


生物技术进展 ›› 2021, Vol. 11 ›› Issue (6): 668-675.DOI: 10.19586/j.2095-2341.2021.0167
收稿日期:2021-10-11
接受日期:2021-10-28
出版日期:2021-11-25
发布日期:2021-11-26
通讯作者:
王磊,张兰
作者简介:李彦娇 E-mail: 1217558152@qq.com
基金资助:
Yanjiao LI1( ), Yuan GAO1, Lei WANG1,2(
), Yuan GAO1, Lei WANG1,2( ), Lan ZHANG1,2(
), Lan ZHANG1,2( )
)
Received:2021-10-11
Accepted:2021-10-28
Online:2021-11-25
Published:2021-11-26
Contact:
Lei WANG,Lan ZHANG
摘要:
三烯生育酚和生育酚统称为维生素E,是重要的脂溶性维生素。维生素E只能在植物或者光合细菌中合成,是人类和动物必需且只能通过食物等摄取的重要维生素。一直以来,由于三烯生育酚与生育酚相比,生物活性较低且分布范围较小,人们对其研究相对较少。近些年的研究发现,由于三烯生育酚和生育酚的结构相似,因此三烯生育酚具有与生育酚相同的抗氧化等功能;但又由于三烯生育酚含有不饱和的植基侧链,使得三烯生育酚还具有一些不同于生育酚的功能,比如保护神经免受损伤、降低胆固醇、保护脑细胞免受损伤等。因此,三烯生育酚逐渐成为了研究热点。根据维生素E的生物合成途径,人们也开始了对三烯生育酚的生物强化研究,其合成途径中第一个关键酶基因HGGT的过表达是目前三烯生育酚含量提高的最有效途径;将来还需结合其合成调控的分子机制及其吸收利用问题,开发针对三烯生育酚的功能型产品。从三烯生育酚的合成途径、生物学功能、生物强化等方面进行了综述,并对今后的研究重点提出了展望。
中图分类号:
李彦娇, 高媛, 王磊, 张兰. 三烯生育酚研究进展[J]. 生物技术进展, 2021, 11(6): 668-675.
Yanjiao LI, Yuan GAO, Lei WANG, Lan ZHANG. Research Progress of Tocotrienol[J]. Current Biotechnology, 2021, 11(6): 668-675.
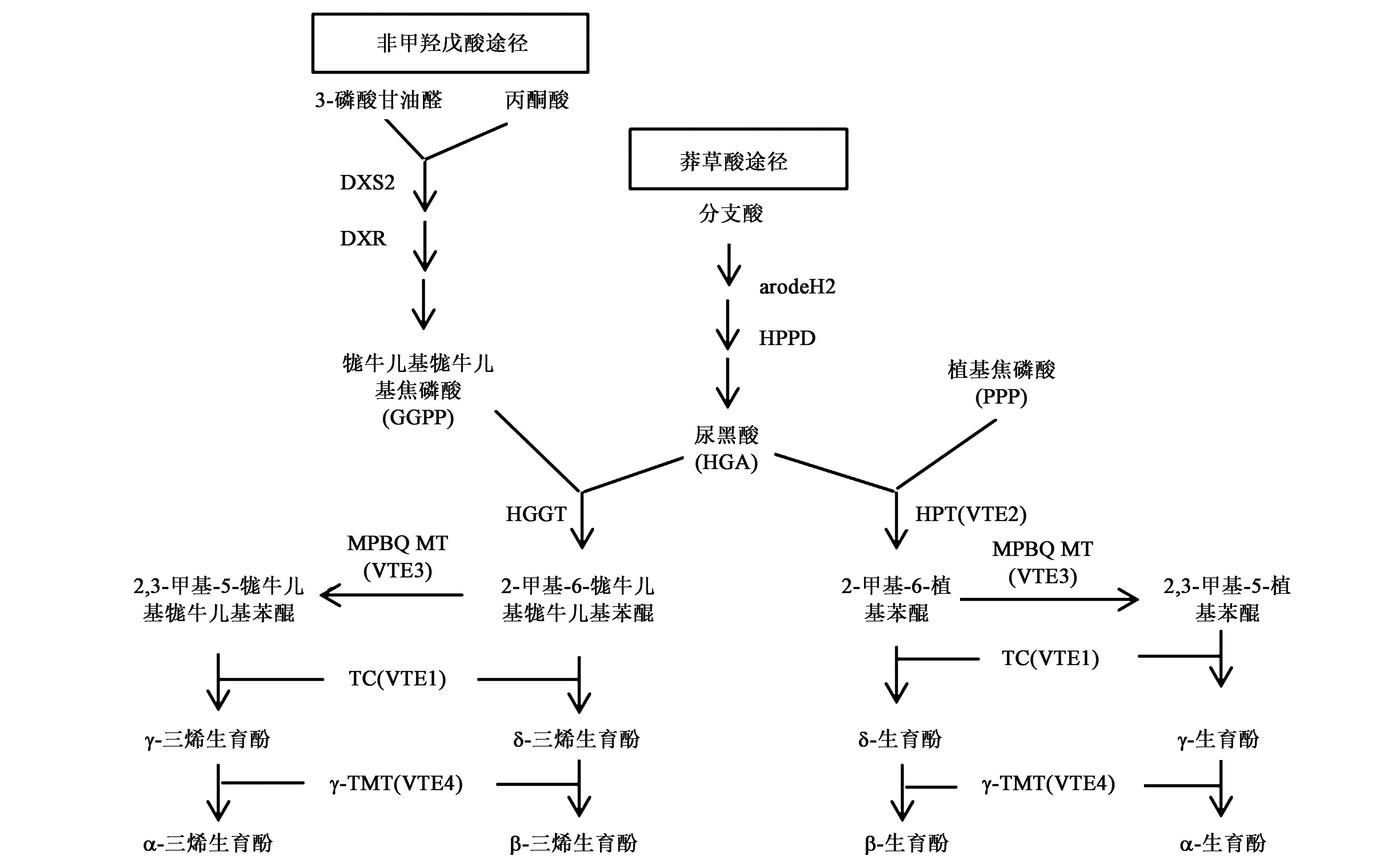
图 1 三烯生育酚/生育酚的生物合成途径注:DXS—1?脱氧?D?木酮糖?5?磷酸合酶;DXR—1?脱氧?D?木酮糖?5?磷酸还原异构酶;arodeH2—无机酸/预苯酸脱氢酶家族蛋白;HPPD—对羟基苯丙酮酸双加氧酶;HGGT—尿黑酸牻牛儿牻牛儿基转移酶;HPT(VTE2)—尿黑酸植基转移酶;MPBQ MT(VTE3)—2?甲基?6?植基苯醌甲基转移酶;TC(VTE1)—生育酚环化酶;γ?TMT(VTE4)—γ?生育酚甲基转移酶。
Fig.1 Biosynthetic pathway of tocotrienol/tocopherol
| 1 | EVANS H M, BISHOP K S. On the existence fo a hitherto unrecognized dietary factor essential for reproduction [J]. Science, 1922, 56(1458): 650-651. |
| 2 | VALENTIN H E, QI Q. Biotechnological production and application of vitamin E: current state and prospects[J]. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol., 2005. 68(4): 436-444. |
| 3 | 张兰,王磊. 植物中维生素E的生物学功能研究进展[J]. 生物技术进展,2016,6(6):389-395. |
| 4 | BABURA S R, NOR S, ABDULLAH A, et al.. Advances in genetic improvement for tocotrienol production: a review[J]. J. Nutr. Sci. Vitaminol., 2017, 63(4):215-221. |
| 5 | 姚兴兰,王磊,张兰. 植物维生素E生物强化研究进展[J]. 生物技术进展, 2020,10(05):45-52. |
| 6 | SALIMATH S S, ROMSDAHL T B, KONDA A R, et al.. Production of tocotrienols in seeds of cotton (Gossypium hirsutum L.) enhances oxidative stability and offers nutraceutical potential[J]. Plant Biotechnol. J., 2021, 19(6):1268-1282. |
| 7 | SEN C K, KHANNA S, ROY S. Tocotrienols: vitamin E beyond tocopherols[J]. Life Sci., 2006, 78(18):2088-2098. |
| 8 | AGGARWAL B B, SUNDARAM C, PRASAD S, et al.. Tocotrienols, the vitamin E of the 21st century: its potential against cancer and other chronic diseases[J]. Biochem. Pharmacol., 2010, 80(11):1613-1631. |
| 9 | HORVATH G, WESSJOHANN L, BIGIRIMANA J, et al.. Differential distribution of tocopherols and tocotrienols in photosynthetic and non-photosynthetic tissues[J]. Phytochemistry, 2006, 67(12):1185-1195. |
| 10 | FALK J, MUNNÉ-BOSCH S. Tocochromanol functions in plants: antioxidation and beyond[J]. J. Exp. Bot., 2010, 61(6):1549-1566. |
| 11 | MUNNE-BOSCH S, ALEGRE L. The function of tocopherols and tocotrienols in plants[J]. Crit. Rev. Plant Sci., 2002, 21(1):31-57. |
| 12 | CAHOON E B, HALL S E, RIPP K G, et al.. Metabolic redesign of vitamin E biosynthesis in plants for tocotrienol production and increased antioxidant content[J]. Nat. Biotechnol., 2003, 21(9):1082-1087. |
| 13 | ZENG Z, HAN N, LIU C, et al.. Functional dissection of HGGT and HPT in barley vitamin E biosynthesis via CRISPR/Cas9-enabled genome editing[J]. Ann. Bot., 2020. 126(5):929-942. |
| 14 | HU, X, LIU J, LI W, et al.. Biosynthesis and accumulation of multi-vitamins in black sweet corn (Zea mays L.) during kernel development[J]. J. Sci. Food Agric., 2020, 100(14):5230-5238. |
| 15 | ZHANG G Y, LIU R R, XU G, et al.. Increased α-tocotrienol content in seeds of transgenic rice overexpressing Arabidopsis γ-tocopherol methyltransferase[J]. Transgenic Res., 2013, 22(1):89-99. |
| 16 | HASSANIEN M M M, ABDEL-RAZEK A G, RUDZINSKA M, et al.. Phytochemical contents and oxidative stability of oils from non-traditional sources[J]. Eur. J. Lipid Sci. Technol., 2014, 116(11):1563-1571. |
| 17 | WONG R S Y, RADHAKRISHNAN A K. Tocotrienol research: past into present[J]. Nutr. Rev., 2012, 70(9):483-490. |
| 18 | SUZUKI Y J, TSUCHIYA M, WASSALL S R, et al.. Structural and dynamic membrane properties of alpha-tocopherol and alpha-tocotrienol: implication to the molecular mechanism of their antioxidant potency[J]. Biochemistry, 1993, 32(40):10692-10699. |
| 19 | KHOSLA P, PATEL V, WHINTER J M, et al.. Postprandial levels of the natural vitamin E tocotrienol in human circulation[J]. Antiox. Redox Sign., 2006, 8(5-6):1059-1068. |
| 20 | MATRINGE M, KSAS B, REY P, et al.. Tocotrienols, the unsaturated forms of vitamin E, can function as antioxidants and lipid protectors in tobacco leaves[J]. Plant Physiol., 2008, 147(2):764-778. |
| 21 | CHE P, ZHAO Z Y, GLASSMAN K, et al.. Elevated vitamin E content improves all-trans beta-carotene accumulation and stability in biofortified sorghum[J]. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 2016, 113(39):11040-11045. |
| 22 | STEINBERG D, PARTHASARATHY S, CAREW T E, et al.. Beyond cholesterol. modifications of low-density lipoprotein that increase its atherogenicity[J]. New Eng. J. Med., 1989, 320(14):915-924. |
| 23 | VALENZA M, SERBINOVA E, PACKER L, et al.. Nitecapone protects the Langendorff perfused heart against ischemia-reperfusion injury[J]. Biochem. Mol. Biol. Intern., 1993, 29(3):443-449. |
| 24 | AGGARWAL B B. Inflammation, a silent killer in cancer is not so silent! [J]. Curr. Opin. Pharmacol., 2009, 9(4):347-350. |
| 25 | GRIVENNIKOV S I, GRETEN F R, Immunity KARIN M., inflammation, and cancer[J]. Cell, 2010, 140(6):883-899. |
| 26 | PRASAD K. Tocotrienols and cardiovascular health[J]. Curr. Pharm. Des., 2011, 17(21):2147-2154. |
| 27 | WU S J, LIU P L, NG L T. Tocotrienol-rich fraction of palm oil exhibits anti-inflammatory property by suppressing the expression of inflammatory mediators in human monocytic cells[J]. Mol. Nutr. Food Res., 2008, 52(8):921-929. |
| 28 | AHN K S, SETHI G, KRISHNAN K, et al.. Gamma-tocotrienol inhibits nuclear factor-kappaB signaling pathway through inhibition of receptor-interacting protein and TAK1 leading to suppression of antiapoptotic gene products and potentiation of apoptosis[J]. J. Biol. Chem., 2007, 282(1):809-820. |
| 29 | SYLVESTER P W, AYOUB N M. Tocotrienols target PI3K/Akt signaling in anti-breast cancer therapy[J]. Antican. Agents Med. Chem., 2013, 13(7):1039-1047. |
| 30 | WEI L H, KUO M L, CHEN C A, et al.. The anti-apoptotic role of interleukin-6 in human cervical cancer is mediated by up-regulation of Mcl-1 through a PI 3-K/Akt pathway[J]. Oncogene, 2001, 20(41):5799-5809. |
| 31 | HUSAIN K, FRANCOIS R A, YAMAUCHI T, et al.. Vitamin E δ-tocotrienol augments the antitumor activity of gemcitabine and suppresses constitutive NF-κB activation in pancreatic cancer[J]. Mol. Cancer Ther., 2011, 10(12):2363-2372. |
| 32 | REN Z, PAE M, DAO M C, et al.. Dietary supplementation with tocotrienols enhances immune function in C57BL/6 mice[J]. J. Nutr., 2010, 140(7):1335-1341. |
| 33 | MAHALINGAM D, RADHAKRISHNAN A K, AMOM Z, et al.. Effects of supplementation with tocotrienol-rich fraction on immune response to tetanus toxoid immunization in normal healthy volunteers[J]. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr., 2011, 65(1):63-69. |
| 34 | ZHAO L, YAGIZ Y, XU C, et al.. Muscadine grape seed oil as a novel source of tocotrienols to reduce adipogenesis and adipocyte inflammation[J]. Food Funct., 2015, 6(7):2293-2302. |
| 35 | KHANNA S, ROY S, PARINANDI N L, et al.. Characterization of the potent neuroprotective properties of the natural vitamin E alpha-tocotrienol[J]. J. Neurochem., 2006, 98(5):1474-1486. |
| 36 | SEN C K, KHANNA S, ROY S, et al.. Molecular basis of vitamin E action. Tocotrienol potently inhibits glutamate-induced pp60(c-Src) kinase activation and death of HT4 neuronal cells[J]. J. Biol. Chem., 2000, 275(17):13049-13055. |
| 37 | KHANNA S, ROY S, RYU H, et al.. Molecular basis of vitamin E action: tocotrienol modulates 12-lipoxygenase, a key mediator of glutamate-induced neurodegeneration[J]. J. Biol. Chem., 2003, 278(44):43508-43515. |
| 38 | SEN C K, KHANNA S, ROY S. Tocotrienols in health and disease: the other half of the natural vitamin E family[J]. Mol. Aspects Med., 2007, 28(5-6):692-728. |
| 39 | KHANNA S, PARINANDI N L, KOTHA S R, et al.. Nanomolar vitamin E alpha-tocotrienol inhibits glutamate-induced activation of phospholipase A2 and causes neuroprotection[J]. J. Neurochem., 2010, 112(5):1249-1260. |
| 40 | OSAKADA F, HASHINO A, KUME T, et al.. Alpha-tocotrienol provides the most potent neuroprotection among vitamin E analogs on cultured striatal neurons[J]. Neuropharmacology, 2004, 47(6):904-915. |
| 41 | QURESHI A A, SAMI S A, SALSER W A, et al.. Synergistic effect of tocotrienol-rich fraction [TRF(25)] of rice bran and lovastatin on lipid parameters in hypercholesterolemic humans[J]. J. Nutr. Biochem., 2001, 12(6):318-329. |
| 42 | QURESHI A A, SAMI S A, SALSER W A, et al.. Dose-dependent suppression of serum cholesterol by tocotrienol-rich fraction (TRF25) of rice bran in hypercholesterolemic humans[J]. Atherosclerosis, 2002, 161(1):199-207. |
| 43 | CICERO A F, GADDI A. Rice bran oil and gamma-oryzanol in the treatment of hyperlipoproteinaemias and other conditions[J]. Phytother. Res., 2001, 15(4):277-289. |
| 44 | PARKER R A, PEARCE B C, CLARK R W, et al.. Tocotrienols regulate cholesterol production in mammalian cells by post-transcriptional suppression of 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-coenzyme A reductase[J]. J. Biol. Chem., 1993, 268(15):11230-11238. |
| 45 | TANAKA, H, YABUTA Y, TAMOI M, et al.. Generation of transgenic tobacco plants with enhanced tocotrienol levels through the ectopic expression of rice homogentisate geranylgeranyl transferase[J]. Plant Biotechnol., 2015, 32(3):233-238. |
| 46 | KONDA A R, NAZARENUS T J, NGUYEN H, et al.. Metabolic engineering of soybean seeds for enhanced vitamin E tocochromanol content and effects on oil antioxidant properties in polyunsaturated fatty acid-rich germplasm[J]. Metab. Eng., 2020, 57:63-73. |
| 47 | KIM Y H, LEE Y Y, KIM Y H, et al.. Antioxidant activity and inhibition of lipid peroxidation in germinating seeds of transgenic soybean expressing OsHGGT[J]. J. Agric. Food Chem., 2011, 59(2):584-591. |
| 48 | KARUNANANDAA B, QI Q, HAO M, et al.. Metabolically engineered oilseed crops with enhanced seed tocopherol[J]. Metab. Engin., 2005, 7(5-6):384-400. |
| 49 | RIPPERT P, SCIMEMI C, DUBALD M, et al.. Engineering plant shikimate pathway for production of tocotrienol and improving herbicide resistance[J]. Plant Physiol., 2004, 134(1):92-100. |
| 50 | ZHANG C, CAHOON R E, HUNTER S C, et al.. Genetic and biochemical basis for alternative routes of tocotrienol biosynthesis for enhanced vitamin E antioxidant production[J]. Plant J., 2013, 73(4):628-639. |
| 51 | ESTÉVEZ J M, CANTERO A, REINDL A, et al.. 1-Deoxy-D-xylulose-5-phosphate synthase, a limiting enzyme for plastidic isoprenoid biosynthesis in plants[J]. J. Biol. Chem., 2001, 276(25):22901-22909. |
| 52 | WRIGHT L P, ROHWER J M, GHIRARDO A,et al.. Deoxyxylulose 5-phosphate synthase controls flux through the methylerythritol 4-phosphate pathway in Arabidopsis[J]. Plant Physiol., 2014, 165(4):1488-1504. |
| 53 | CARRETERO-PAULET L, CAIRÓ A, BOTELLA-PAVÍA P, et al.. Enhanced flux through the methylerythritol 4-phosphate pathway in Arabidopsis plants overexpressing deoxyxylulose 5-phosphate reductoisomerase[J]. Plant Mol. Biol., 2006, 62(4-5):683-695. |
| 54 | RUIZ-SOLA M Á, COMAN D, BECK G, et al.. Arabidopsis GERANYLGERANYL DIPHOSPHATE SYNTHASE 11 is a hub isozyme required for the production of most photosynthesis-related isoprenoids[J]. New Phytol., 2016, 209(1):252-264. |
| 55 | 姚兴兰,杨文竹,罗彦忠等, 转phyA2,ZmTMT和Bar玉米的获得及其特性分析[J]. 中国农业科学, 2020, 53(24):75-84. |
| 56 | MUNUSAMY U, NOR S, ABDULLAH A, et al.. Metabolic engineering of α-tocotrienol through PTGS mechanisms and isoprenoid/non-mevalonate pathways in perennial crops[J]. Plant Cell Biotechnol. Mol. Biol., 2015,16(3&4):119-129. |
| 57 | DOLDE D, WANG T. Oxidation of crude corn oil with and without elevated tocotrienols[J]. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc., 2011, 88(9):1367-1372. |
| 58 | DIEPENBROCK C H, KANDIANIS C B, LIPKA A E, et al.. Novel loci underlie natural variation in vitamin E levels in maize grain[J]. Plant Cell, 2017, 29(10):2374-2392. |
| 59 | SUN T, ZHU Q, WEI Z, et al.. Multi-strategy engineering greatly enhances provitamin A carotenoid accumulation and stability in Arabidopsis seeds[J]. aBIOTECH, 2021,2(3):191-214. |
| 60 | CORDOBA E, SALMI M, LEÓN P. Unravelling the regulatory mechanisms that modulate the MEP pathway in higher plants[J]. J. Exp. Bot., 2009, 60(10):2933-2943. |
| 61 | KONG S L, ABDULLAH S N A, HO C L, et al.. Molecular cloning, gene expression profiling and in silico sequence analysis of vitamin E biosynthetic genes from the oil palm[J]. Plant Gene, 2016, 5:100-108. |
| [1] | 范一铭, 高桂珍, 薛羽君, 伍晓明. 植物神经酸研究进展[J]. 生物技术进展, 2022, 12(5): 664-672. |
| [2] | 张融雪,孙玥,苏京平,王胜军,佟卉,刘燕清,孙林静. 植物褪黑素研究进展[J]. 生物技术进展, 2021, 11(3): 297-303. |
| [3] | 姚兴兰,王磊,张兰. 植物维生素E生物强化研究进展[J]. 生物技术进展, 2020, 10(5): 479-486. |
| [4] | YAO Mawulikplimi Adzavon,赵鹏翔,张旭娟,王丽敏,马雪梅. 巨噬细胞迁移抑制因子分子机制研究进展[J]. 生物技术进展, 2018, 8(5): 389-396. |
| [5] | 张斌,刘晓志,周敬华,魏敬双,高健,王志明. 抗体药物糖化检测方法及其生物学功能研究进展[J]. 生物技术进展, 2018, 8(1): 28-33. |
| [6] | 龙云川,陈轩,周少奇,. 高产铁载体根际菌的筛选鉴定及硒活化特性评价[J]. 生物技术进展, 2017, 7(5): 402-408. |
| [7] | 姜凌,张春义. 植物维生素生物强化进展[J]. 生物技术进展, 2016, 6(6): 381-388. |
| [8] | 李路平,张金磊,. 中国生物强化项目的成本收益和成本有效性分析——以生物强化富铁小麦为例[J]. 生物技术进展, 2016, 6(6): 414-421. |
| [9] | 杨泽伟,王龙海,朱莉,郎志宏,罗学刚. γ-氨基丁酸代谢旁路在植物响应逆境胁迫中的作用机制研究[J]. 生物技术进展, 2014, 4(2): 77-84. |
| [10] | 刘文文,李文学. 植物bHLH转录因子研究进展[J]. 生物技术进展, 2013, 3(1): 7-11. |
| [11] | 李广旭,陈华民,吴静,吴茂森,何晨阳. OsBTF3过表达转基因水稻株系的创制及其分子鉴定[J]. 生物技术进展, 2012, 2(1): 39-43. |
| [12] | 宫硖,薛静,张晓东. 植物花青素合成途径中的调控基因研究进展[J]. 生物技术进展, 2011, 1(6): 381-90. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
版权所有 © 2021《生物技术进展》编辑部