


生物技术进展 ›› 2024, Vol. 14 ›› Issue (5): 839-847.DOI: 10.19586/j.2095-2341.2024.0064
• 研究论文 • 上一篇
王博文1( ), 王金星2, 邱成尧2, 秦庆宪2, 王菊香1, 姚博2, 李红艳2, 谭官鑫2, 杨应伟2(
), 王金星2, 邱成尧2, 秦庆宪2, 王菊香1, 姚博2, 李红艳2, 谭官鑫2, 杨应伟2( ), 姬广海1(
), 姬广海1( )
)
收稿日期:2024-03-28
接受日期:2024-05-22
出版日期:2024-09-25
发布日期:2024-10-22
通讯作者:
杨应伟,姬广海
作者简介:王博文 E-mail: l481623593@qq.com;
基金资助:
Bowen WANG1( ), Jinxing WANG2, Chengyao QIU2, Qingxian QIN2, Juxiang WANG1, Bo YAO2, Hongyan LI2, Guanxin TAN2, Yingwei YANG2(
), Jinxing WANG2, Chengyao QIU2, Qingxian QIN2, Juxiang WANG1, Bo YAO2, Hongyan LI2, Guanxin TAN2, Yingwei YANG2( ), Guanghai JI1(
), Guanghai JI1( )
)
Received:2024-03-28
Accepted:2024-05-22
Online:2024-09-25
Published:2024-10-22
Contact:
Yingwei YANG,Guanghai JI
摘要:
烟草是重要的经济作物,烟草青枯病对烟草产业造成了极大的经济损失。因此需要一种安全有效的方法防止烟草青枯病的发生。前期研究中发现可溶性钙肥和生防菌均能有效抑制青枯病菌的生长。在田间种植烟草时,通过单施或组合施用不同的含钙土壤调理剂和生防菌,筛选防治烟草青枯病的最佳组合;采集不同处理的烟草根际土,运用荧光定量PCR和高通量测序技术,探究不同处理下烟草根际土壤中青枯菌数量的变化以及微生物群落组成和结构的变化。田间试验表明,土壤调理剂和生防菌的施用均能有效降低烟草青枯病的发生,但3种含钙调理剂中只有硝酸铵钙能更好地与生防菌GT11复合。该组合处理能降低土壤中青枯病菌的数量,改善烟草根际土壤微生物的群落组成与结构,显著降低烟草青枯病的发病率和病情指数,田间防效达60%。研究证实硝酸铵钙与贝莱斯芽孢杆菌GT11的联合施用能够有效防治烟草青枯病,为烟草生产中青枯病的防治提供了新的思路和理论依据。
中图分类号:
王博文, 王金星, 邱成尧, 秦庆宪, 王菊香, 姚博, 李红艳, 谭官鑫, 杨应伟, 姬广海. 贝莱斯芽孢杆菌联合含钙土壤调理剂对烟草青枯病的防治[J]. 生物技术进展, 2024, 14(5): 839-847.
Bowen WANG, Jinxing WANG, Chengyao QIU, Qingxian QIN, Juxiang WANG, Bo YAO, Hongyan LI, Guanxin TAN, Yingwei YANG, Guanghai JI. Control of Tobacco Bacterial Wilt by Bacillus velezensis Combined with Calcium-containing Soil Conditioner[J]. Current Biotechnology, 2024, 14(5): 839-847.
| 处理编号 | 具体处理方式 |
|---|---|
| T | 碳酸氢铵+氧化钙 |
| S | 硅钙肥 |
| N | 硝酸铵钙 |
| B | 生物有机肥GT11 |
| BT | 生物有机肥GT11+碳酸氢铵+氧化钙 |
| BS | 生物有机肥GT11+硅钙肥 |
| BN | 生物有机肥GT11+硝酸铵钙 |
| CK | 空白对照 |
表1 田间处理及编号
Table 1 Field treatments and numbering
| 处理编号 | 具体处理方式 |
|---|---|
| T | 碳酸氢铵+氧化钙 |
| S | 硅钙肥 |
| N | 硝酸铵钙 |
| B | 生物有机肥GT11 |
| BT | 生物有机肥GT11+碳酸氢铵+氧化钙 |
| BS | 生物有机肥GT11+硅钙肥 |
| BN | 生物有机肥GT11+硝酸铵钙 |
| CK | 空白对照 |
| 处理 | 发病率/% | 病情指数 | 相对防效/% |
|---|---|---|---|
| T | 70.00±2.88 b | 9.63±0.19 bcd | 46.70±1.03 abc |
| S | 60.00±0 cd | 8.33±0.32 cd | 53.86±1.77 ab |
| N | 52.50±4.33 de | 8.05±1.12 cd | 55.36±6.21 ab |
| B | 65.00±0 bc | 8.89±0.96 bcd | 50.77±5.34 abc |
| BT | 70.00±2.89 b | 10.00±0.32 bc | 44.63±1.79 bc |
| BS | 65.00±2.89 bc | 11.11±1.28 b | 38.48±7.1 c |
| BN | 46.67±4.41 e | 7.72±0 d | 60.00±0.02 a |
| CK | 87.50±1.44 a | 18.06±0.8 a | — |
表2 各处理对青枯病的田间防效
Table 2 Field control effectiveness of each treatment against bacterial wilt
| 处理 | 发病率/% | 病情指数 | 相对防效/% |
|---|---|---|---|
| T | 70.00±2.88 b | 9.63±0.19 bcd | 46.70±1.03 abc |
| S | 60.00±0 cd | 8.33±0.32 cd | 53.86±1.77 ab |
| N | 52.50±4.33 de | 8.05±1.12 cd | 55.36±6.21 ab |
| B | 65.00±0 bc | 8.89±0.96 bcd | 50.77±5.34 abc |
| BT | 70.00±2.89 b | 10.00±0.32 bc | 44.63±1.79 bc |
| BS | 65.00±2.89 bc | 11.11±1.28 b | 38.48±7.1 c |
| BN | 46.67±4.41 e | 7.72±0 d | 60.00±0.02 a |
| CK | 87.50±1.44 a | 18.06±0.8 a | — |
| 处理 | pH | 有机质/(g·kg-1) | 水解性氮/(mg·kg-1) | 有效磷/(mg·kg-1) | 速效钾/(mg·kg-1) | 交换性钙/(mg·kg-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NH | 5.49±0.03 a | 17.67±0.47 d | 95.33±3.05 d | 75.97±1.16 b | 413.33±6.81 d | 832.33±12.67 c |
| ND | 5.33±0.07 b | 23.07±0.55 c | 113.33±4.16 b | 62.93±1.46 d | 333.33±12.86 e | 493.67±8.08 e |
| BH | 5.50±0.03 a | 22.50±0.61 c | 103.00±2.00 c | 82.37±0.99 a | 689.00±8.19 a | 905.67±7.02 b |
| BD | 5.29±0.04 b | 22.80±0.30 c | 107.00±2.00 bc | 71.67±0.72 c | 455.00±7.00 c | 733.00±12.00 d |
| CKH | 5.30±0.04 b | 24.80±0.35 b | 96.33±1.52 d | 46.63±1.18 f | 631.67±10.69 b | 935.33±7.51 ab |
| CKD | 5.14±0.06 c | 30.67±0.40 a | 136.33±5.51 a | 60.13±0.94 e | 444.00±34.66 cd | 722.00±19.97 d |
| YS | 5.04±0.03 d | 25.30±0.10 b | 141.00±2.00 a | 38.70±0.75 g | 122.00±11.52 f | 958.57±31.34 a |
表3 各处理对土壤理化性质的影响
Table 3 Effects of different treatments on soil physical and chemical properties
| 处理 | pH | 有机质/(g·kg-1) | 水解性氮/(mg·kg-1) | 有效磷/(mg·kg-1) | 速效钾/(mg·kg-1) | 交换性钙/(mg·kg-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NH | 5.49±0.03 a | 17.67±0.47 d | 95.33±3.05 d | 75.97±1.16 b | 413.33±6.81 d | 832.33±12.67 c |
| ND | 5.33±0.07 b | 23.07±0.55 c | 113.33±4.16 b | 62.93±1.46 d | 333.33±12.86 e | 493.67±8.08 e |
| BH | 5.50±0.03 a | 22.50±0.61 c | 103.00±2.00 c | 82.37±0.99 a | 689.00±8.19 a | 905.67±7.02 b |
| BD | 5.29±0.04 b | 22.80±0.30 c | 107.00±2.00 bc | 71.67±0.72 c | 455.00±7.00 c | 733.00±12.00 d |
| CKH | 5.30±0.04 b | 24.80±0.35 b | 96.33±1.52 d | 46.63±1.18 f | 631.67±10.69 b | 935.33±7.51 ab |
| CKD | 5.14±0.06 c | 30.67±0.40 a | 136.33±5.51 a | 60.13±0.94 e | 444.00±34.66 cd | 722.00±19.97 d |
| YS | 5.04±0.03 d | 25.30±0.10 b | 141.00±2.00 a | 38.70±0.75 g | 122.00±11.52 f | 958.57±31.34 a |
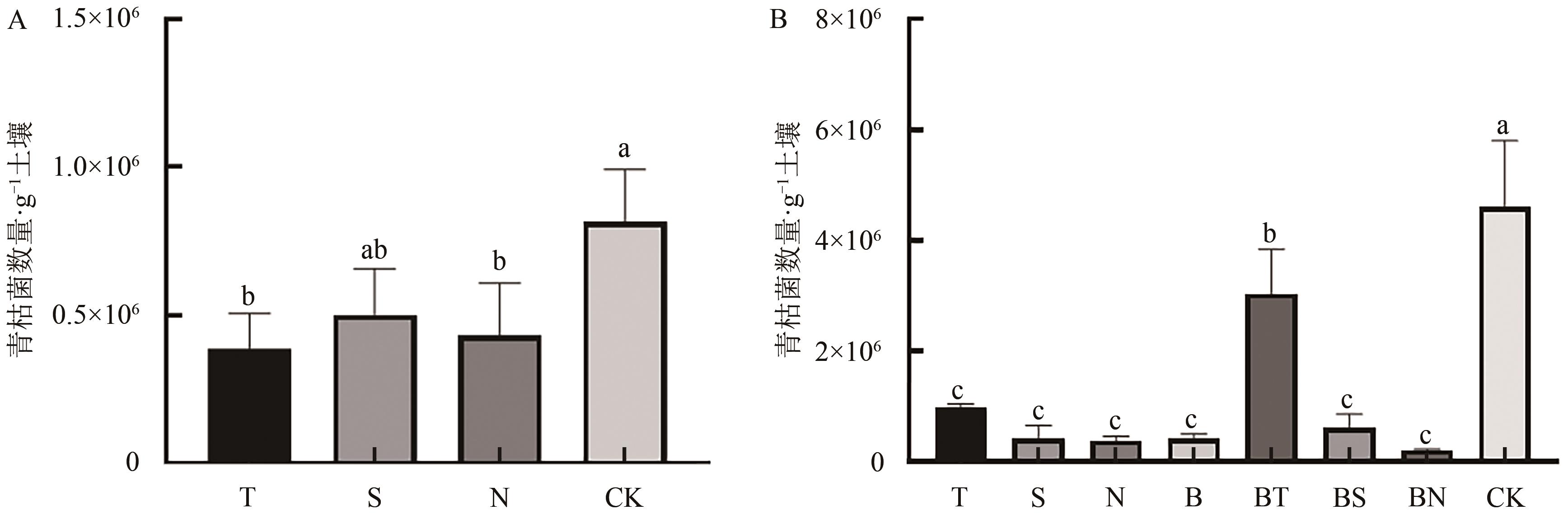
图1 不同处理对土壤中青枯菌数量变化的影响A:经过T、S、N处理15 d后及空白对照尚未种植烟草时土壤中青枯菌的数量;B:各处理烟草种植60 d后烟草根际土中青枯菌的数量;误差线上不同小写字母表示处理间差异显著(P<0.05)。
Fig. 1 Effect of different treatments on the number change of Ralstonia in soil
| 处理 | Chao1指数 | Ace指数 | Shannon指数 | Simpson指数 | 覆盖度 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S | 205.00±4.16a | 205.00±4.16a | 4.34±0.67a | 0.18±0.01c | 1 |
| N | 179.30±7.13b | 179.33±7.13b | 3.68±0.16b | 0.25±0.03abc | 1 |
| B | 124.30±5.24c | 124.33±5.24c | 2.77±0.81c | 0.28±0.01ab | 1 |
| BN | 203.30±5.36a | 203.33±5.36a | 3.73±0.24b | 0.27±0.05ab | 1 |
| CKH | 179.00±7.00b | 179.00±7.00b | 3.82±0.57b | 0.22±0.02bc | 1 |
| CKD | 163.00±6.66b | 163.00±6.66b | 3.17±0.65c | 0.33±0.02a | 1 |
表4 Alpha多样性指数分析
Table 4 Alpha diversity index analysis
| 处理 | Chao1指数 | Ace指数 | Shannon指数 | Simpson指数 | 覆盖度 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S | 205.00±4.16a | 205.00±4.16a | 4.34±0.67a | 0.18±0.01c | 1 |
| N | 179.30±7.13b | 179.33±7.13b | 3.68±0.16b | 0.25±0.03abc | 1 |
| B | 124.30±5.24c | 124.33±5.24c | 2.77±0.81c | 0.28±0.01ab | 1 |
| BN | 203.30±5.36a | 203.33±5.36a | 3.73±0.24b | 0.27±0.05ab | 1 |
| CKH | 179.00±7.00b | 179.00±7.00b | 3.82±0.57b | 0.22±0.02bc | 1 |
| CKD | 163.00±6.66b | 163.00±6.66b | 3.17±0.65c | 0.33±0.02a | 1 |
| 1 | LIU Y, WU D, LIU Q, et al.. The sequevar distribution of Ralstonia solanacearum in tobacco-growing zones of China is structured by elevation[J]. Eur. J. Plant Pathol., 2017, 147(3): 541-551. |
| 2 | 徐进,冯洁.植物青枯菌遗传多样性及致病基因组学研究进展[J].中国农业科学,2013,46(14):2902-2909. |
| XU J, FENG J. Advances in research of genetic diversity and pathogenome of Ralstonia solanacearum species complex[J]. Sci. Agric. Sin., 2013, 46(14): 2902-2909. | |
| 3 | LI X, HUANG X, CHEN G, et al.. Complete genome sequence of the sesame pathogen Ralstonia solanacearum strain SEPPX 05[J]. Genes Genom., 2018, 40(6): 657-668. |
| 4 | 丁传雨.生物有机肥对土传马铃薯青枯病的防控技术及机理研究[D].南京:南京农业大学,2012. |
| DING C Y. Biocontrol technology of soil-borne disease of Potato bacterial wilt and its mechanism of action[D]. Nanjing: Nanjing Agricultural University,2012. | |
| 5 | 韩松庭,丁伟.烟草青枯病的化学防治研究进展[J].植物医生,2019(5):20-25. |
| HAN S T, DING W. Advances in chemical control of tobacco bacterial wilt[J]. Plant Dr., 2019(5): 20-25. | |
| 6 | 冯吉,黎妍妍,程玲,等.烟草青枯病的生物防治研究进展[J].安徽农业科学,2016,44(1):203-205+215. |
| FENG J, LI Y Y, CHENG L, et al.. Research advances in biological control of tobacco bacterial wilt[J]. J. Anhui Agric. Sci., 2016, 44(1): 203-205+215. | |
| 7 | 李世斌,耿锐梅,肖志亮,等.烟草青枯病抗性育种研究进展[J/OL].分子植物育种,2023 [2023-03-16].. |
| LI S B, GENG R M, XIAO Z L, et al.. Research progresses on breeding for resistance to bacterial wilt of tobacco (Nicotiana tabacum L.)[J/OL]. Mol. Plant Breed., 2023 [2023-03-16]. . | |
| 8 | 万川,蒋珍茂,赵秀兰,等.深翻和施用土壤改良剂对烟草青枯病发生的影响[J].烟草科技,2015,48(2):11-15+26. |
| WAN C, JIANG Z M, ZHAO X L, et al.. Effects of deep-ploughing and soil amendment application on incidence of tobacco bacterial wilt[J]. Tob. Sci. Technol., 2015, 48(2): 11-15, 26. | |
| 9 | IMAZAKI I, NAKAHO K. Pyruvate-amended modified SMSA medium: improved sensitivity for detection of Ralstonia solanacearum [J]. J. Gen. Plant Pathol., 2010, 76(1): 52-61. |
| 10 | WU S X, GAO F Y, ZHANG R P, et al.. Research progress in biological control of tomato bacterial wilt[J]. Chin. J. Appl. Ecol., 2023, 34(9): 2585-2592. |
| 11 | 喻延.土壤pH值及不同调控措施对烟草青枯病发生情况的影响[D].重庆:西南大学,2016. |
| YU Y. Effects of soil pH and different control measures on tobacco bacterial wilt status[D]. Chongqing: Southwest University, 2016. | |
| 12 | 李信申,陈建,肖运萍,等.中生菌素和生石灰对芝麻青枯病的联合防控效果[J].中国生物防治学报,2020,36(3):472-478. |
| LI X S, CHEN J, XIAO Y P, et al.. Joint control of sesame bacterial wilt with lime and zhongshengmycin[J]. Chin. J. Biol. Contr., 2020, 36(3): 472-478. | |
| 13 | 王杰,龙世芳,王正文,等.番茄青枯病防治研究进展[J].中国蔬菜,2020(1):22-30. |
| WANG J, LONG S F, WANG Z W, et al.. Research progress in controlling tomato bacterial wilt[J]. China Veg., 2020(1): 22-30. | |
| 14 | 单晓鹏.烟草青枯病的防治研究进展[J].现代农业科技,2021(11):111-113. |
| SHAN X P. Research progress on control of tobacco bacterial wilt[J]. Mod. Agric. Sci. Technol., 2021(11): 111-113. | |
| 15 | WHIPPS J M. Microbial interactions and biocontrol in the rhizosphere[J]. J. Exp. Bot., 2001, 52(1): 487-511. |
| 16 | GROSCH R, DEALTRY S, SCHREITER S, et al.. Biocontrol of Rhizoctonia solani: complex interaction of biocontrol strains, pathogen and indigenous microbial community in the rhizosphere of lettuce shown by molecular methods[J]. Plant Soil, 2012, 361(1): 343-357. |
| 17 | 段平成,郑凯,张宇宏,等.拮抗菌BJB01抗黄萎病的抗病效果评价[J].生物技术进展,2023,13(6):913-918. |
| DUAN P C, ZHENG K, ZHANG Y H, et al.. Evaluation of the anti-disease effect of antagonistic bacterium BJB01 against Verticillium wilt[J]. Curr. Biotechnol., 2023, 13(6): 913-918. | |
| 18 | AHMED W, DAI Z, ZHANG J, et al.. Plant-microbe interaction: mining the impact of native Bacillus amyloliquefaciens WS-10 on tobacco bacterial wilt disease and rhizosphere microbial communities[J/OL]. Microbiol. Spectr., 2022, 10(4): e0147122[2023-03-16]. . |
| 19 | AHMED W, ZHOU G, YANG J, et al.. Bacillus amyloliquefaciens WS-10 as a potential plant growth-promoter and biocontrol agent for bacterial wilt disease of flue-cured tobacco[J/OL]. Egypt. J. Biol. Pest Contr., 2022, 32(1): 25[2023-03-16]. . |
| 20 | SUI X, HAN X, CAO J, et al.. Biocontrol potential of Bacillus velezensis EM-1 associated with suppressive rhizosphere soil microbes against tobacco bacterial wilt[J/OL]. Front. Microbiol., 2022, 13: 940156[2023-03-16]. . |
| 21 | MA L, ZHANG H Y, ZHOU X K, et al.. Biological control tobacco bacterial wilt and black shank and root colonization by bio-organic fertilizer containing bacterium Pseudomonas aeruginosa NXHG29[J]. Appl. Soil Ecol., 2018, 129: 136-144. |
| 22 | 李向阳,刘国顺,杨永锋,等.烤烟叶片高光谱参数与多种生理生化指标关系研究[J].中国农业科学,2007,40(5):987-994. |
| LI X Y, LIU G S, YANG Y F, et al.. Relationship between hyperspectra parameters and physiological and biochemical indexes of flue-cured tobacco leaves[J]. Sci. Agric. Sin., 2007, 40(5): 987-994. | |
| 23 | WU X, LI H, WANG Y, et al.. Effects of bio-organic fertiliser fortified by Bacillus cereus QJ-1 on tobacco bacterial wilt control and soil quality improvement[J]. Biocontrol Sci. Technol., 2020, 30(4): 351-369. |
| 24 | YANG H, LI J, XIAO Y, et al.. An integrated insight into the relationship between soil microbial community and tobacco bacterial wilt disease[J/OL]. Front. Microbiol., 2017, 8: 2179[2023-03-16]. . |
| 25 | YUAN S, WANG L, WU K, et al.. Evaluation of Bacillus-fortified organic fertilizer for controlling tobacco bacterial wilt in greenhouse and field experiments[J]. Appl. Soil Ecol., 2014, 75: 86-94. |
| 26 | 鲍士旦.土壤农化分析[M].3版.北京:中国农业出版社,2000. |
| 27 | SCHÖNFELD J, HEUER H, VAN ELSAS J D, et al.. Specific and sensitive detection of Ralstonia solanacearum in soil on the basis of PCR amplification of fliC fragments[J]. Appl. Environ. Microbiol., 2003, 69(12): 7248-7256. |
| 28 | 吴晓宗,王岩.生物有机肥防治烟草青枯病及对土壤微生物多样性的影响[J].中国土壤与肥料,2019(4):193-199. |
| WU X Z, WANG Y. Research of bio-organic fertilizer on prevention of tobacco bacterial wilt and its effects on soil microbial diversity[J]. Soil Fertil. Sci. China, 2019(4): 193-199. | |
| 29 | 张德锋,高艳侠,王亚军,等.贝莱斯芽孢杆菌的分类、拮抗功能及其应用研究进展[J].微生物学通报,2020,47(11):3634-3649. |
| ZHANG D F, GAO Y X, WANG Y J, et al.. Advances in taxonomy, antagonistic function and application of Bacillus velezensis [J]. Microbiol. China, 2020, 47(11): 3634-3649. | |
| 30 | 李坤,洪秀杰,王欣悦,等.贝莱斯芽孢杆菌TC-52的分离鉴定及其对水稻幼苗生长和立枯病的影响[J].江苏农业科学,2024,52(10):129-137. |
| LI K, HONG X J, WANG X Y, et al.. Isolation and identification of Bacillus velezensis TC-52 and its effect on rice seedling growth and blight[J]. Jiangsu Agric. Sci., 2024, 52(10): 129-137. | |
| 31 | 曹宇,陈鹏泽,曹秀兰,等.贝莱斯芽孢杆菌HNU24高效拮抗茄雷尔氏菌和促进植物生长活性的研究[J].海南师范大学学报(自然科学版),2022,35(1):50-56. |
| CAO Y, CHEN P Z, CAO X L, et al.. Studies on Bacillus velezensis strain HNU24 with significant antagonistic activity against Ralstonia solanacearum and promoting plant growth activity[J]. J. Hainan Norm. Univ. Nat. Sci., 2022, 35(1): 50-56. | |
| 32 | HU Y, LI Y, YANG X, et al.. Effects of integrated biocontrol on bacterial wilt and rhizosphere bacterial community of tobacco[J/OL]. Sci. Rep., 2021, 11(1): 2653[2023-03-16]. . |
| 33 | YUAN S, LI M, FANG Z, et al.. Biological control of tobacco bacterial wilt using Trichoderma harzianum amended bioorganic fertilizer and the arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi Glomus mosseae [J]. Biol. Contr., 2016, 92: 164-171. |
| 34 | LIU Y, SHI J, FENG Y, et al.. Tobacco bacterial wilt can be biologically controlled by the application of antagonistic strains in combination with organic fertilizer[J]. Biol. Fertil. Soils, 2013, 49(4): 447-464. |
| 35 | 于威,依艳丽,杨蕾.土壤中钙、氮含量对番茄枯萎病抗性的影响[J].中国土壤与肥料,2016(1):134-140. |
| YU W, YI Y L, YANG L. Effect of different available calcium and nitrogen in soil on effectiveness of disease resistance to blight of tomato[J]. Soil Fertil. Sci. China, 2016(1): 134-140. | |
| 36 | 田甜.硅缓解水稻硼胁迫的效应及其土壤化学机制[D].沈阳:沈阳农业大学,2022. |
| TIAN G. Effect of silicon in alleviating boron stress in rice and its soil chemical mechanism[D]. Shenyang: Shenyang Agricultural University, 2022. | |
| 37 | 尚双华.设施土壤氮素积累条件下番茄枯萎病发生的微生态机制研究[D].沈阳:沈阳农业大学,2016. |
| SHANG S H. Micro-ecological mechanis m of soil-borne Tomato fusarium wilt in the nitrogen-rich facilities cultivation soil[D]. Shenyang: Shenyang Agricultural University, 2016. | |
| 38 | 郑世燕,丁伟,杜根平,等.增施矿质营养对烟草青枯病的控病效果及其作用机理[J].中国农业科学,2014,47(6):1099-1110. |
| ZHENG S Y, DING W, DU G P, et al.. Control efficacy and action mechanism of mineral nutrition on tobacco bacterial wilt[J]. Sci. Agric. Sin., 2014, 47(6): 1099-1110. | |
| 39 | 樊俊,谭军,王瑞,等.烟草青枯病发病土壤理化性状及细菌群落结构分析[J].中国烟草科学,2021,42(6):15-21. |
| FAN J, TAN J, WANG R, et al.. Analysis of soil physical and chemical properties and bacterial community structure with tobacco bacterial wilt infection[J]. Chin. Tob. Sci., 2021, 42(6): 15-21. | |
| 40 | YAMAZAKI H, ISHIZUKA O, HOSHINA T. Relationship between resistance to bacterial wilt and nutrient uptake in tomato seedlings[J]. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr., 1996, 42(1): 203-208. |
| 41 | JIANG J F, LI J G, DONG Y H. Effect of calcium nutrition on resistance of tomato against bacterial wilt induced by Ralstonia solanacearum [J]. Eur. J. Plant Pathol., 2013, 136(3): 547-555. |
| 42 | IRIKIIN Y, NISHIYAMA M, OTSUKA S, et al.. Rhizobacterial community-level, sole carbon source utilization pattern affects the delay in the bacterial wilt of tomato grown in rhizobacterial community model system[J]. Appl. Soil Ecol., 2006, 34(1): 27-32. |
| 43 | WU M, ZHANG H, LI X, et al.. Soil fungistasis and its relations to soil microbial composition and diversity: a case study of a series of soils with different fungistasis[J]. J. Environ. Sci. China, 2008, 20(7): 871-877. |
| 44 | 施河丽,向必坤,谭军,等.烟草青枯病发病烟株根际土壤细菌群落分析[J].中国烟草学报,2018,24(5):57-65. |
| SHI H L, XIANG B K, TAN J, et al.. Analysis of bacterial community in rhizosphere soil of tobacco plant infected by bacterial wilt disease[J]. Acta Tabacaria Sin., 2018, 24(5): 57-65. | |
| 45 | BONILLA N, GUTIÉRREZ-BARRANQUERO J, VICENTE A, et al.. Enhancing soil quality and plant health through suppressive organic amendments[J]. Diversity, 2012, 4(4): 475-491. |
| 46 | 贺纪正,李晶,郑袁明.土壤生态系统微生物多样性-稳定性关系的思考[J].生物多样性,2013,21(4):412-421. |
| HE J Z, LI J, ZHENG Y M. Thoughts on the microbial diversity-stability relationship in soil ecosystems[J]. Biodivers. Sci., 2013, 21(4): 412-421. | |
| 47 | 付丽娜,魏兰芳,王震铄,等.三七根际微生物群落组成及多样性研究[J].生物技术进展,2017,7(3):211-216. |
| FU L N, WEI L F, WANG Z S, et al.. Study on composition and diversity of rhizospheric microbial community from Panax notoginseng [J]. Curr. Biotechnol., 2017, 7(3): 211-216. | |
| 48 | 黎妍妍,王林,彭五星,等.烟草青枯病不同发病阶段根际土壤微生物群落变化趋势分析[J].中国烟草科学,2020,41(5):73-78. |
| LI Y Y, WANG L, PENG W X, et al.. Analysis of the changing trend of microbial community in rhizosphere soil during different stages of tobacco bacterial wilt infection[J]. Chin. Tob. Sci., 2020, 41(5): 73-78. | |
| 49 | 陈乾锦,林书震,李红丽,等.邵武烟田土壤微生物群落结构变化与烟草青枯病发生关系初报[J].中国烟草学报,2019,25(4):64-71. |
| CHEN Q J, LIN S Z, LI H L, et al.. A preliminary report on relationship between variation of microbial community structure in soil and occurrence of tobacco bacterial wilt in tobacco field in Shaowu[J]. Acta Tabacaria Sin., 2019, 25(4): 64-71. | |
| 50 | 何洪令.烟草青枯菌拮抗细菌的筛选鉴定及其生防特性研究[D].重庆:西南大学,2021. |
| HE H L. Screening, identification and biocontrol characteristics of antagonistic bacteria against Ralstonia solanacearum[D]. Chongqing: Southwest University, 2021. |
| [1] | 吴焕振, 杨野, 崔秀明, 刘源. 农业生物防治技术的现状及改进策略[J]. 生物技术进展, 2024, 14(5): 697-711. |
| [2] | 段平成, 郑凯, 张宇宏, 张国丽, 孙国清. 拮抗菌BJB01抗黄萎病的抗病效果评价[J]. 生物技术进展, 2023, 13(6): 913-918. |
| [3] | 孙政玺, 胡思嘉, 周益雷, 胡怡, 江宁, 李磊, 李韬. sRNA的研究概述及其在小麦赤霉病防治中的应用展望[J]. 生物技术进展, 2021, 11(5): 653-659. |
| [4] | 侯旭,张国庆,胡晓,闫立春,刘悦萍. 果树内生生防菌研究进展[J]. 生物技术进展, 2017, 7(2): 149-154. |
| [5] | 代京莎,李安章,朱红惠. 粘细菌在植物病害生物防治中的作用[J]. 生物技术进展, 2016, 6(4): 229-234. |
| [6] | 李梦娇,彭晟,徐绍忠,余代宏,赵明富,文国松 . 克雷伯氏菌在农业与环境治理上的应用[J]. 生物技术进展, 2014, 4(6): 415-420. |
| [7] | 王静,郑永华. 拮抗菌在果蔬采后病害生物防治中的应用[J]. 生物技术进展, 2013, 3(6): 393-398. |
| [8] | 马桂美,车建美,刘波,史怀,陈峥. 短短芽胞杆菌功能基因的研究及其应用[J]. 生物技术进展, 2012, 2(2): 92-97. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
版权所有 © 2021《生物技术进展》编辑部