


生物技术进展 ›› 2024, Vol. 14 ›› Issue (4): 631-639.DOI: 10.19586/j.2095-2341.2024.0019
• 研究论文 • 上一篇
张永红1( ), 苏振国1, 罗家福1, 李春峰2(
), 苏振国1, 罗家福1, 李春峰2( ), 敖宝林3
), 敖宝林3
收稿日期:2024-02-04
接受日期:2024-04-24
出版日期:2024-07-25
发布日期:2024-08-07
通讯作者:
李春峰
作者简介:张永红 E-mail: zhang200503@126.com;
基金资助:
Yonghong ZHANG1( ), Zhenguo SU1, Jiafu LUO1, Chunfeng LI2(
), Zhenguo SU1, Jiafu LUO1, Chunfeng LI2( ), Baolin AO3
), Baolin AO3
Received:2024-02-04
Accepted:2024-04-24
Online:2024-07-25
Published:2024-08-07
Contact:
Chunfeng LI
摘要:
家蚕微孢子虫(Nosema bombycis)是蚕业生产上一种重要病害——微粒子病的病原体。探讨家蚕微孢子虫种内的遗传多样性,可为云南蚕区家蚕微粒子病的防控提供参考依据。从云南省不同养蚕地区收集了感染微孢子虫的病蚕样品,分离纯化家蚕微孢子虫并提取基因组,克隆SSU rDNA(small subunit ribosomal DNA)和ITS(internal transcribed spacer)序列并进行生物信息学分析。结果发现,云南蚕区Nosema bombycis 分离株SSU rDNA序列同源性高达99%以上,遗传距离小于0.006,它们在长度和多个位点存在差异,呈现不同程度的多态性;ITS遗传差异较为显著,序列中存在多碱基的插入或缺失、单碱基的转换和颠换。基于SSU rDNA和rDNA-ITS序列构建系统发生树,结果显示,云南蚕区家蚕微孢子虫分离株系间存在遗传分化,种群间亲缘关系与地理位置无直接联系。研究结果丰富了云南蚕区家蚕微孢子虫的种内遗传多样性。
中图分类号:
张永红, 苏振国, 罗家福, 李春峰, 敖宝林. 云南蚕区家蚕微孢子虫遗传多样性分析[J]. 生物技术进展, 2024, 14(4): 631-639.
Yonghong ZHANG, Zhenguo SU, Jiafu LUO, Chunfeng LI, Baolin AO. Analysis of Genetic Diversity of Nosema bombycis in Yunnan Sericulture Region[J]. Current Biotechnology, 2024, 14(4): 631-639.
| 名称 | 宿主 | SSU rDNA GenBank登录号 | ITS GenBank登录号 | 地理来源 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| YNMZCB1 | Bombyx mori | OQ970549 | OQ974967 | 云南省蒙自市 |
| YNMZCB2 | OQ970550 | OQ974968 | 云南省蒙自市 | |
| YNMZLQ | OQ970551 | OQ974969 | 云南省蒙自市 | |
| YNCXDY | OR597059 | OR597057 | 云南省大姚县 | |
| YNQJLL | OR597056 | OR597058 | 云南省陆良县 | |
| YN1 | JF334596 | JF443647 | 云南省 | |
| YN2 | JF334597 | JF443648 | 云南省 | |
| YN3 | JF334598 | JF443649 | 云南省 | |
| YN4 | JF334599 | JF443650 | 云南省 | |
| SC1 | JF334592 | JF443631 | 四川省 | |
| CQ1 | EU350391 | EU350394 | 重庆市 | |
| GX1 | JF443547 | JF443600 | 广西壮族自治区 | |
| GD1 | JF334582 | JF443619 | 广东省 | |
| AH | GQ334399 | — | 安徽省 | |
| JS | AY616662 | — | 江苏省 | |
| TW | AY209011 | AY209011 | 台湾省 | |
| J-IK | AY259631 | AY259631 | 日本茨城县 | |
| Nosema ceranae | Apis mellifera | DQ486027 | — | 台湾省 |
| Nosema apis | Apis cerana | U97150 | — | 美国加利福尼亚州 |
| Nosema sp.SC | Samia cynthia ricini | FJ767862 | — | 江苏省 |
| Nosema sp.PX1 | Plutella xylostae | AY960986 | — | 台湾省 |
| Nosema sp.C01 | Pieris rapae | AY383655 | — | 江苏省 |
| Nosema plutellae | Plutella xylostea | AY960987 | — | 台湾省 |
| Nosema spodoptrae | Spodoptera litura | AY747307 | — | 台湾省 |
| Beauveria bassiana | Blattaria | EU334679 | — | 加拿大魁北克省 |
| Nosema antheraeae | Antherea pernyi | — | DQ073396 | 河南省 |
| Nosema disstriae | Malacasoma disstria | — | EU221229 | 加拿大安大略省 |
表1 昆虫微孢子虫SSU rDNA与ITS序列来源
Table 1 Source of the SSU rDNA and ITS sequences of microsporidia
| 名称 | 宿主 | SSU rDNA GenBank登录号 | ITS GenBank登录号 | 地理来源 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| YNMZCB1 | Bombyx mori | OQ970549 | OQ974967 | 云南省蒙自市 |
| YNMZCB2 | OQ970550 | OQ974968 | 云南省蒙自市 | |
| YNMZLQ | OQ970551 | OQ974969 | 云南省蒙自市 | |
| YNCXDY | OR597059 | OR597057 | 云南省大姚县 | |
| YNQJLL | OR597056 | OR597058 | 云南省陆良县 | |
| YN1 | JF334596 | JF443647 | 云南省 | |
| YN2 | JF334597 | JF443648 | 云南省 | |
| YN3 | JF334598 | JF443649 | 云南省 | |
| YN4 | JF334599 | JF443650 | 云南省 | |
| SC1 | JF334592 | JF443631 | 四川省 | |
| CQ1 | EU350391 | EU350394 | 重庆市 | |
| GX1 | JF443547 | JF443600 | 广西壮族自治区 | |
| GD1 | JF334582 | JF443619 | 广东省 | |
| AH | GQ334399 | — | 安徽省 | |
| JS | AY616662 | — | 江苏省 | |
| TW | AY209011 | AY209011 | 台湾省 | |
| J-IK | AY259631 | AY259631 | 日本茨城县 | |
| Nosema ceranae | Apis mellifera | DQ486027 | — | 台湾省 |
| Nosema apis | Apis cerana | U97150 | — | 美国加利福尼亚州 |
| Nosema sp.SC | Samia cynthia ricini | FJ767862 | — | 江苏省 |
| Nosema sp.PX1 | Plutella xylostae | AY960986 | — | 台湾省 |
| Nosema sp.C01 | Pieris rapae | AY383655 | — | 江苏省 |
| Nosema plutellae | Plutella xylostea | AY960987 | — | 台湾省 |
| Nosema spodoptrae | Spodoptera litura | AY747307 | — | 台湾省 |
| Beauveria bassiana | Blattaria | EU334679 | — | 加拿大魁北克省 |
| Nosema antheraeae | Antherea pernyi | — | DQ073396 | 河南省 |
| Nosema disstriae | Malacasoma disstria | — | EU221229 | 加拿大安大略省 |

图1 普通光学显微镜下家蚕微孢子虫形态特征A:重庆株CQ;B:YNMZCB1;C:YNMZCB2;D:YNMZLQ;E:YNCXDY;F:YNQJLL
Fig. 1 Morphological characteristics of N. bombycis under ordinary optical microscopy
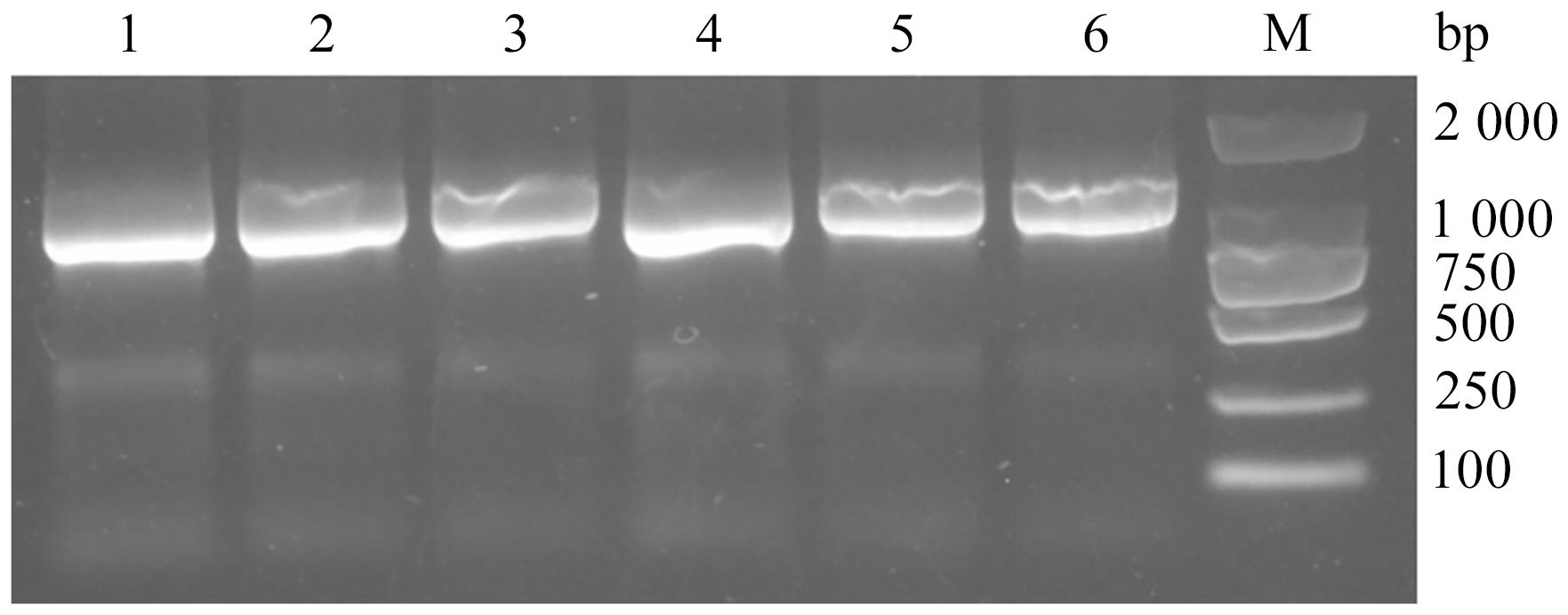
图2 病蚕样品SSU rDNA基因PCR扩增结果注:1—重庆株CQ;2—YNMZCB1;3—YNMZCB2;4—YNMZLQ;5—YNCXDY;6—YNQJLL;M—DNA marker。
Fig. 2 PCR amplification results of SSU rDNA gene among the diseased silkworm samples
| 分离株 | 核苷酸位点 | ||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 79 | 102 | 294 | 445 | 471 | 558 | 565 | 591 | 640 | 651 | 696 | 703 | 823 | 844 | 861 | |
| YNMZCB1 | G | G | T | G | — | T | G | G | — | C | A | T | G | A | C |
| YNMZCB2 | G | G | C | G | T | T | A | G | — | T | A | C | A | G | T |
| YNMZLQ | A | G | C | G | — | T | A | G | — | T | A | C | G | G | C |
| YNCXDY | G | G | C | C | — | T | A | G | — | T | A | C | G | G | C |
| YNQJLL | G | G | C | G | — | T | A | G | — | T | A | C | G | G | C |
| JS | G | A | C | G | — | G | A | A | C | C | T | C | G | G | C |
表2 家蚕微孢子虫SSU rDNA基因序列的差异位点
Table 2 Differential loci of SSU rDNA gene sequence in N. bombycis
| 分离株 | 核苷酸位点 | ||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 79 | 102 | 294 | 445 | 471 | 558 | 565 | 591 | 640 | 651 | 696 | 703 | 823 | 844 | 861 | |
| YNMZCB1 | G | G | T | G | — | T | G | G | — | C | A | T | G | A | C |
| YNMZCB2 | G | G | C | G | T | T | A | G | — | T | A | C | A | G | T |
| YNMZLQ | A | G | C | G | — | T | A | G | — | T | A | C | G | G | C |
| YNCXDY | G | G | C | C | — | T | A | G | — | T | A | C | G | G | C |
| YNQJLL | G | G | C | G | — | T | A | G | — | T | A | C | G | G | C |
| JS | G | A | C | G | — | G | A | A | C | C | T | C | G | G | C |
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 | 16 | 17 | 名称 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0.006 | 0.005 | 0.005 | 0.004 | 0.010 | 0.011 | 0.006 | 0.009 | 0.006 | 0.004 | 0.006 | 0.011 | 0.006 | 0.006 | 0.006 | 0.004 | YNMZCB1 | |
| 2 | 99.4 | 0.002 | 0.002 | 0.002 | 0.006 | 0.006 | 0.000 | 0.006 | 0.004 | 0.003 | 0.002 | 0.008 | 0.004 | 0.006 | 0.002 | 0.002 | YNMZCB2 | |
| 3 | 99.5 | 99.8 | 0.002 | 0.001 | 0.007 | 0.007 | 0.002 | 0.006 | 0.003 | 0.001 | 0.002 | 0.007 | 0.003 | 0.005 | 0.002 | 0.001 | YNMZLQ | |
| 4 | 99.5 | 99.8 | 99.8 | 0.001 | 0.007 | 0.007 | 0.002 | 0.006 | 0.003 | 0.002 | 0.002 | 0.007 | 0.003 | 0.005 | 0.002 | 0.001 | YNCXDY | |
| 5 | 99.6 | 99.8 | 99.9 | 99.9 | 0.006 | 0.006 | 0.002 | 0.005 | 0.002 | 0.002 | 0.002 | 0.006 | 0.002 | 0.004 | 0.002 | 0.000 | YNQJLL | |
| 6 | 99.0 | 99.4 | 99.3 | 99.3 | 99.4 | 0.011 | 0.006 | 0.011 | 0.008 | 0.007 | 0.006 | 0.012 | 0.008 | 0.010 | 0.006 | 0.006 | YN1 | |
| 7 | 98.9 | 99.4 | 99.3 | 99.3 | 99.4 | 98.9 | 0.006 | 0.011 | 0.009 | 0.008 | 0.006 | 0.013 | 0.006 | 0.011 | 0.006 | 0.006 | YN2 | |
| 8 | 99.4 | 100.0 | 99.8 | 99.8 | 99.8 | 99.4 | 99.4 | 0.006 | 0.004 | 0.003 | 0.002 | 0.008 | 0.004 | 0.006 | 0.002 | 0.002 | YN3 | |
| 9 | 99.1 | 99.4 | 99.4 | 99.4 | 99.5 | 98.9 | 98.9 | 99.4 | 0.007 | 0.006 | 0.006 | 0.011 | 0.007 | 0.009 | 0.006 | 0.005 | YN4 | |
| 10 | 99.4 | 99.6 | 99.7 | 99.7 | 99.8 | 99.2 | 99.1 | 99.6 | 99.3 | 0.004 | 0.004 | 0.007 | 0.005 | 0.006 | 0.004 | 0.002 | SC1 | |
| 11 | 99.6 | 99.7 | 99.9 | 99.8 | 99.8 | 99.3 | 99.2 | 99.7 | 99.4 | 99.6 | 0.003 | 0.008 | 0.004 | 0.006 | 0.003 | 0.002 | CQ1 | |
| 12 | 99.4 | 99.8 | 99.8 | 99.8 | 99.8 | 99.4 | 99.4 | 99.8 | 99.4 | 99.6 | 99.7 | 0.008 | 0.004 | 0.006 | 0.002 | 0.002 | GX1 | |
| 13 | 98.9 | 99.2 | 99.3 | 99.3 | 99.4 | 98.8 | 98.7 | 99.2 | 98.9 | 99.3 | 99.2 | 99.2 | 0.009 | 0.009 | 0.008 | 0.006 | GD1 | |
| 14 | 99.4 | 99.6 | 99.7 | 99.7 | 99.8 | 99.2 | 99.4 | 99.6 | 99.3 | 99.5 | 99.6 | 99.6 | 99.1 | 0.006 | 0.004 | 0.002 | AH | |
| 15 | 99.4 | 99.4 | 99.5 | 99.5 | 99.6 | 99.0 | 98.9 | 99.4 | 99.1 | 99.4 | 99.4 | 99.4 | 99.1 | 99.4 | 0.006 | 0.004 | JS | |
| 16 | 99.4 | 99.8 | 99.8 | 99.8 | 99.8 | 99.4 | 99.4 | 99.8 | 99.4 | 99.6 | 99.7 | 99.8 | 99.2 | 99.6 | 99.4 | 0.002 | TW | |
| 17 | 99.6 | 99.8 | 99.9 | 99.9 | 100.0 | 99.4 | 99.4 | 99.8 | 99.5 | 99.8 | 99.8 | 99.8 | 99.4 | 99.8 | 99.6 | 99.8 | J-IK |
表3 不同蚕区来源家蚕微孢子虫SSU rDNA序列同源性(左下角)和遗传距离(右上角)分析
Table 3 Analysis on sequence homology (bottom left half) and genetic distance (upper right half) of SSU rDNA of N. bombycis from different sericulture regions
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 | 16 | 17 | 名称 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0.006 | 0.005 | 0.005 | 0.004 | 0.010 | 0.011 | 0.006 | 0.009 | 0.006 | 0.004 | 0.006 | 0.011 | 0.006 | 0.006 | 0.006 | 0.004 | YNMZCB1 | |
| 2 | 99.4 | 0.002 | 0.002 | 0.002 | 0.006 | 0.006 | 0.000 | 0.006 | 0.004 | 0.003 | 0.002 | 0.008 | 0.004 | 0.006 | 0.002 | 0.002 | YNMZCB2 | |
| 3 | 99.5 | 99.8 | 0.002 | 0.001 | 0.007 | 0.007 | 0.002 | 0.006 | 0.003 | 0.001 | 0.002 | 0.007 | 0.003 | 0.005 | 0.002 | 0.001 | YNMZLQ | |
| 4 | 99.5 | 99.8 | 99.8 | 0.001 | 0.007 | 0.007 | 0.002 | 0.006 | 0.003 | 0.002 | 0.002 | 0.007 | 0.003 | 0.005 | 0.002 | 0.001 | YNCXDY | |
| 5 | 99.6 | 99.8 | 99.9 | 99.9 | 0.006 | 0.006 | 0.002 | 0.005 | 0.002 | 0.002 | 0.002 | 0.006 | 0.002 | 0.004 | 0.002 | 0.000 | YNQJLL | |
| 6 | 99.0 | 99.4 | 99.3 | 99.3 | 99.4 | 0.011 | 0.006 | 0.011 | 0.008 | 0.007 | 0.006 | 0.012 | 0.008 | 0.010 | 0.006 | 0.006 | YN1 | |
| 7 | 98.9 | 99.4 | 99.3 | 99.3 | 99.4 | 98.9 | 0.006 | 0.011 | 0.009 | 0.008 | 0.006 | 0.013 | 0.006 | 0.011 | 0.006 | 0.006 | YN2 | |
| 8 | 99.4 | 100.0 | 99.8 | 99.8 | 99.8 | 99.4 | 99.4 | 0.006 | 0.004 | 0.003 | 0.002 | 0.008 | 0.004 | 0.006 | 0.002 | 0.002 | YN3 | |
| 9 | 99.1 | 99.4 | 99.4 | 99.4 | 99.5 | 98.9 | 98.9 | 99.4 | 0.007 | 0.006 | 0.006 | 0.011 | 0.007 | 0.009 | 0.006 | 0.005 | YN4 | |
| 10 | 99.4 | 99.6 | 99.7 | 99.7 | 99.8 | 99.2 | 99.1 | 99.6 | 99.3 | 0.004 | 0.004 | 0.007 | 0.005 | 0.006 | 0.004 | 0.002 | SC1 | |
| 11 | 99.6 | 99.7 | 99.9 | 99.8 | 99.8 | 99.3 | 99.2 | 99.7 | 99.4 | 99.6 | 0.003 | 0.008 | 0.004 | 0.006 | 0.003 | 0.002 | CQ1 | |
| 12 | 99.4 | 99.8 | 99.8 | 99.8 | 99.8 | 99.4 | 99.4 | 99.8 | 99.4 | 99.6 | 99.7 | 0.008 | 0.004 | 0.006 | 0.002 | 0.002 | GX1 | |
| 13 | 98.9 | 99.2 | 99.3 | 99.3 | 99.4 | 98.8 | 98.7 | 99.2 | 98.9 | 99.3 | 99.2 | 99.2 | 0.009 | 0.009 | 0.008 | 0.006 | GD1 | |
| 14 | 99.4 | 99.6 | 99.7 | 99.7 | 99.8 | 99.2 | 99.4 | 99.6 | 99.3 | 99.5 | 99.6 | 99.6 | 99.1 | 0.006 | 0.004 | 0.002 | AH | |
| 15 | 99.4 | 99.4 | 99.5 | 99.5 | 99.6 | 99.0 | 98.9 | 99.4 | 99.1 | 99.4 | 99.4 | 99.4 | 99.1 | 99.4 | 0.006 | 0.004 | JS | |
| 16 | 99.4 | 99.8 | 99.8 | 99.8 | 99.8 | 99.4 | 99.4 | 99.8 | 99.4 | 99.6 | 99.7 | 99.8 | 99.2 | 99.6 | 99.4 | 0.002 | TW | |
| 17 | 99.6 | 99.8 | 99.9 | 99.9 | 100.0 | 99.4 | 99.4 | 99.8 | 99.5 | 99.8 | 99.8 | 99.8 | 99.4 | 99.8 | 99.6 | 99.8 | J-IK |
| 分离株 | 长度/bp | GC含量/% |
|---|---|---|
| YNMZCB1 | 187 | 15.51 |
| YNMZCB2 | 186 | 19.35 |
| YNMZLQ | 180 | 20.56 |
| YNCXDY | 184 | 21.20 |
| YNQJLL | 181 | 18.23 |
| YN1~YN18 | 179~192 | 15.51~21.11 |
| SC1~SC16 | 181~186 | 16.67~18.68 |
| GX1~GX19 | 179~190 | 15.51~21.05 |
| GD1~GD12 | 179~190 | 17.13~20.54 |
| CQ1~CQ10 | 180~187 | 15.51~20.54 |
表4 家蚕微孢子虫rDNA-ITS基因序列长度以及GC含量分析
Table 4 Sequence length and GC content analysis of rDNA-ITS gene sequence of N. bombycis
| 分离株 | 长度/bp | GC含量/% |
|---|---|---|
| YNMZCB1 | 187 | 15.51 |
| YNMZCB2 | 186 | 19.35 |
| YNMZLQ | 180 | 20.56 |
| YNCXDY | 184 | 21.20 |
| YNQJLL | 181 | 18.23 |
| YN1~YN18 | 179~192 | 15.51~21.11 |
| SC1~SC16 | 181~186 | 16.67~18.68 |
| GX1~GX19 | 179~190 | 15.51~21.05 |
| GD1~GD12 | 179~190 | 17.13~20.54 |
| CQ1~CQ10 | 180~187 | 15.51~20.54 |
| 1 | CAPELLA-GUTIÉRREZ S, MARCET-HOUBEN M, GABALDÓN T. Phylogenomics supports microsporidia as the earliest diverging clade of sequenced fungi[J/OL]. BMC Biol., 2012, 10: 47[2024-05-12]. . |
| 2 | HAN B, WEISS L M. Microsporidia: obligate intracellular pathogens within the fungal kingdom[J/OL]. Microbiol. Spectrum., 2017, 5(2): FUNK-0018-2016[2024-05-12]. . |
| 3 | STENTIFORD G D, FEIST S W, STONE D M, et al.. Microsporidia: diverse, dynamic, and emergent pathogens in aquatic systems[J]. Trends Parasitol., 2013, 29(11): 567-578. |
| 4 | 刘吉平,曾玲.微孢子虫生物多样性研究的述评[J].昆虫知识,2006,43(2):153-158. |
| LIU J P, ZENG L. An overview of research on the microsporidian biodiversity[J]. Chin. Bull. Entomol., 2006, 43(2): 153-158. | |
| 5 | CALI A, WEISS L M, TAKVORIAN P M. An analysis of the microsporidian genus Brachiola, with comparisons of human and insect isolates of Brachiola algerae[J]. J. Eukaryot. Microbiol., 2004, 51(6): 678-685. |
| 6 | WEISS L M. The first united workshop on microsporidia from invertebrate and vertebrate hosts[J]. Folia Parasitol. Praha., 2005, 52(1-2): 1-7. |
| 7 | BAKER M D, VOSSBRINCK C R, DIDIER E S, et al.. Small subunit ribosomal DNA phylogeny of various microsporidia with emphasis on AIDS related forms[J]. J. Eukaryot. Microbiol., 1995, 42(5): 564-570. |
| 8 | HIRT R P, LOGSDON J M, HEALY B, et al.. Microsporidia are related to Fungi: evidence from the largest subunit of RNA polymerase Ⅱ and other proteins[J]. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 1999, 96(2): 580-585. |
| 9 | CORNMAN R S, CHEN Y P, SCHATZ M C, et al.. Genomic analyses of the microsporidian Nosema ceranae, an emergent pathogen of honey bees[J/OL]. PLoS Pathog., 2009, 5(6): e1000466[2024-05-12]. . |
| 10 | PAN G, XU J, LI T, et al.. Comparative genomics of parasitic silkworm microsporidia reveal an association between genome expansion and host adaptation[J/OL]. BMC Genom., 2013, 14: 186[2024-05-12]. . |
| 11 | XU J, HE Q, MA Z, et al.. The genome of Nosema sp. isolate YNPr: a comparative analysis of genome evolution within the Nosema/Vairimorpha clade [J/OL]. PLoS One, 2016, 11(9): e0162336[2024-05-12]. . |
| 12 | BALCH W E, MAGRUM L J, FOX G E, et al.. An ancient divergence among the bacteria[J]. J. Mol. Evol., 1977, 9(4): 305-311. |
| 13 | KEL C E N, ISSI I V. Effect of changes in insect hosts on the pathogenicity and spore formation in microsporidia[J]. Parazitologigya, 1991, 25(6): 512-519. |
| 14 | 黄少康,鲁兴萌.家蚕微粒子虫(Nosema bombycis)与其形态变异株的侵染性及孢子表面蛋白的比较研究[J].中国农业科学,2004,37(11):1682-1687. |
| HUANG S K, LU X M. Comparative study on the infectivity and spore surface protein of Nosema bombycis and its morphological variant strain[J]. Sci. Agric. Sin., 2004, 37(11): 1682-1687. | |
| 15 | 张素贞,何超,王艳丽,等.重庆地区蜜蜂微孢子虫的鉴定及分子遗传多样性分析[J].西南农业学报,2015,28(5):2323-2330. |
| ZHANG S Z, HE C, WANG Y L, et al.. Identification and genetic diversity of microsporidia Nosema ceranae isolated from Chongqing based on multilocus molecular markers[J]. Southwest China J. Agric. Sci., 2015, 28(5): 2323-2330. | |
| 16 | HATAKEYAMA Y, ODA H, TSUNODA R, et al.. Genome profiling implies high genetic diversity in microsporidia isolated from the common cutworm, Spodoptera litura (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae), in Vietnam[J]. Appl. Entomol. Zool., 2011, 46(3): 293-299. |
| 17 | XING D, LI Q, ZHANG J, et al.. Phylogenetic analysis of the complete rRNA gene sequence of Nosema sp. SE isolated from the beet armyworm Spodoptera exigua [J]. J. Parasitol., 2019, 105(6): 878-881. |
| 18 | 时连辉,邱宝利,高绘菊.不同地域来源的家蚕微孢子虫DNA特异片段序列及同源性分析[J].蚕业科学,2003,29(4):384-386. |
| SHI L H, QIU B L, GAO H J. Study on the comparision of sequence similarity of three Nosema bombycis geographical strains[J]. Acta Sericologica Sin., 2003, 29(4): 384-386. | |
| 19 | 申子刚,潘国庆,许金山,等.重庆地区家蚕微孢子虫遗传多态性分析[J].自然科学进展,2008,18(5):579-586. |
| 20 | 黄旭华,罗梅兰,汤庆坤,等.家蚕病原性微孢子虫多样性调查分析[J].南方农业学报,2018,49(6):1208-1214. |
| HUANG X H, LUO M L, TANG Q K, et al.. Diversity of pathogenic microsporidan of Bombyx mori [J]. J. South. Agric., 2018, 49(6): 1208-1214. | |
| 21 | LIU H, PAN G, LUO B, et al.. Intraspecific polymorphism of rDNA among five Nosema bombycis isolates from different geographic regions in China[J]. J. Invertebr. Pathol., 2013, 113(1): 63-69. |
| 22 | 周成,潘国庆,万永继,等.家蚕微孢子虫N. bombycis分离纯化方法的优化[J].蚕学通讯,2002,22(1):7-9+6. |
| ZHOU C, PAN G Q, WAN Y J, et al.. Optimization of the procedures of isolation and purification of nosema bombycis in silkworm[J]. Newsl. Sericultural. Sci., 2002, 22(1): 7-9+6. | |
| 23 | 潘敏慧, 万永继, 鲁成. 不同种类微孢子虫DNA制备方法的研究[J]. 西南农业大学学报, 2001, 23(2):111-112. |
| 24 | HUANG W F, BOCQUET M, LEE K C, et al.. The comparison of rDNA spacer regions of Nosema ceranae isolates from different hosts and locations[J]. J. Invertebr. Pathol., 2008, 97(1): 9-13. |
| 25 | KUMAR S, STECHER G, TAMURA K. MEGA7: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 7.0 for bigger datasets[J]. Mol. Biol. Evol., 2016, 33(7): 1870-1874. |
| 26 | HUANG W F, TSAI S J, LO C F, et al.. The novel organization and complete sequence of the ribosomal RNA gene of Nosema bombycis [J]. Fungal. Genet. Biol., 2004, 41(5): 473-481. |
| 27 | ZHANG Y H, TANG F F, SHAO Y L, et al.. Molecular epidemiology of Bombyx mori nucleopolyhedrovirus in Yunnan sericulture region, China[J]. Sci. Asia, 2019, 45(4):332-341. |
| 28 | 王敏,许金山,王林玲,等.两株不同地域的家蚕微孢子虫分离株的细胞侵染力比较及遗传多样性分析[J].遗传,2009,31(11):1121-1126. |
| WANG M, XU J S, WANG L L, et al.. Pathogenicity and genetic divergence of two isolates of microsporidia Nosema bombycis [J]. Hereditas, 2009, 31(11): 1121-1126. | |
| 29 | 郑祥明,杨琼,方定坚,等.广东省昆虫微孢子虫资源调查及交叉感染的研究[J].蚕业科学,2003,29(4):380-383. |
| ZHENG X M, YANG Q, FANG D J, et al.. Studies on insect microsporidia resources in Guangdong Province and cross infection among some insects[J]. Acta Sericol. Sin., 2003, 29(4): 380-383. | |
| 30 | 黄旭华,潘志新,朱方容,等.广西野外昆虫微孢子虫对家蚕交叉感染情况调查[J].广西蚕业,2010,47(4):15-20. |
| HUANG X H, PAN Z X, ZHU F R, et al.. Investigation on cross-infection of insect microsporidia to silkworm in Guangxi[J]. Guangxi Seric., 2010, 47(4): 15-20. | |
| 31 | 陈世良,肖圣燕,潘秋玲,等.梨花迁粉蝶微孢子虫对家蚕的侵染力与胚传性[J].昆虫学报,2017,60(2):155-162. |
| CHEN S L, XIAO S Y, PAN Q L, et al.. Infectivity and transmissibility of Nosema sp. CP isolated from Catopsilia pyranthe (Lepidoptera: Pieridae) in the domestic silkworm (Bombyx mori)[J]. Acta Entomol. Sin., 2017, 60(2): 155-162. |
| [1] | 闫晓睿, 薛帼珍, 杨晓霞, 王宇, 杜晨晖, 张朔生, 刘计权. 不同居群北柴胡ISSR遗传多样性分析[J]. 生物技术进展, 2023, 13(6): 919-924. |
| [2] | 高勤学, 杨文科, 蒙永刚, 牙生江·纳斯尔, 买买提吐尔干·库瓦西. 新疆克孜勒苏柯尔克孜地区帕米尔牦牛mtDNA COⅠ 的遗传多样性分析[J]. 生物技术进展, 2022, 12(4): 568-576. |
| [3] | 李静,王莉,道敏,胡平,肖逸,韩建林,王玉涛. 喀喇昆仑-帕米尔地区牦牛mtDNA Cytb遗传多样性及系统发育分析[J]. 生物技术进展, 2019, 9(5): 509-517. |
| [4] | 张志明,汤才国,杨三维,乔麟轶,常建忠,赵翠荣4,5,郑军. 小麦(Triticum aestivum L.)野生资源的发掘、利用研究进展[J]. 生物技术进展, 2016, 6(5): 305-311. |
| [5] | 董志刚,刘政海,李晓梅,谭伟,王新平,茹慧玲 ,唐晓萍. SSR标记技术在葡萄品种鉴别及遗传育种上的应用[J]. 生物技术进展, 2016, 6(2): 137-140. |
| [6] | 何真,韵晓东,武凯,姬虎太,常建忠,乔麟轶,郑军. 大豆种质资源遗传多样性研究进展[J]. 生物技术进展, 2015, 5(2): 103-108. |
| [7] | 王世锋,李静,王玉涛. 多浪羊mtDNA D-loop区遗传多样性及系统发育分析[J]. 生物技术进展, 2014, 4(6): 429-434. |
| [8] | 何虎翼,谭冠宁,何新民,何海旺,李丽淑,唐洲萍,王晖. 几种基于PCR的分子标记在甘薯遗传多样性研究中的应用[J]. 生物技术进展, 2014, 4(4): 245-250. |
| [9] | 王寒玉,杜艳伟,李萍,张喜文,朱晶莹,赵晋锋,余爱丽. 40份玉米自交系的ISSR遗传多样性分析[J]. 生物技术进展, 2011, 1(3): 214-218. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
版权所有 © 2021《生物技术进展》编辑部