indole diketopiperazines produced by the plant endophytic Aspergillus fumigatus using the one strain-many compounds method[J]. J. Agric. Food Chem., 2013, 61(47): 11447-11452. |
| 48 | 郭永霞, 孔祥清. 天然除草活性化合物研究进展[J]. 植物保护, 2005, 6: 11-16. |
| 49 | TRIOLET M, GUILLEMIN J P, ANDRE O, et al.. Fungal‐based bioherbicides for weed control: a myth or a reality?[J]. Weed Res., 2019, 60: 60-77. |
| 50 | 王国增, 李轶女, 张志芳, 等. 除草剂抗性基因的研究进展[J]. 生物技术进展, 2011, 1(6): 398-402. |
| 51 | YAN Y, LIU Q, ZANG X, et al.. Resistance-gene-directed discovery of a natural-product herbicide with a new mode of action[J]. Nature, 2018, 559(7714): 415-418. |
| 52 | HE W, QIN Y, YANJING G, et al.. Structure-based ligand design and discovery of novel tenuazonic acid derivatives with high herbicidal activity[J]. J. Adv. Res., 2021, 40: 29-44. |
| 53 | 吴晓峰, 刘秀, 金晨钟, 等. 我国化学除草剂剂型研究进展 [J]. 现代农药, 2015, 14(5): 10-13. |
| [1] | 于鲲, 薛佳琪, 王进宽, 余永涛. CRISPR/Cas9基因编辑技术在丝状真菌中的应用[J]. 生物技术进展, 2022, 12(5): 696-704. |
| [2] | 王竹,余善君,吉林佳,李咏婷,杨传雄,黄燕妮. 海南红树林淡紫拟青霉胞外多糖提取条件的优化[J]. 生物技术进展, 2021, 11(1): 105-110. |
| [3] | 马莉莉,宋培勇. 紫杉醇产生菌生物多样性研究进展[J]. 生物技术进展, 2016, 6(6): 462-468. |
| [4] | 杨庆丽,刘宇峰,夏尊民,石杰. 一株大麻雨露脱胶真菌的分离鉴定及其脱胶性能研究[J]. 生物技术进展, 2016, 6(4): 261-264. |
| [5] | 李玲玲. 青蒿内生真菌研究进展[J]. 生物技术进展, 2016, 6(3): 185-187. |
| [6] | 李梦瀛,闫培生,高秀君,孙晓磊. 深海真菌多样性及其代谢产物生物活性的研究进展[J]. 生物技术进展, 2015, 5(3): 170-175. |
| [7] | 孙晓磊,闫培生,王凯,王文威,李梦瀛. 深海细菌及其活性物质防控植物病原真菌的研究进展[J]. 生物技术进展, 2015, 5(3): 176-184. |
| [8] | 王晓婧,陆伟,徐玉泉,梁晓东. 真菌苯二酚内酯聚酮类化合物生物合成研究进展 [J]. 生物技术进展, 2015, 5(2): 89-94. |
| [9] | 白净,陆伟,徐玉泉,陈明. 苯二酚内酯合成途径中的聚酮合酶组合表达研究[J]. 生物技术进展, 2015, 5(1): 54-59. |
| [10] | 李军勤,殷小雯,宋培勇. 南方红豆杉内生真菌分离时的表面消毒方法探索[J]. 生物技术进展, 2014, 4(6): 443-446. |
| [11] | 王维才,张付云,刘晔,卢航,李振,赵宇. 江蓠内生真菌NSS1蛋白活性的初步研究[J]. 生物技术进展, 2014, 4(2): 124-128. |
| [12] | 宋飞飞,苏德伟. 粉虱类害虫综合防治途径的研究现状[J]. 生物技术进展, 2013, 3(2): 115-119. |
| [13] | 伍水龙,江黎明. 红树林放线菌研究进展[J]. 生物技术进展, 2012, 2(5): 335-340. |
| [14] | . 几种云南野生石斛内生真菌的鉴定及分布[J]. 生物技术进展, 2012, 2(3): 190-194. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
版权所有 © 2021《生物技术进展》编辑部