


生物技术进展 ›› 2025, Vol. 15 ›› Issue (2): 263-275.DOI: 10.19586/j.2095-2341.2024.0183
• 研究论文 • 上一篇
收稿日期:2024-11-24
接受日期:2025-01-21
出版日期:2025-03-25
发布日期:2025-04-29
通讯作者:
周晓今,逄森
作者简介:刘卓颖E-mail:zz9629@126.com
基金资助:
Zhuoying LIU1( ), Xiaojin ZHOU2(
), Xiaojin ZHOU2( ), Yanli HUANG3, Sen PANG1(
), Yanli HUANG3, Sen PANG1( )
)
Received:2024-11-24
Accepted:2025-01-21
Online:2025-03-25
Published:2025-04-29
Contact:
Xiaojin ZHOU,Sen PANG
摘要:
玉米是重要的粮饲兼用作物,盐胁迫严重影响其生长发育,导致产量和品质下降。茉莉酸及其衍生物(jasmonates, JAs)是与植物防御相关的天然植物激素,基于模式植物的研究表明,JAs在响应盐胁迫中发挥重要作用。为探究玉米中JAs介导的盐胁迫响应的具体机制,分别对100 μmol·L-1 MeJA和200 mmol·L-1 NaCl处理6 h玉米幼苗的地上和地下部组织进行转录组测序,交叉分析得到JA诱导且响应高盐胁迫的差异表达基因(differential expression genes, DEGs),并挑选8个DEGs通过RT-qPCR进行验证。结果发现地上和地下部组织中分别共有362和803个基因差异表达,GO和KEGG富集分析显示这些基因涉及糖的合成转运、防御性次生代谢物合成、抗氧化酶合成以及脱落酸和乙烯信号通路。研究结果提示JA信号通路诱导玉米高盐胁迫响应的潜在关键基因和代谢途径,为进一步挖掘JA信号通路调控抗盐性的具体分子机制提供了线索。
中图分类号:
刘卓颖, 周晓今, 黄燕丽, 逄森. 玉米盐胁迫和MeJA处理下的转录组联合分析[J]. 生物技术进展, 2025, 15(2): 263-275.
Zhuoying LIU, Xiaojin ZHOU, Yanli HUANG, Sen PANG. Joint Transcriptome Analysis of Maize Under Salt Stress and MeJA Treatment[J]. Current Biotechnology, 2025, 15(2): 263-275.
| 基因名称(ID) | 上游引物序列(5'→3') | 下游引物序列(5'→3') |
|---|---|---|
| ZmActin (Zm00001d013410) | 5'-ATGTTTCCTGGGATTGCCGAT-3' | 5'-CCAGTTTCGTCATACTCTCCCTTG-3' |
| SWEET6a (Zm00001d044421) | 5'-CGAGACGTGCTTTACCCACA-3' | 5'-GAATGGCAAACACAGCCACA-3' |
| CKX4 (Zm00001d043293) | 5'-CGGCCGACTCGTAACGTAAT-3' | 5'-CACGCGATTAACAACCCCAC-3' |
| POD64 (Zm00001d040705) | 5'-GTGCCCAACTCCTACTCTGG-3' | 5'-TGACACACGAACTACGCACT-3' |
| EREB113 (Zm00001d010175) | 5'-GCCAAGGCAGCAGCAGTCA-3' | 5'-GGCACAGAAGCCACGGTAA-3' |
| WRKY114 (Zm00001d036726) | 5'-CTAGCTCTAGCACGTACGCC-3' | 5'-GAGCGGTACAAACTCGGTCA-3' |
| ZIM27 (Zm00001d027900) | 5'-AGGAAGGTGTCGCTAAAGAG-3' | 5'-CTGCCGTCGATGAGATTG-3' |
| TPS11 (Zm00001d018342) | 5'-CGGCGTGGTGTAGGATTGAT-3' | 5'-ACCATGCGGGCATATACAGG-3' |
| LOX10 (Zm00001d053675) | 5'-TTCCAAACAGCATCTCCATT-3' | 5'-GCCTTATTACAACAGTCCTCACG-3' |
表1 qPCR所用引物序列
Table 1 Primer sequences used for qPCR analysis
| 基因名称(ID) | 上游引物序列(5'→3') | 下游引物序列(5'→3') |
|---|---|---|
| ZmActin (Zm00001d013410) | 5'-ATGTTTCCTGGGATTGCCGAT-3' | 5'-CCAGTTTCGTCATACTCTCCCTTG-3' |
| SWEET6a (Zm00001d044421) | 5'-CGAGACGTGCTTTACCCACA-3' | 5'-GAATGGCAAACACAGCCACA-3' |
| CKX4 (Zm00001d043293) | 5'-CGGCCGACTCGTAACGTAAT-3' | 5'-CACGCGATTAACAACCCCAC-3' |
| POD64 (Zm00001d040705) | 5'-GTGCCCAACTCCTACTCTGG-3' | 5'-TGACACACGAACTACGCACT-3' |
| EREB113 (Zm00001d010175) | 5'-GCCAAGGCAGCAGCAGTCA-3' | 5'-GGCACAGAAGCCACGGTAA-3' |
| WRKY114 (Zm00001d036726) | 5'-CTAGCTCTAGCACGTACGCC-3' | 5'-GAGCGGTACAAACTCGGTCA-3' |
| ZIM27 (Zm00001d027900) | 5'-AGGAAGGTGTCGCTAAAGAG-3' | 5'-CTGCCGTCGATGAGATTG-3' |
| TPS11 (Zm00001d018342) | 5'-CGGCGTGGTGTAGGATTGAT-3' | 5'-ACCATGCGGGCATATACAGG-3' |
| LOX10 (Zm00001d053675) | 5'-TTCCAAACAGCATCTCCATT-3' | 5'-GCCTTATTACAACAGTCCTCACG-3' |
| 样本 | 原始Reads | 过滤后Reads | Q20 | Q30 | GC含量 | Uniquely mapped |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK-S-1 | 43678100 | 43047426 | 98.30 % | 95.06 % | 55.69 % | 95.74 % |
| CK-S-2 | 50852996 | 50083122 | 98.18 % | 94.75 % | 55.37 % | 95.44 % |
| CK-S-3 | 43444624 | 42661464 | 98.27 % | 94.99 % | 55.15 % | 95.64 % |
| CK-S-4 | 51020748 | 50012420 | 98.19 % | 94.90 % | 56.15 % | 95.19 % |
| CK-R-1 | 47340142 | 46607418 | 98.23 % | 94.92 % | 55.15 % | 93.16 % |
| CK-R-2 | 42318602 | 41636470 | 98.28 % | 95.09 % | 55.11 % | 95.27 % |
| CK-R-3 | 42916752 | 42228274 | 98.32 % | 95.14 % | 54.54 % | 93.34 % |
| CK-R-4 | 47196988 | 46286054 | 98.24 % | 94.94 % | 55.29 % | 93.58 % |
| NaCl-S-1 | 44346810 | 43693600 | 98.41 % | 95.37 % | 55.97 % | 95.90 % |
| NaCl-S-2 | 44482508 | 43736948 | 98.13 % | 94.64 % | 56.02 % | 95.60 % |
| NaCl-S-3 | 45904696 | 45070904 | 98.23 % | 94.89 % | 55.94 % | 96.16 % |
| NaCl-S-4 | 55913340 | 54947042 | 98.20 % | 94.86 % | 55.90 % | 95.91 % |
| NaCl-R-1 | 47132296 | 46300150 | 98.25 % | 95.00 % | 55.83 % | 93.94 % |
| NaCl-R-2 | 42765116 | 42001334 | 98.09 % | 94.64 % | 55.81 % | 93.33 % |
| NaCl-R-3 | 44430198 | 43679556 | 98.17 % | 94.79 % | 56.33 % | 93.88 % |
| NaCl-R-4 | 44579594 | 43831320 | 98.28 % | 95.08 % | 56.02 % | 94.16 % |
| MeJA-S-1 | 53707412 | 52824432 | 98.23 % | 94.92 % | 54.87 % | 94.11 % |
| MeJA-S-2 | 43478130 | 42516802 | 98.24 % | 94.97 % | 54.42 % | 94.95 % |
| MeJA-S-3 | 40559722 | 39809098 | 97.95 % | 94.15 % | 54.50 % | 95.22 % |
| MeJA-S-4 | 46413454 | 45685218 | 98.37 % | 95.28 % | 54.46 % | 95.43 % |
| MeJA-R-1 | 42939854 | 41593670 | 98.30 % | 95.02 % | 54.49 % | 88.28 % |
| MeJA-R-2 | 43131000 | 42474978 | 97.98 % | 94.26 % | 54.20 % | 90.04 % |
| MeJA-R-3 | 40744494 | 40164434 | 98.36 % | 95.20 % | 54.64 % | 90.73 % |
| MeJA-R-4 | 48265060 | 47530412 | 98.31 % | 95.09 % | 54.41 % | 93.33 % |
表2 测序数据质量分析和图谱统计结果
Table 2 The quality analysis and mapping statistics of the RNA sequencing data
| 样本 | 原始Reads | 过滤后Reads | Q20 | Q30 | GC含量 | Uniquely mapped |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK-S-1 | 43678100 | 43047426 | 98.30 % | 95.06 % | 55.69 % | 95.74 % |
| CK-S-2 | 50852996 | 50083122 | 98.18 % | 94.75 % | 55.37 % | 95.44 % |
| CK-S-3 | 43444624 | 42661464 | 98.27 % | 94.99 % | 55.15 % | 95.64 % |
| CK-S-4 | 51020748 | 50012420 | 98.19 % | 94.90 % | 56.15 % | 95.19 % |
| CK-R-1 | 47340142 | 46607418 | 98.23 % | 94.92 % | 55.15 % | 93.16 % |
| CK-R-2 | 42318602 | 41636470 | 98.28 % | 95.09 % | 55.11 % | 95.27 % |
| CK-R-3 | 42916752 | 42228274 | 98.32 % | 95.14 % | 54.54 % | 93.34 % |
| CK-R-4 | 47196988 | 46286054 | 98.24 % | 94.94 % | 55.29 % | 93.58 % |
| NaCl-S-1 | 44346810 | 43693600 | 98.41 % | 95.37 % | 55.97 % | 95.90 % |
| NaCl-S-2 | 44482508 | 43736948 | 98.13 % | 94.64 % | 56.02 % | 95.60 % |
| NaCl-S-3 | 45904696 | 45070904 | 98.23 % | 94.89 % | 55.94 % | 96.16 % |
| NaCl-S-4 | 55913340 | 54947042 | 98.20 % | 94.86 % | 55.90 % | 95.91 % |
| NaCl-R-1 | 47132296 | 46300150 | 98.25 % | 95.00 % | 55.83 % | 93.94 % |
| NaCl-R-2 | 42765116 | 42001334 | 98.09 % | 94.64 % | 55.81 % | 93.33 % |
| NaCl-R-3 | 44430198 | 43679556 | 98.17 % | 94.79 % | 56.33 % | 93.88 % |
| NaCl-R-4 | 44579594 | 43831320 | 98.28 % | 95.08 % | 56.02 % | 94.16 % |
| MeJA-S-1 | 53707412 | 52824432 | 98.23 % | 94.92 % | 54.87 % | 94.11 % |
| MeJA-S-2 | 43478130 | 42516802 | 98.24 % | 94.97 % | 54.42 % | 94.95 % |
| MeJA-S-3 | 40559722 | 39809098 | 97.95 % | 94.15 % | 54.50 % | 95.22 % |
| MeJA-S-4 | 46413454 | 45685218 | 98.37 % | 95.28 % | 54.46 % | 95.43 % |
| MeJA-R-1 | 42939854 | 41593670 | 98.30 % | 95.02 % | 54.49 % | 88.28 % |
| MeJA-R-2 | 43131000 | 42474978 | 97.98 % | 94.26 % | 54.20 % | 90.04 % |
| MeJA-R-3 | 40744494 | 40164434 | 98.36 % | 95.20 % | 54.64 % | 90.73 % |
| MeJA-R-4 | 48265060 | 47530412 | 98.31 % | 95.09 % | 54.41 % | 93.33 % |

图1 样本组间的相关系数(R2)热图A:CK组地上部和地下部样品间相关系数热图;B:高盐胁迫组地上部和地下部样品间相关系数热图;C:MeJA处理组地上部和地下部样品间相关系数热图
Fig. 1 Heatmaps of the correlation coefficient between sample groups
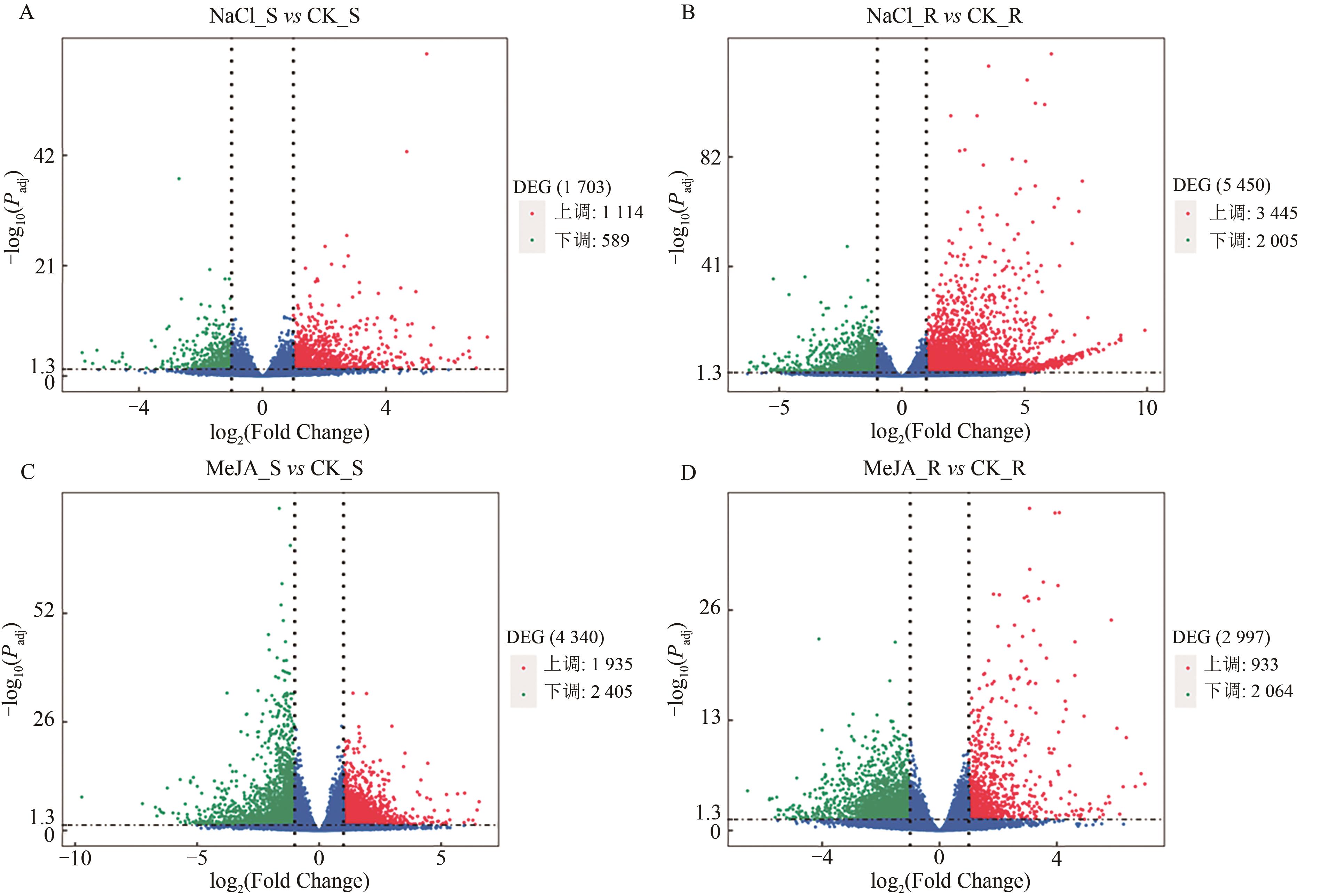
图2 处理组与对照组间差异表达基因火山图A:高盐胁迫组地上部与对照组差异表达基因火山图;B:高盐胁迫组地下部与对照组差异表达基因火山图;C:MeJA处理组地上部与对照组差异表达基因火山图;D:MeJA处理组地下部与对照组差异表达基因火山图。横坐标表示基因在不同样本中表达倍数变化(log2 Fold Change);纵坐标表示基因表达量变化的统计学显著性(-log10 Padj),红色点表示有显著性差异表达的上调基因,绿色点表示有显著性差异表达的下调基因,蓝色点表示表达变化不显著的基因。
Fig. 2 Volcano plots showing DEGs between the treatment and control groups

图4 处理组与对照组间差异表达基因GO富集柱状图A:高盐胁迫组地上部差异表达基因的GO富集柱状图;B:高盐胁迫组地下部差异表达基因的GO富集柱状图;C:MeJA处理组地上部差异表达基因的GO富集柱状图;D:MeJA处理组地下部差异表达基因的GO富集柱状图
Fig. 4 GO enrichment of DEGs between the treatment group and the control group
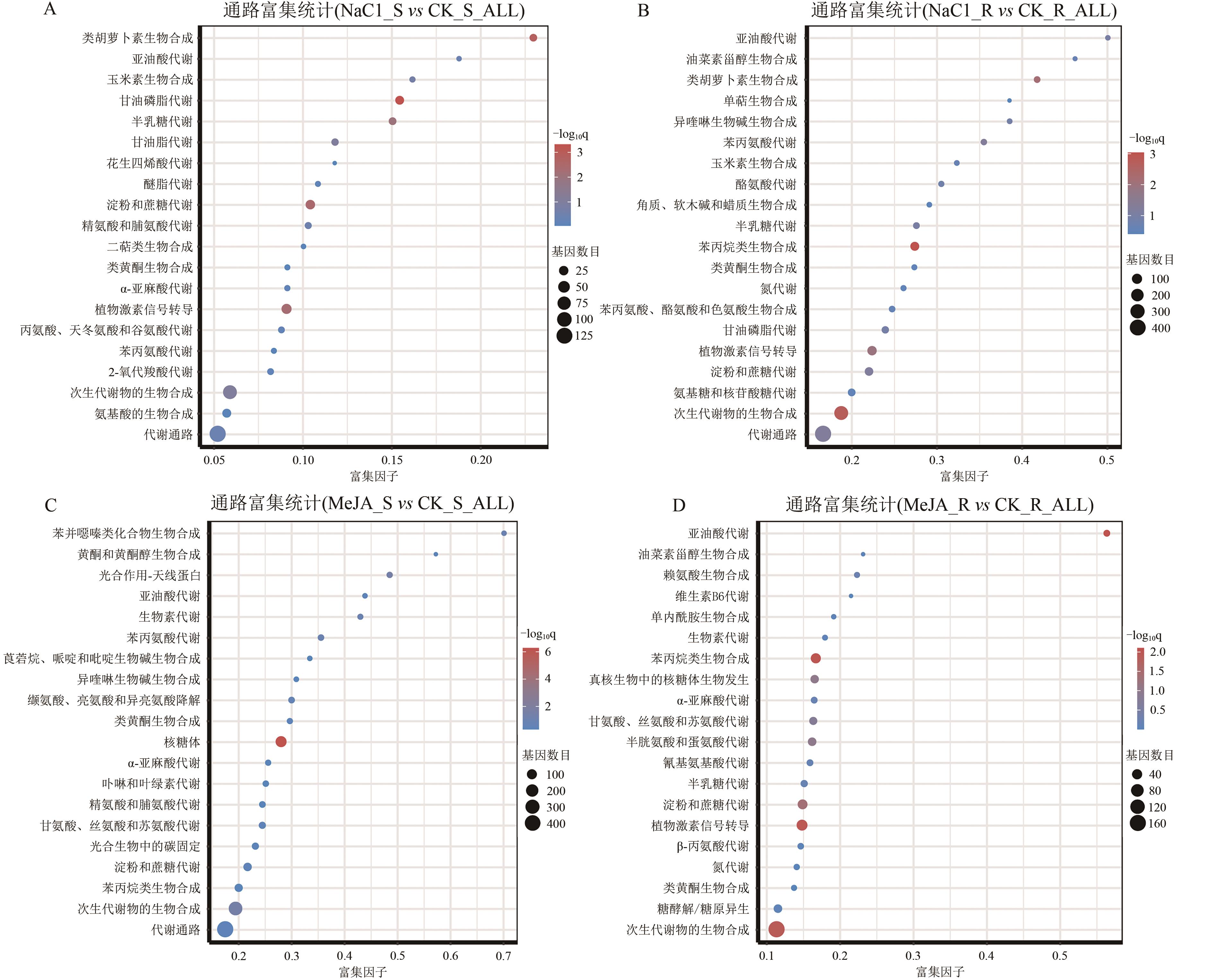
图5 处理组与对照组间差异基因KEGG富集散点图A:高盐胁迫组地上部差异表达基因KEGG富集散点图;B:高盐胁迫组地下部差异表达基因KEGG富集散点图;C:MeJA处理组地上部差异表达基因KEGG富集散点图;D:MeJA处理组地下部差异表达基因KEGG富集散点图。纵坐标表示通路名称,横坐标表示富集因子(rich factor),点的大小表示此通路中DEGs个数,点的颜色对应于不同q值范围。
Fig. 5 Scatter plot of KEGG enrichment of DEGs between the treatment group and the control group
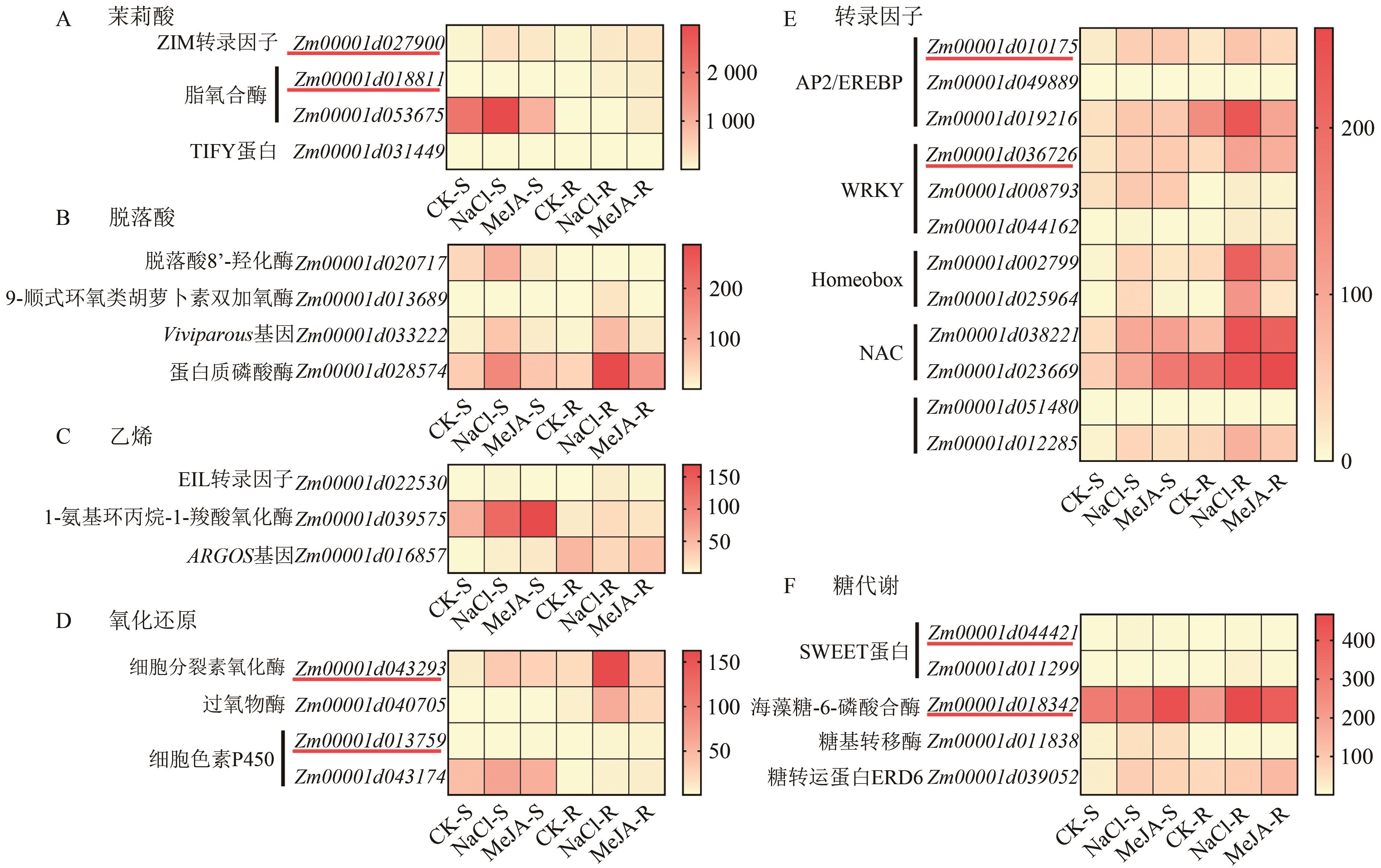
图6 候选基因的FPKM热图A:茉莉酸相关的基因;B:脱落酸相关的基因;C:乙烯相关的基因;D:氧化还原相关的基因;E:转录因子相关的基因;F:糖代谢相关的基因。右侧标尺表示不同颜色对应的FPKM值,红色下划线标记的为后续荧光实时定量PCR验证的候选基因。
Fig. 6 FPKM heatmap of candidate genes
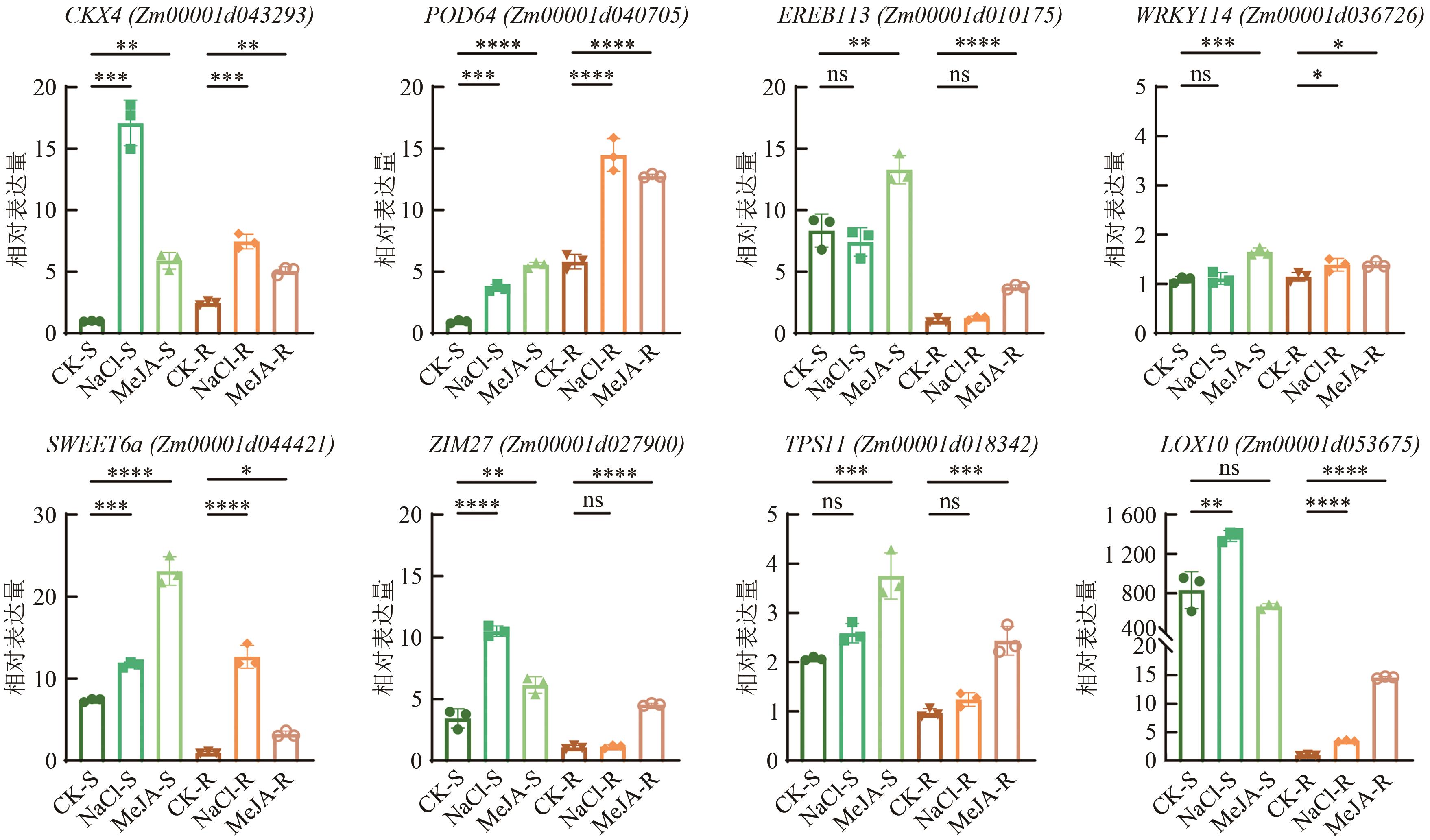
图7 候选基因的荧光实时定量PCR检测注:按2-ΔΔCt计算相对表达量,ns表示数据间无统计学差异(P>0.05),*,**,***,****分别表示数据在P<0.05、P<0.01、P<0.001、P<0.000 1水平有统计学差异。
Fig. 7 RT-qPCR analysis result of candidate genes
| 1 | GONG F, YANG L, TAI F, et al.. “Omics” of maize stress response for sustainable food production: opportunities and challenges[J]. OMICS, 2014, 18(12): 714-732. |
| 2 | HICKEY L T, HAFEEZ A N, ROBINSON H, et al.. Breeding crops to feed 10 billion[J]. Nat. Biotechnol., 2019, 37(7): 744-754. |
| 3 | LIU S, ZENDA T, LI J, et al.. Comparative transcriptomic analysis of contrasting hybrid cultivars reveal key drought-responsive genes and metabolic pathways regulating drought stress tolerance in maize at various stages[J/OL]. PLoS One, 2020, 15(10): e0240468[2024-10-24]. . |
| 4 | ZHANG C, YANG R, ZHANG T, et al.. ZmTIFY16, a novel maize TIFY transcription factor gene, promotes root growth and development and enhances drought and salt tolerance in Arabidopsis and Zea mays[J]. Plant Growth Regul., 2023, 100(1): 149-160. |
| 5 | LI C. Breeding crops by design for future agriculture[J]. J. Zhejiang Univ. Sci. B, 2020, 21(6): 423-425. |
| 6 | LIU Y, WANG F, ZHANG A, et al.. Improvement of salinity tolerance in water-saving and drought-resistance rice (WDR)[J/OL]. Int. J. Mol. Sci., 2023, 24(6): 5444[2024-10-24]. . |
| 7 | YANG C, LV D, JIANG S, et al.. Soil salinity regulation of soil microbial carbon metabolic function in the Yellow River Delta, China[J/OL]. Sci. Total Environ., 2021, 790: 148258[2024-10-24]. . |
| 8 | ZHOU J, QIAO J, WANG J, et al.. OsQHB improves salt tolerance by scavenging reactive oxygen species in rice[J/OL]. Front. Plant Sci., 2022, 13: 848891[2024-10-24]. . |
| 9 | ZHAO S, ZHANG Q, LIU M, et al.. Regulation of plant responses to salt stress[J/OL]. Int. J. Mol. Sci., 2021, 22(9): 4609[2024-10-24]. . |
| 10 | GOOSSENS J, FERNÁNDEZ-CALVO P, SCHWEIZER F, et al.. Jasmonates: signal transduction components and their roles in environmental stress responses[J]. Plant Mol. Biol., 2016, 91(6): 673-689. |
| 11 | WANG Y, MOSTAFA S, ZENG W, et al.. Function and mechanism of jasmonic acid in plant responses to abiotic and biotic stresses[J/OL]. Int. J. Mol. Sci., 2021, 22(16): 8568[2024-10-24]. . |
| 12 | WANG J, SONG L, GONG X, et al.. Functions of jasmonic acid in plant regulation and response to abiotic stress[J/OL]. Int. J. Mol. Sci., 2020, 21(4): 1446[2024-10-24]. . |
| 13 | FU J, WU H, MA S, et al.. OsJAZ1 attenuates drought resistance by regulating JA and ABA signaling in rice[J/OL]. Front. Plant Sci., 2017, 8: 2108[2024-10-24]. . |
| 14 | SEO J S, JOO J, KIM M J, et al.. OsbHLH148, a basic helix-loop-helix protein, interacts with OsJAZ proteins in a jasmonate signaling pathway leading to drought tolerance in rice[J]. Plant J., 2011, 65(6): 907-921. |
| 15 | DU H, LIU H, XIONG L. Endogenous auxin and jasmonic acid levels are differentially modulated by abiotic stresses in rice[J/OL]. Front. Plant Sci., 2013, 4: 397[2024-10-24]. . |
| 16 | HU Y, JIANG L, WANG F, et al.. Jasmonate regulates the inducer of cbf expression-C-repeat binding factor/DRE binding factor1 cascade and freezing tolerance in Arabidopsis [J]. Plant Cell, 2013, 25(8): 2907-2924. |
| 17 | WANG L, CHEN H, CHEN G, et al.. Transcription factor SlWRKY50 enhances cold tolerance in tomato by activating the jasmonic acid signaling[J]. Plant Physiol., 2024, 194(2): 1075-1090. |
| 18 | DING F, WANG C, ZHANG S, et al.. A jasmonate-responsive glutathione S-transferase gene SlGSTU24 mitigates cold-induced oxidative stress in tomato plants[J/OL]. Sci. Hortic., 2022, 303: 111231[2024-10-24]. . |
| 19 | SHANG C, LIU X, CHEN G, et al.. SlWRKY81 regulates Spd synthesis and Na(+)/K(+) homeostasis through interaction with SlJAZ1 mediated JA pathway to improve tomato saline-alkali resistance[J]. Plant J., 2024, 118(6): 1774-1792. |
| 20 | WU H, YE H, YAO R, et al.. OsJAZ9 acts as a transcriptional regulator in jasmonate signaling and modulates salt stress tolerance in rice[J]. Plant Sci., 2015, 232: 1-12. |
| 21 | QIU Z, GUO J, ZHU A, et al.. Exogenous jasmonic acid can enhance tolerance of wheat seedlings to salt stress[J]. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf., 2014, 104: 202-208. |
| 22 | 王芳, 周娟,黄兴华, 等. 外源MeJA对盐胁迫下玉米幼苗生长及抗氧化酶基因表达的影响[J]. 玉米科学, 2022, 30(2): 75-81. |
| WANG F, ZHOU J, HUANG X H, et al.. Effects of exogenous MeJA on growth and antioxidant enzyme gene expression of maize seedlings under salt stress[J]. J. Maize Sci., 2022, 30(2): 75-81. | |
| 23 | 陈芳, 杨双龙, 张莉, 等. 外源茉莉酸甲酯对盐胁迫下玉米幼苗AsA-GSH循环的影响[J]. 生物学通报, 2021, 56(11): 44-48. |
| CHEN F, YANG S L, ZHANG L, et al.. Effects of exogenous methyl jasmonate on ascorbate-glutathione cycle in Zea mays seedlings under salt stress[J]. Bull. Biol., 2021, 56(11): 44-48. | |
| 24 | YU Z, DUAN X, LUO L, et al.. How plant hormones mediate salt stress responses[J]. Trends Plant Sci., 2020, 25(11): 1117-1130. |
| 25 | LIU S, ZHANG P, LI C, et al.. The moss jasmonate ZIM-domain protein PnJAZ1 confers salinity tolerance via crosstalk with the abscisic acid signalling pathway[J]. Plant Sci., 2019, 280: 1-11. |
| 26 | 史庆玲, 李忠峰, 董永彬, 等. 植物乙烯信号转导通路及其相关基因的研究进展[J]. 生物技术进展, 2019, 9(5): 449-454. |
| SHI Q L, LI Z F, DONG Y B, et al.. Progress on ethylene signal transduction pathway and related genes in plants[J]. Curr. Biotechnol., 2019, 9(5): 449-454. | |
| 27 | RAZA A, CHARAGH S, ZAHID Z, et al.. Jasmonic acid: a key frontier in conferring abiotic stress tolerance in plants[J]. Plant Cell Rep., 2021, 40(8): 1513-1541. |
| 28 | CAO H, ZHANG K, LI W, et al.. ZmMYC7 directly regulates ZmERF147 to increase maize resistance to Fusarium graminearum [J]. Crop J., 2023, 11(1): 79-88. |
| 29 | MA C, LI R, SUN Y, et al.. ZmMYC2s play important roles in maize responses to simulated herbivory and jasmonate[J]. J. Integr. Plant Biol., 2023, 65(4): 1041-1058. |
| 30 | HE Y, BORREGO E J, GORMAN Z, et al.. Relative contribution of LOX10, green leaf volatiles and JA to wound-induced local and systemic oxylipin and hormone signature in Zea mays (maize)[J/OL]. Phytochemistry, 2020, 174: 112334[2024-10-24]. . |
| 31 | ZHANG X, LIU P, QING C, et al.. Comparative transcriptome analyses of maize seedling root responses to salt stress[J/OL]. PeerJ, 2021, 9: e10765[2024-10-24]. . |
| 32 | KAZAN K. Diverse roles of jasmonates and ethylene in abiotic stress tolerance[J]. Trends Plant Sci., 2015, 20(4): 219-229. |
| 33 | WANG M, FAN X, DING F. Jasmonate: a hormone of primary importance for temperature stress response in plants[J/OL]. Plants (Basel), 2023, 12(24): 4080[2024-10-24]. . |
| 34 | WANG W, CAO J, HUANG S, et al.. Integrated transcriptomics and metabolomics analyses provide insights into salt-stress response in germination and seedling stage of wheat (Triticum aestivum L.)[J/OL]. Curr. Plant Biol., 2023, 33: 100274[2024-10-24]. . |
| 35 | XIONG H, GUO H, XIE Y, et al.. RNAseq analysis reveals pathways and candidate genes associated with salinity tolerance in a spaceflight-induced wheat mutant[J/OL]. Sci. Rep., 2017, 7(1): 2731[2024-10-24]. . |
| 36 | LUO Q, TENG W, FANG S, et al.. Transcriptome analysis of salt-stress response in three seedling tissues of common wheat[J]. Crop J., 2019, 7(3): 378-392. |
| 37 | XIONG Y, YAN H, LIANG H, et al.. RNA-Seq analysis of Clerodendrum inerme (L.) roots in response to salt stress[J/OL]. BMC Genomics, 2019, 20(1): 724[2024-10-24]. . |
| 38 | ZHU M, LIU Y, CAI P, et al.. Jasmonic acid pretreatment improves salt tolerance of wheat by regulating hormones biosynthesis and antioxidant capacity[J/OL]. Front. Plant Sci., 2022, 13: 968477[2024-10-24]. . |
| 39 | LIU S, HE Y, FU Y, et al.. Transcriptome sequencing revealed the mechanism of promoting floret opening by exogenous methyl jasmonate in Sorghum [J/OL]. 3 Biotech, 2021, 11(4): 181[2024-10-24]. . |
| 40 | NIE G, ZHOU J, JIANG Y, et al.. Transcriptome characterization of candidate genes for heat tolerance in perennial ryegrass after exogenous methyl Jasmonate application[J/OL]. BMC Plant Biol., 2022, 22(1): 68[2024-10-24]. . |
| 41 | ZHU J, WEI X, YIN C, et al.. ZmEREB57 regulates OPDA synthesis and enhances salt stress tolerance through two distinct signalling pathways in Zea mays [J]. Plant Cell Environ., 2023, 46(9): 2867-2883. |
| 42 | JIANG J, MA S, YE N, et al.. WRKY transcription factors in plant responses to stresses[J]. J. Integr. Plant Biol., 2017, 59(2): 86-101. |
| 43 | LUO P, CHEN Y, RONG K, et al.. ZmSNAC13, a maize NAC transcription factor conferring enhanced resistance to multiple abiotic stresses in transgenic Arabidopsis [J]. Plant Physiol. Biochem., 2022, 170: 160-170. |
| 44 | WU J, JIANG Y, LIANG Y, et al.. Expression of the maize MYB transcription factor ZmMYB3R enhances drought and salt stress tolerance in transgenic plants[J]. Plant Physiol. Biochem., 2019, 137: 179-188. |
| 45 | CHENG C, AN L, LI F, et al.. Wide-range portrayal of AP2/ERF transcription factor family in maize (Zea mays L.) development and stress responses[J/OL]. Genes (Basel), 2023, 14(1): 194[2024-10-24]. . |
| 46 | WANG Y M, YANG Q, XU H, et al.. Physiological and transcriptomic analysis provide novel insight into cobalt stress responses in willow[J/OL]. Sci. Rep., 2020, 10(1): 2308[2024-10-24]. . |
| 47 | MATHAN J, SINGH A, RANJAN A. Sucrose transport in response to drought and salt stress involves ABA-mediated induction of OsSWEET13 and OsSWEET15 in rice[J]. Physiol. Plant., 2021, 171(4): 620-637. |
| 48 | ZHANG J, ZHOU Y, LIU L, et al.. Overexpression of OsSWEET5 in rice causes growth retardation and precocious senescence[J/OL]. PLoS One, 2014, 9(4): e94210[2024-10-24]. . |
| 49 | GAUTAM T, DUTTA M, JAISWAL V, et al.. Emerging roles of SWEET sugar transporters in plant development and abiotic stress responses[J/OL]. Cells, 2022, 11(8): 1303[2024-10-24]. . |
| 50 | ROBERT C A M, MATEO P. The chemical ecology of benzoxazinoids[J]. Chimia (Aarau), 2022, 76(11): 928-938. |
| 51 | 王颖, 梅馨月, 刘屹湘, 等. 植物中防御相关物质苯并嗯嗪类的研究进展[J]. 植物生理学报, 2021, 57(4): 767-779. |
| WANG Y, MEI X Y, LIU Y X, et al.. Research progress of benzoxazinoids as defense related substances in plants[J]. Plant Physiol. J., 2021, 57(4): 767-779. |
| [1] | 张青云, 马蕾, 胥华, 靳礼安, 邹俊杰, 王宝宝, 陈全家, 徐妙云. 根系木质素含量影响玉米耐盐性的机制研究[J]. 生物技术进展, 2025, 15(1): 67-77. |
| [2] | 齐鑫, 李欣然, 郭亚宁, 王丹, 李凯, 吴琼, 李亮. 基于数字PCR方法的玉米内标准基因比较研究[J]. 生物技术进展, 2025, 15(1): 78-85. |
| [3] | 万令飞, 潘文婷, 雍雨婷, 李元帅, 赵悦, 阎新龙. 单细胞转录组测序技术在肝纤维化中的研究进展[J]. 生物技术进展, 2024, 14(5): 793-804. |
| [4] | 谭景胜, 赵官涛, 朱莉, 李玉斌. 玉米rMrh/Mrh双元转座系统体细胞转座特性分析[J]. 生物技术进展, 2024, 14(4): 601-609. |
| [5] | 马叶子, 夏美娟, 刘翠翠, 王洪涛, 周家喜. 新型冠状病毒奥密克戎感染下血小板转录组与蛋白质组的对比分析[J]. 生物技术进展, 2024, 14(4): 649-656. |
| [6] | 张奇雨, 吕晓桂, 包锦. 冷等离子体处理对盐胁迫下燕麦种子萌发及幼苗生长的影响[J]. 生物技术进展, 2024, 14(3): 413-421. |
| [7] | 张慧, 刘愽愽, 李凤梅, 崔健. 生长素信号途径参与南瓜白粉菌胁迫的响应研究[J]. 生物技术进展, 2024, 14(3): 433-441. |
| [8] | 乔红梅. 红树科陆生植物竹节树的转录组分析[J]. 生物技术进展, 2024, 14(2): 228-236. |
| [9] | 赵官涛, 谭景胜, 朱莉, 李玉斌. 玉米非自主性转座子rDt的体细胞转座序列特征[J]. 生物技术进展, 2024, 14(2): 248-256. |
| [10] | 李凌燕, 肖冰, 张旭冬, 张华, 陈子言, 王颢潜, 张秀杰, 陈红, 梁晋刚. 转基因玉米MON87411实时荧光PCR定性检测方法的建立及其标准化[J]. 生物技术进展, 2024, 14(2): 257-262. |
| [11] | 王彩虹, 邵煜涵, 蒋梦媛. IL-17抑制铜绿假单胞菌感染肺上皮细胞的机制研究[J]. 生物技术进展, 2024, 14(2): 304-311. |
| [12] | 刘勤勤, 黄柏铭, 马叶子, 刘翠翠, 王洪涛, 周家喜. 急性感染条件下巨核细胞与血小板转录组变化的对比分析[J]. 生物技术进展, 2023, 13(3): 465-472. |
| [13] | 李敏, 王磊, 邹俊杰. 我国转基因抗虫耐除草剂玉米产业化应用面临的机遇与挑战[J]. 生物技术进展, 2023, 13(2): 157-165. |
| [14] | 肖克, 周晓今, 陈茹梅, 逄森. 玉米中ClassⅠ和ClassⅡ NAS蛋白之间的BiFC互作研究[J]. 生物技术进展, 2022, 12(5): 728-736. |
| [15] | 刘婷婷, 仝涛, 黄昆仑. 转基因玉米的研究进展和食用安全性评价[J]. 生物技术进展, 2022, 12(4): 523-531. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
版权所有 © 2021《生物技术进展》编辑部