


生物技术进展 ›› 2024, Vol. 14 ›› Issue (6): 1004-1015.DOI: 10.19586/j.2095-2341.2024.0086
汪苏洁1( ), 顾梦丽1, 陶界锰1,2, 童治军3, 郭俊佳1, 金静静1,2, 徐梦晓1, 孟利军1, 张剑锋1,2, 曹培健1,2, 卢鹏1,2(
), 顾梦丽1, 陶界锰1,2, 童治军3, 郭俊佳1, 金静静1,2, 徐梦晓1, 孟利军1, 张剑锋1,2, 曹培健1,2, 卢鹏1,2( )
)
收稿日期:2024-04-17
接受日期:2024-06-21
出版日期:2024-11-25
发布日期:2024-12-27
通讯作者:
卢鹏
作者简介:汪苏洁 E-mail: wangsujie951230@163.com;
基金资助:
Sujie WANG1( ), Mengli GU1, Jiemeng TAO1,2, Zhijun TONG3, Junjia GUO1, Jingjing JIN1,2, Mengxiao XU1, Lijun MENG1, Jianfeng ZHANG1,2, Peijian CAO1,2, Peng LU1,2(
), Mengli GU1, Jiemeng TAO1,2, Zhijun TONG3, Junjia GUO1, Jingjing JIN1,2, Mengxiao XU1, Lijun MENG1, Jianfeng ZHANG1,2, Peijian CAO1,2, Peng LU1,2( )
)
Received:2024-04-17
Accepted:2024-06-21
Online:2024-11-25
Published:2024-12-27
Contact:
Peng LU
摘要:
烟草疫霉(Phytophthora nicotianae)是一种可引发烟草黑胫病的土传卵菌,对烟草生产造成极大危害。为了应对这一问题,筛选出一株对烟草疫霉菌具有较强生防功能的菌株XC-29,通过解析基因组信息,挖掘其拮抗代谢产物及拮抗基因。采用平板对峙法和盆栽试验鉴定生防菌XC-29的抑菌活性和防治效果;通过形态观察和16S rRNA扩增子测序技术准确鉴定了XC-29菌株;利用全基因组测序、转录组测序探究菌株拮抗机制。结果表明,根际土分离的拮抗菌株XC-29鉴定为沙福芽孢杆菌(Bacillus safensis),其全基因组测序预测出136种碳水化合物活性酶和11个编码次生代谢产物合成相关的基因簇,其中6个基因簇已被确认为抗菌物质合成簇,分别编码地衣素、双效菌素、schizokinen、丰原素、杆菌溶素和嗜铁素;转录组测序结果进一步确定菌株基因具有编码相应抑菌物质的能力。综上,沙福芽孢杆菌XC-29对烟草疫霉菌具有较强的拮抗作用,全基因组和转录组分析初步揭示了沙福芽孢杆菌XC-29的抑病机理,为进一步探究拮抗菌的抑菌机制和生物防控提供理论依据。
中图分类号:
汪苏洁, 顾梦丽, 陶界锰, 童治军, 郭俊佳, 金静静, 徐梦晓, 孟利军, 张剑锋, 曹培健, 卢鹏. 烟草疫霉拮抗菌XC-29的分离鉴定及其全基因组序列分析[J]. 生物技术进展, 2024, 14(6): 1004-1015.
Sujie WANG, Mengli GU, Jiemeng TAO, Zhijun TONG, Junjia GUO, Jingjing JIN, Mengxiao XU, Lijun MENG, Jianfeng ZHANG, Peijian CAO, Peng LU. Isolation, Identification and Whole-genome Sequence Analysis of Phytophthora nicotianae Antagonistic Bacteria XC-29[J]. Current Biotechnology, 2024, 14(6): 1004-1015.
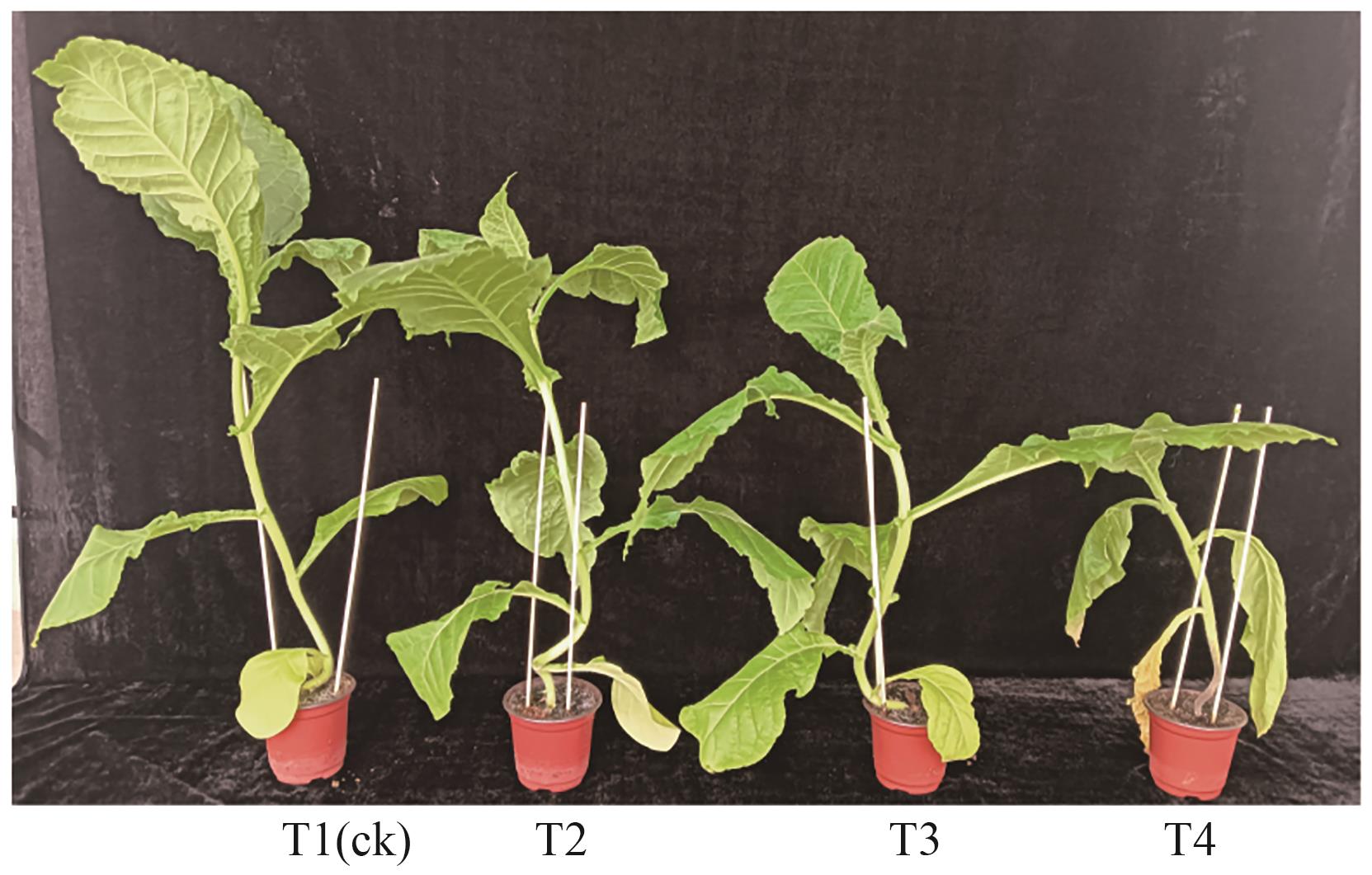

图2 生防菌XC-29对对烟草黑胫病的盆栽防效注:T1—不处理;T2—生防菌处理;T3—生防菌+烟草疫霉菌谷处理;T4—烟草疫霉菌谷处理。
Fig. 2 The control effects of biocontrol bacteria XC-29 against tobacco black shank disease in pot-control
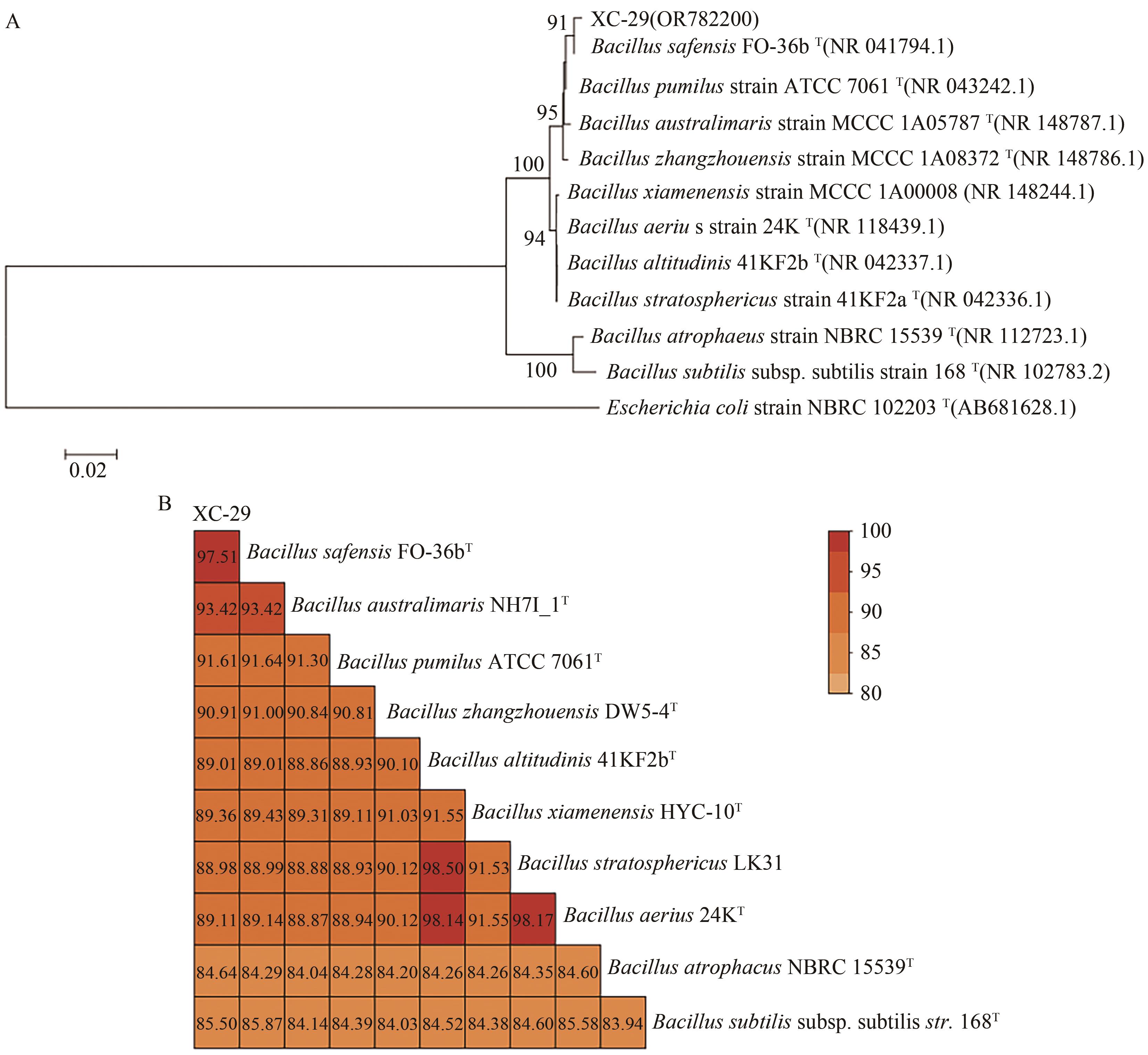
图4 生防菌XC-29及其相似细菌的16S rRNA基因序列构建系统进化关系及ANI值分析A:基于16S rRNA基因序列的生防菌XC-29及其相似细菌系统进化树;括号内表示为各菌株的GenBank登录号;“T”表示模式菌株;分支上的数值代表支持率(此处只显示支持率>90%的分支);标尺表示2%的序列进化差异;B:生防菌XC-29与其相似细菌的ANI值(%)比较;图中展示的数字表示核苷酸一致性(ANI)值,单位为百分比(%);图中颜色越红表示ANI值越高。图中涉及的菌种包括:Bacillus safensis—沙福芽孢杆菌;Bacillus pumilus—短小芽孢杆菌;Bacillus australimaris—南海芽胞杆菌;Bacillus zhangzhouensis—漳州芽孢杆菌;Bacillus xiamenensis—厦门芽孢杆菌;Bacillus aerius—空气芽孢杆菌;Bacillus altitudinis—高地芽孢杆菌;Bacillus stratosphericus—同温层芽孢杆菌;Bacillus atrophaeus—萎缩芽孢杆菌;Bacillus subtilis subsp. subtilis—枯草芽孢杆菌的一个亚种。
Fig. 4 Phylogenetic relationship and ANI value analysis based on the 16S rRNA gene sequences of biocontrol bacteria XC-29 and its similar bacteria
| 类型 | 特征 | 数值 |
|---|---|---|
| 基因组 | 染色体个数 | 1 |
| 基因组序列总长度/bp | 3 719 058 | |
| 编码蛋白基因 | 基因数 | 3 870 |
| 基因总长度/bp | 3 310 209 | |
| 基因平均长度/bp | 855 | |
| 基因序列中GC含量/% | 42.24 | |
| 基因间区 | 基因间区总长度/bp | 408 849 |
| 基因间区GC含量/% | 37.87 | |
| 非编码 | tRNA拷贝数 | 81 |
| 5S rRNA拷贝数 | 8 | |
| 16S rRNA拷贝数 | 8 | |
| 23S rRNA拷贝数 | 8 | |
| sRNA拷贝数 | 7 |
表1 生防菌XC-29全基因组序列分析
Table 1 Whole genome sequence analysis of biocontrol strain XC-29
| 类型 | 特征 | 数值 |
|---|---|---|
| 基因组 | 染色体个数 | 1 |
| 基因组序列总长度/bp | 3 719 058 | |
| 编码蛋白基因 | 基因数 | 3 870 |
| 基因总长度/bp | 3 310 209 | |
| 基因平均长度/bp | 855 | |
| 基因序列中GC含量/% | 42.24 | |
| 基因间区 | 基因间区总长度/bp | 408 849 |
| 基因间区GC含量/% | 37.87 | |
| 非编码 | tRNA拷贝数 | 81 |
| 5S rRNA拷贝数 | 8 | |
| 16S rRNA拷贝数 | 8 | |
| 23S rRNA拷贝数 | 8 | |
| sRNA拷贝数 | 7 |
| 类型 | 基因数 | 占总基因百分比 |
|---|---|---|
| COG | 2 896 | 74.83% |
| GO | 2 708 | 69.97% |
| KEGG | 3 652 | 94.37% |
| CAZy | 136 | 3.51% |
表2 生防菌XC-29基因功能注释数据库分布情况
Table 2 Database distribution of gene functional annotation from the biocontrol bacterium XC-29
| 类型 | 基因数 | 占总基因百分比 |
|---|---|---|
| COG | 2 896 | 74.83% |
| GO | 2 708 | 69.97% |
| KEGG | 3 652 | 94.37% |
| CAZy | 136 | 3.51% |
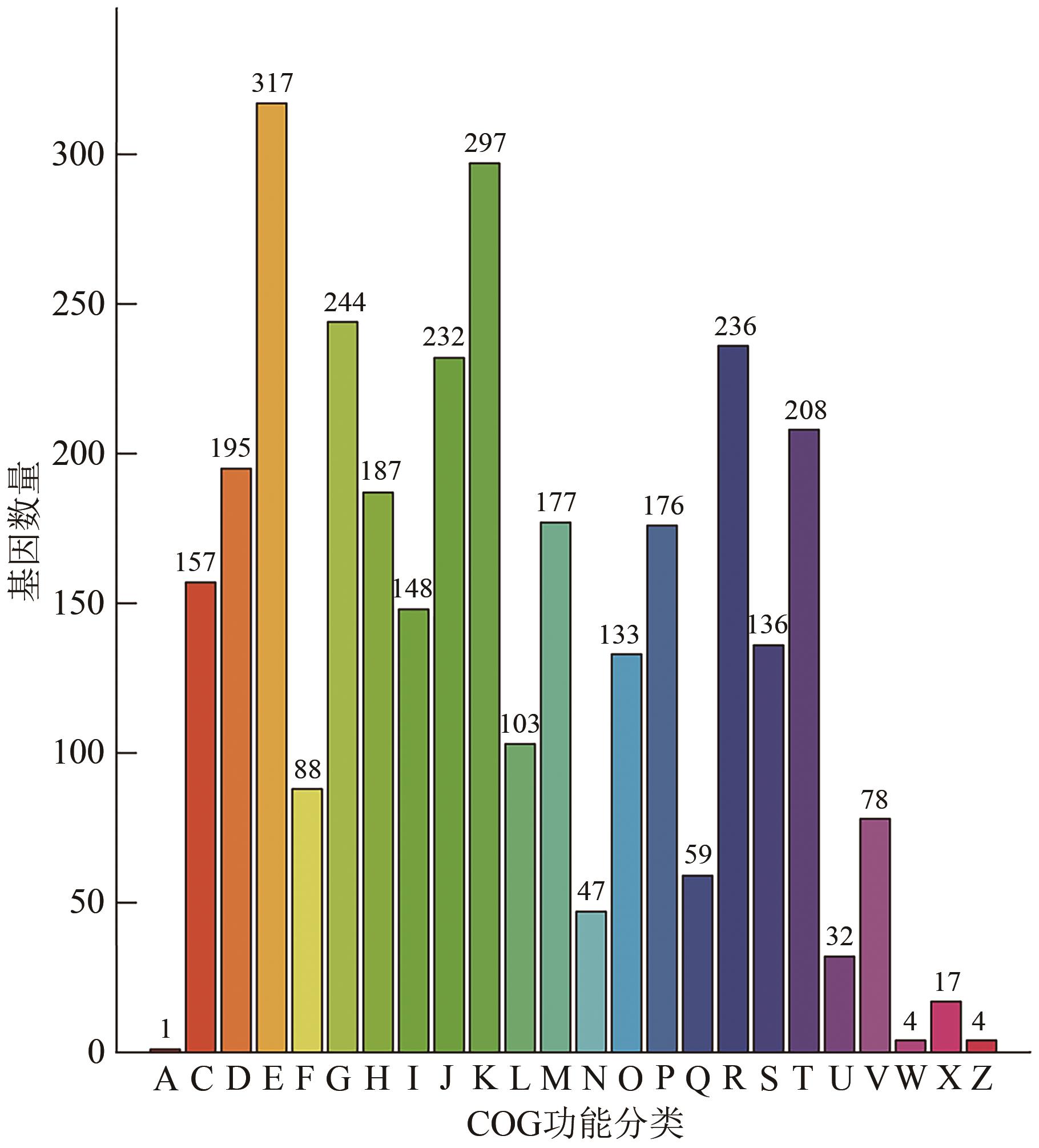
图5 生防菌XC-29基因组COG功能注释图注:A—RNA加工修饰;C—能量生成和转换;D—细胞周期控制、细胞分裂和染色体分裂;E—氨基酸转运代谢;F—核苷酸转运和代谢;G—碳水化合物转运代谢;H—辅酶转运和代谢;I—脂质转运代谢;J—翻译、核糖体结构和生物合成;K—转录;L—复制,重组和修复;M—细胞壁/膜/被膜的生物合成;N—细胞运动;O—翻译后修饰,蛋白质折叠和伴侣蛋白;P—无机离子转运代谢;Q—次级代谢物生物合成、转运和代谢;R—主要功能预测;S—未知功能;T—信号转导机制;U—胞内转运、分泌和小泡运输;V—抵御机制;W—胞外结构;X—动员组—噬菌体原、转座子;Z—细胞骨架。
Fig. 5 COG function annotation of biocontrol bacterium XC-29 genome
| 通路编号 | 类目 | 基因数(>40) |
|---|---|---|
| Map01100 | 代谢途径 | 566 |
| Map01110 | 次生代谢物的生物合成 | 276 |
| Map01130 | 抗生素的生物合成 | 211 |
| Map01120 | 不同环境下的微生物代谢 | 170 |
| Map02010 | ABC转运蛋白 | 138 |
| Map01230 | 氨基酸的生物合成 | 130 |
| Map02020 | 双组分调节系统 | 111 |
| Map01200 | 碳代谢 | 98 |
| Map02024 | 群体效应 | 70 |
| Map00230 | 嘌呤代谢 | 59 |
| Map03010 | 核糖体 | 52 |
| Map00240 | 嘧啶代谢 | 45 |
| Map00010 | 糖酵解/糖异生 | 44 |
| Map00620 | 丙酮酸代谢 | 44 |
| Map00270 | 半胱氨酸与蛋氨酸代谢 | 40 |
表3 生防菌XC-29基因组KEGG主要代谢通路分析
Table 3 Main metabolic pathways of the biocontrol bacterium XC-29 from KEGG
| 通路编号 | 类目 | 基因数(>40) |
|---|---|---|
| Map01100 | 代谢途径 | 566 |
| Map01110 | 次生代谢物的生物合成 | 276 |
| Map01130 | 抗生素的生物合成 | 211 |
| Map01120 | 不同环境下的微生物代谢 | 170 |
| Map02010 | ABC转运蛋白 | 138 |
| Map01230 | 氨基酸的生物合成 | 130 |
| Map02020 | 双组分调节系统 | 111 |
| Map01200 | 碳代谢 | 98 |
| Map02024 | 群体效应 | 70 |
| Map00230 | 嘌呤代谢 | 59 |
| Map03010 | 核糖体 | 52 |
| Map00240 | 嘧啶代谢 | 45 |
| Map00010 | 糖酵解/糖异生 | 44 |
| Map00620 | 丙酮酸代谢 | 44 |
| Map00270 | 半胱氨酸与蛋氨酸代谢 | 40 |
| 类型 | 家族成员 | 基因数 |
|---|---|---|
| AA | AA1 | 1 |
| CBM | CBM12、CBM13、CBM48、CBM50 | 35 |
| CE | CE0、CE12、CE14、CE4、CE7、CE8、CE9 | 18 |
| GH | GH0、GH1、GH3、GH4、GH5、GH9、GH10、GH11、GH13、GH16、GH18、GH23、GH28、GH30、GH32、GH33、GH38、GH42、GH43、GH48、GH51、GH53、GH73、GH101、GH105、GH126、GH170、GH171 | 55 |
| GT | GT0、GT1、GT4、GT9、GT26、GT28、GT30、GT51、GT58 | 28 |
| PL | PL1、PL9 | 2 |
表4 生防菌XC-29基因组CAZy数据库功能注释
Table 4 CAZy database function annotation of biocontrol bacterium XC-29 genome
| 类型 | 家族成员 | 基因数 |
|---|---|---|
| AA | AA1 | 1 |
| CBM | CBM12、CBM13、CBM48、CBM50 | 35 |
| CE | CE0、CE12、CE14、CE4、CE7、CE8、CE9 | 18 |
| GH | GH0、GH1、GH3、GH4、GH5、GH9、GH10、GH11、GH13、GH16、GH18、GH23、GH28、GH30、GH32、GH33、GH38、GH42、GH43、GH48、GH51、GH53、GH73、GH101、GH105、GH126、GH170、GH171 | 55 |
| GT | GT0、GT1、GT4、GT9、GT26、GT28、GT30、GT51、GT58 | 28 |
| PL | PL1、PL9 | 2 |
| 基因簇 | 次级代谢产物类型 | 基因数量 | 相似基因簇 | 相似度 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 簇1 | 非核糖体肽合成酶 | 43 | 地衣素 | BGC0000381(92%) |
| 簇2 | 非核糖体肽合成酶、Ⅰ型聚酮类化合物 | 48 | 双效菌素 | BGC0001059(18%) |
| 簇3 | 包含Rev响应元件 | 24 | 铁载体二异羟肟酸酯 | - |
| 簇4 | 萜类化合物、镍-铁载体 | 27 | - | BGC0002683(60%) |
| 簇5 | β-内酯 | 24 | 丰原素 | BGC0001095(53%) |
| 簇6 | 萜类化合物、镍-铁载体 | 21 | - | - |
| 簇7 | Ⅲ型聚酮类化合物 | 47 | - | - |
| 簇8 | 核糖体合成和翻译后修饰肽类似物 | 15 | - | - |
| 簇9 | β-内酯 | 33 | - | - |
| 簇10 | 其他 | 46 | 杆菌溶素 | BGC0001184(85%) |
| 簇11 | 非核糖体肽-载体、非核糖体肽合成酶 | 39 | 嗜铁素bacilibactin(E/F) | BGC0002695(80%) |
| 嗜铁素bacilibactin | BGC0000309(100%) | |||
| 嗜铁素paenibactin | BGC0000401(100%) | |||
| 嗜铁素bacilibactin | BGC0001185(100%) |
表5 生防菌XC-29次级代谢产物预测结果
Table 5 The secondary metabolite ofbiocontrol bacterium XC-29 predicted by antiSMASH
| 基因簇 | 次级代谢产物类型 | 基因数量 | 相似基因簇 | 相似度 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 簇1 | 非核糖体肽合成酶 | 43 | 地衣素 | BGC0000381(92%) |
| 簇2 | 非核糖体肽合成酶、Ⅰ型聚酮类化合物 | 48 | 双效菌素 | BGC0001059(18%) |
| 簇3 | 包含Rev响应元件 | 24 | 铁载体二异羟肟酸酯 | - |
| 簇4 | 萜类化合物、镍-铁载体 | 27 | - | BGC0002683(60%) |
| 簇5 | β-内酯 | 24 | 丰原素 | BGC0001095(53%) |
| 簇6 | 萜类化合物、镍-铁载体 | 21 | - | - |
| 簇7 | Ⅲ型聚酮类化合物 | 47 | - | - |
| 簇8 | 核糖体合成和翻译后修饰肽类似物 | 15 | - | - |
| 簇9 | β-内酯 | 33 | - | - |
| 簇10 | 其他 | 46 | 杆菌溶素 | BGC0001184(85%) |
| 簇11 | 非核糖体肽-载体、非核糖体肽合成酶 | 39 | 嗜铁素bacilibactin(E/F) | BGC0002695(80%) |
| 嗜铁素bacilibactin | BGC0000309(100%) | |||
| 嗜铁素paenibactin | BGC0000401(100%) | |||
| 嗜铁素bacilibactin | BGC0001185(100%) |
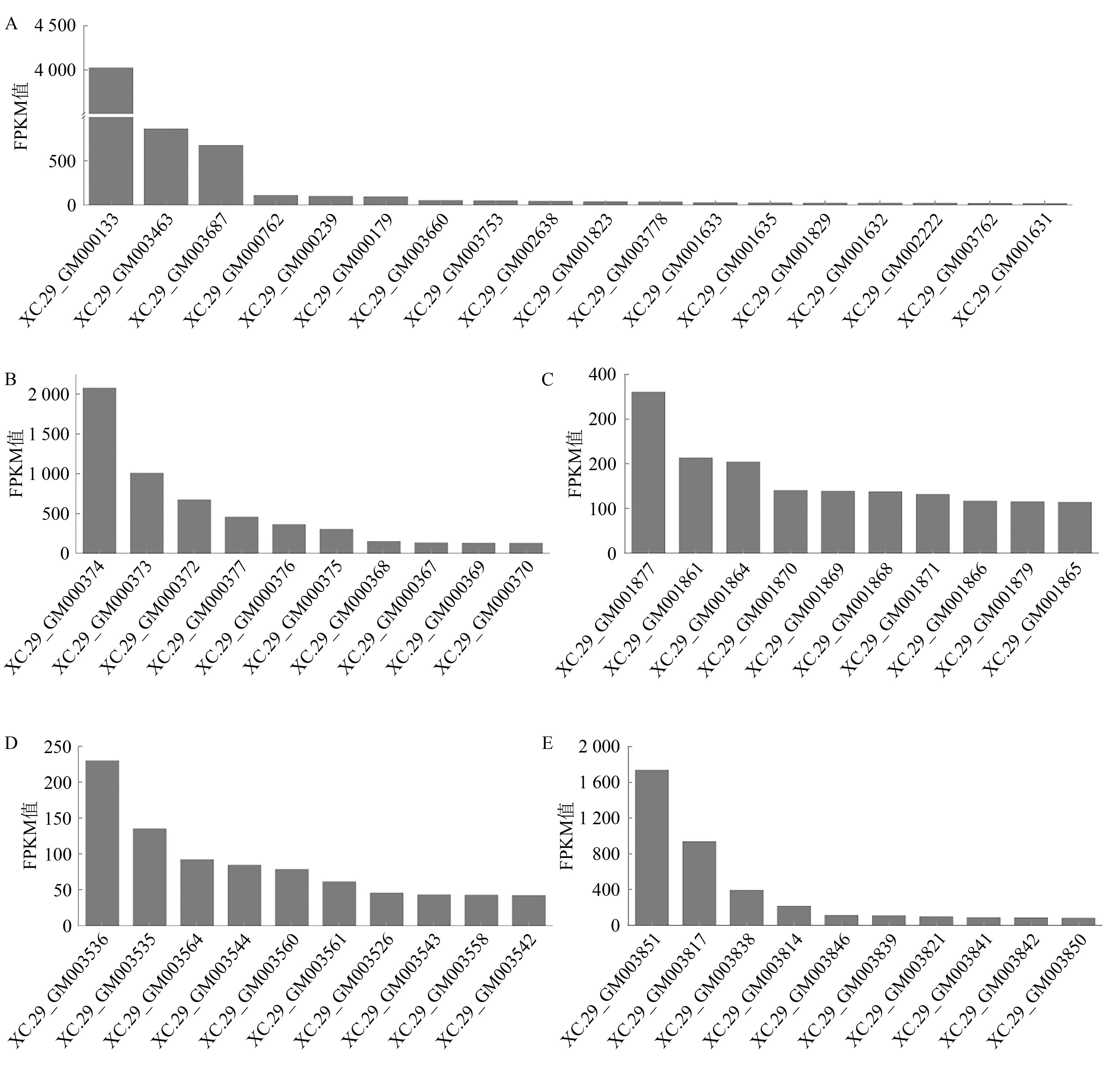
图8 生防菌XC-29编码细胞壁降解酶和次生代谢簇基因表达量A:细胞壁降解酶的基因表达量;B:次生代谢簇1的基因表达量;C:次生代谢簇5的基因表达量;D:次生代谢簇10的基因表达量;E:次生代谢簇11的基因表达量
Fig. 8 The gene expression levels of cell wall-degrading enzymes and secondary metabolite cluster genes in biocontrol bacteria XC-29
| 1 | 赵亚南,黄大野,杨丹,等.烟草黑胫病研究进展[J].湖北农业科学,2022,61(S1):25-28+66. |
| ZHAO Y N, HUANG D Y, YANG D,et al.. Research progress of tobacco black shank disease[J]. Hubei Agric. Sci., 2022, 61(S1): 25-28+66. | |
| 2 | NIU B, WANG W, YUAN Z, et al.. Microbial interactions within multiple-strain biological control agents impact soil-borne plant disease[J/OL]. Front. Microbiol., 2020, 11: 585404[2024-07-25]. . |
| 3 | 蒲欣,吴茂华,刘锋,等.芽孢杆菌对玉米真菌病害生物防治效果的研究进展[J].江苏农业科学,2024,52(4):23-30. |
| PU X, WU M H, LIU F, et al.. Research progress on biological control effect of Bacillus on corn fungal diseases[J]. Jiangsu Agric. Sci., 2024, 52(4): 23-30. | |
| 4 | 刘开辉,刘月,陈妮,等.芽孢杆菌A-1的鉴定及其抗病促生作用研究[J].陕西科技大学学报,2023,41(5):64-69+86. |
| LIU K H, LIU Y, CHEN N, et al.. Study on identification of Bacillus sp. A-1 and its antipathogenic and plant growth-promoting capability[J]. J. Shaanxi Univ. Sci. Technol., 2023, 41(5): 64-69+86. | |
| 5 | 马乔女,李心悦,顾欣,等.芽孢杆菌抗真菌肽的研究进展[J].中国植保导刊,2023,43(5):17-24. |
| MA Q N, LI X Y, GU X, et al.. Research progress of Bacillus antifungal peptides[J]. China Plant Prot., 2023, 43(5): 17-24. | |
| 6 | HUSSAIN S, TAI B, ALI M, et al.. Antifungal potential of lipopeptides produced by the Bacillus siamensis Sh420 strain against Fusarium graminearum [J/OL]. Microbiol. Spectr., 2024, 12(4): e0400823[2024-07-25]. . |
| 7 | 王伟宸,赵进,黄薇颐,等.芽胞杆菌代谢产物防治三种常见植物病原真菌的研究进展[J].生物技术通报,2023,39(3):59-68. |
| WANG W C, ZHAO J, HUANG W Y, et al.. Research progress in metabolites produced by Bacillus against three common plant pathogenic fungi[J]. Biotechnol. Bull., 2023, 39(3): 59-68. | |
| 8 | 王冲,李倩,肖红英,等.贝莱斯芽孢杆菌Vel-HNGD-F2产抗菌物质发酵条件优化及抗菌特性研究[J].河南工业大学学报(自然科学),2024,45(1):73-80. |
| WANG C, LI Q, XIAO H Y, et al.. Optimization of fermentation conditions and antifungal properties of Bacillus velezensis VelHNGD-F2[J]. J. Henan Uni. Technol., 2024, 45(1): 73-80. | |
| 9 | XUE J, SUN L, XU H, et al.. Bacillus atrophaeus NX-12 utilizes exosmotic glycerol from Fusarium oxysporum f. sp. cucumerinum for fengycin production[J]. J. Agric. Food Chem., 2023, 71(28): 10565-10574. |
| 10 | NGALIMAT M S, YAHAYA R S R, BAHARUDIN M M A, et al.. A review on the biotechnological applications of the operational group Bacillus amyloliquefaciens [J/OL]. Microorganisms, 2021, 9(3): 614[2024-07-25]. . |
| 11 | 王怡凡,刘巍,朱其立,等.马铃薯早疫病拮抗细菌WK-1的筛选鉴定及其生物学特性分析[J].西南农业学报,2022,35(4):855-863. |
| WANG Y F, LIU W, ZHU Q L, et al.. Screening and identification of potato early blight antagonistic bacteria WK-1 and analysis of its biological characteristics[J]. Southwest China J. Agric. Sci., 2022, 35(4): 855-863. | |
| 12 | 贾孟媛,王越洋,唐培培,等.烟草黑胫病生防菌的筛选鉴定及其防效[J].湖南农业大学学报(自然科学),2023,49(3):329-334. |
| JIA M Y, WANG Y Y, TANG P P, et al.. Screening and identification of biocontrol bacteria for tobacco black shank disease and evaluation of the control effect[J]. J. Hunan Agric. Univ., 2023, 49(3): 329-334. | |
| 13 | 李苗苗,王晓强,王东坤,等.生防菌复配对烟草黑胫病的防治效果研究[J].中国烟草科学,2020,41(2):32-38. |
| LI M M, WANG X Q, WANG D K, et al.. Effect of biocontrol agents mixture on control of tobacco black shank[J]. Chin. Tob. Sci., 2020, 41(2): 32-38. | |
| 14 | KUMAR S, STECHER G, TAMURA K. MEGA7: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 7.0 for bigger datasets[J]. Mol. Biol. Evol., 2016, 33(7): 1870-1874. |
| 15 | CANTAREL B L, COUTINHO P M, RANCUREL C, et al.. The carbohydrate-active enzymes database (CAZy): an expert resource for glycogenomics[J]. Nucleic Acids Res., 2009, 37(S1): 233-238. |
| 16 | ASHBURNER M, BALL C A, BLAKE J A, et al.. Gene ontology: tool for the unification of biology. The gene ontology Consortium[J]. Cell Death Discov., 2000, 25(1): 25-29. |
| 17 | KANEHISA M, GOTO S, HATTORI M, et al.. From genomics to chemical genomics: new developments in KEGG[J]. Nucleic Acids Res., 2006, 34(S1): 354-357. |
| 18 | TATUSOV R L, FEDOROVA N D, JACKSON J D, et al.. The COG database: an updated version includes eukaryotes[J/OL]. BMC Bioinform., 2003, 4: 41[2024-07-25]. . |
| 19 | MEDEMA M H, BLIN K, CIMERMANCIC P, et al.. AntiSMASH: rapid identification, annotation and analysis of secondary metabolite biosynthesis gene clusters in bacterial and fungal genome sequences[J]. Nucleic Acids Res., 2011, 39(S2): 339-346. |
| 20 | RICHTER M, ROSSELLÓ-MÓRA R, OLIVER GLÖCKNER F, et al.. JSpeciesWS: a web server for prokaryotic species circumscription based on pairwise genome comparison[J]. Bioinformatics, 2016, 32(6): 929-931. |
| 21 | 濮永瑜,包玲凤,何翔,等.烟草青枯病和黑胫病拮抗细菌的筛选、鉴定及防效研究[J].中国农学通报,2022,38(7):116-123. |
| PU Y Y, BAO L F, HE X, et al.. Screening, identification and control efficacy of antagonistic bacteria against Ralstonia solanacearum and Phytophthora parasitica [J]. Chin. Agric. Sci. Bull., 2022, 38(7): 116-123. | |
| 22 | 何明川,施春兰,魏聪聪,等.烟草黑胫病拮抗细菌的分离、鉴定及发酵条件优化[J].南方农业学报,2022,53(6):1604-1615. |
| HE M C, SHI C L, WEI C C, et al.. Isolation, identification and optimization of fermentation conditions of antagonistic bacteria against tobacco black shank[J]. J. South. Agric., 2022, 53(6): 1604-1615. | |
| 23 | 谢强,夏建华,徐传涛,等.巨大芽胞杆菌(Bacillus megaterium,Bm)的抑菌活性及定殖规律分析[J].烟草科技,2022,55(10):19-25. |
| XIE Q, XIA J H, XU C T, et al.. Antibacterial activity of Bacillus megaterium strain Bm and its colonization laws[J]. Tob. Sci. Technol., 2022, 55(10): 19-25. | |
| 24 | 李小杰,李成军,刘红彦,等.烟草疫霉菌拮抗细菌的筛选鉴定及发酵条件优化[J].中国烟草科学,2019,40(1): 68-74. |
| LI X J, LI C J, LIU H Yet al.. Screening and fermentation condition optimization for antagonistic bacteria to Phytophthora nicotianae [J]. Chin. Tob. Sci., 2019, 40(1): 68-74. | |
| 25 | 李颖颖,康业斌,李成军,等.3种拮抗烟草疫霉及产IAA内生细菌的分离鉴定[J].江苏农业科学,2023,51(18):107-114. |
| LI Y Y, KANG Y B, LI C J, et al.. Isolation and identification of three endophytic bacteria antagonizing Phytophthora nicotianae and producing IAA[J]. Jiangsu Agric. Sci., 2023, 51(18): 107-114. | |
| 26 | VOLYNCHIKOVA E, KIM K D. Biological control of oomycete soilborne diseases caused by Phytophthora capsici, Phytophthora infestans, and Phytophthora nicotianae in solanaceous crops[J]. Mycobiology, 2022, 50(5): 269-293. |
| 27 | YANG J, YUE H R, PAN L Y, et al.. Fungal strain improvement for efficient cellulase production and lignocellulosic biorefinery: current status and future prospects[J/OL]. Bioresour. Technol., 2023, 385: 129449[2024-07-25]. . |
| 28 | 刘丽阳,胡彦波,王西,等.酶在植物多糖研究中的应用进展[J].食品研究与开发,2024,45(8):217-224. |
| LIU L Y, HU Y B, WANG X, et al.. Research progress on the application of enzymes in plant polysaccharides[J]. Food Res. Dev., 2024, 45(8): 217-224. | |
| 29 | CHÁVEZ-RAMÍREZ B, RODRÍGUEZ-VELÁZQUEZ N D, MONDRAGÓN-TALONIA C M, et al.. Paenibacillus polymyxa NMA1017 as a potential biocontrol agent of Phytophthora tropicalis, causal agent of cacao black pod rot in Chiapas, Mexico [J]. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek, 2021, 114(1): 55-68. |
| 30 | WANG Y, LIANG J, ZHANG C, et al.. Bacillus megaterium WL-3 lipopeptides collaborate against Phytophthora infestans to control potato late blight and promote potato plant growth[J/OL]. Front. Microbiol., 2020, 11: 1602[2024-07-25]. . |
| 31 | HAN X, SHEN D, XIONG Q, et al.. The plant-beneficial rhizobacterium Bacillus velezensis FZB42 controls the soybean pathogen Phytophthora sojae due to bacilysin production[J/OL]. Appl. Environ. Microbiol., 2021, 87(23): e0160121[2024-07-25]. . |
| 32 | GUO D, YUAN C, LUO Y, et al.. Biocontrol of tobacco black shank disease (Phytophthora nicotianae) by Bacillus velezensis Ba168[J/OL]. Pestic. Biochem. Physiol., 2020, 165: 104523[2024-07-25]. . |
| [1] | 陈巧莉, 黄杰, 陈森瑜, 潘少婷, 唐灵芝, 洪璇. 海洋链霉菌次级代谢产物研究进展[J]. 生物技术进展, 2023, 13(6): 844-852. |
| [2] | 高应瑞, 康福忠, 孟铁健, 刘珂飞, 王调调, 陈金艳, 孙彤. 基于全基因组测序的丁酸梭菌安全性评价[J]. 生物技术进展, 2023, 13(5): 755-759. |
| [3] | 宋开南, 谢李楠, 徐玉泉. 真菌除草活性次级代谢产物研究进展[J]. 生物技术进展, 2023, 13(2): 181-194. |
| [4] | 李玲玲. 青蒿内生真菌研究进展[J]. 生物技术进展, 2016, 6(3): 185-187. |
| [5] | 伍水龙,江黎明. 红树林放线菌研究进展[J]. 生物技术进展, 2012, 2(5): 335-340. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
版权所有 © 2021《生物技术进展》编辑部