


生物技术进展 ›› 2024, Vol. 14 ›› Issue (3): 413-421.DOI: 10.19586/j.2095-2341.2023.0167
• 研究论文 • 上一篇
收稿日期:2023-12-20
接受日期:2024-03-25
出版日期:2024-05-25
发布日期:2024-06-18
通讯作者:
包锦
作者简介:张奇雨 E-mail: 2962888599@qq.com;
基金资助:
Qiyu ZHANG( ), Xiaogui LYU, Jin BAO(
), Xiaogui LYU, Jin BAO( )
)
Received:2023-12-20
Accepted:2024-03-25
Online:2024-05-25
Published:2024-06-18
Contact:
Jin BAO
摘要:
为探究冷等离子体处理对盐胁迫下燕麦耐盐性的影响,以坝莜14号燕麦种子为试验材料,选用5和6 kV的电压对燕麦种子进行不同时长(30 s、15 s×2)的冷等离子体处理,测定不同浓度的NaCl 溶液(0.5、1.0、1.5 g·L-1)胁迫下燕麦种子萌发和幼苗生长及生理指标。结果发现,冷等离子体可以显著提高燕麦种皮亲水性及燕麦种子的吸水率,缓解盐胁迫对燕麦株高和根长的影响。基于隶属函数对燕麦抗盐能力进行综合评价分析发现,冷等离子体处理参数为5 kV、30 s和6 kV、15 s×2时,1.5 g·L-1浓度胁迫下燕麦的抗盐能力提高,且随着胁迫强度的增加,5 kV、30 s参数下,冷等离子体处理对盐胁迫的缓解作用效果逐渐增强。
中图分类号:
张奇雨, 吕晓桂, 包锦. 冷等离子体处理对盐胁迫下燕麦种子萌发及幼苗生长的影响[J]. 生物技术进展, 2024, 14(3): 413-421.
Qiyu ZHANG, Xiaogui LYU, Jin BAO. Effect of Cold Plasma Treatment on Seed Germination and Seedling Growth of Oats Under Salt Stress[J]. Current Biotechnology, 2024, 14(3): 413-421.
| 组别 | CK1 CK2 CK3 | A1 A2 A3 | B1 B2 B3 | C1 C2 C3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 电压/kV | - | 5 | 6 | 6 |
| 处理时间/s | - | 30 30 30 | 15 15 15 | 30 30 30 |
| 处理次数 | - | 1 1 1 | 2 2 2 | 1 1 1 |
| 溶液浓度 /(g·L-1) | 0.5 1.0 1.5 | 0.5 1.0 1.5 | 0.5 1.0 1.5 | 0.5 1.0 1.5 |
表1 各组燕麦种子处理参数
Table 1 Treatment parameters for each group of oat seeds
| 组别 | CK1 CK2 CK3 | A1 A2 A3 | B1 B2 B3 | C1 C2 C3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 电压/kV | - | 5 | 6 | 6 |
| 处理时间/s | - | 30 30 30 | 15 15 15 | 30 30 30 |
| 处理次数 | - | 1 1 1 | 2 2 2 | 1 1 1 |
| 溶液浓度 /(g·L-1) | 0.5 1.0 1.5 | 0.5 1.0 1.5 | 0.5 1.0 1.5 | 0.5 1.0 1.5 |
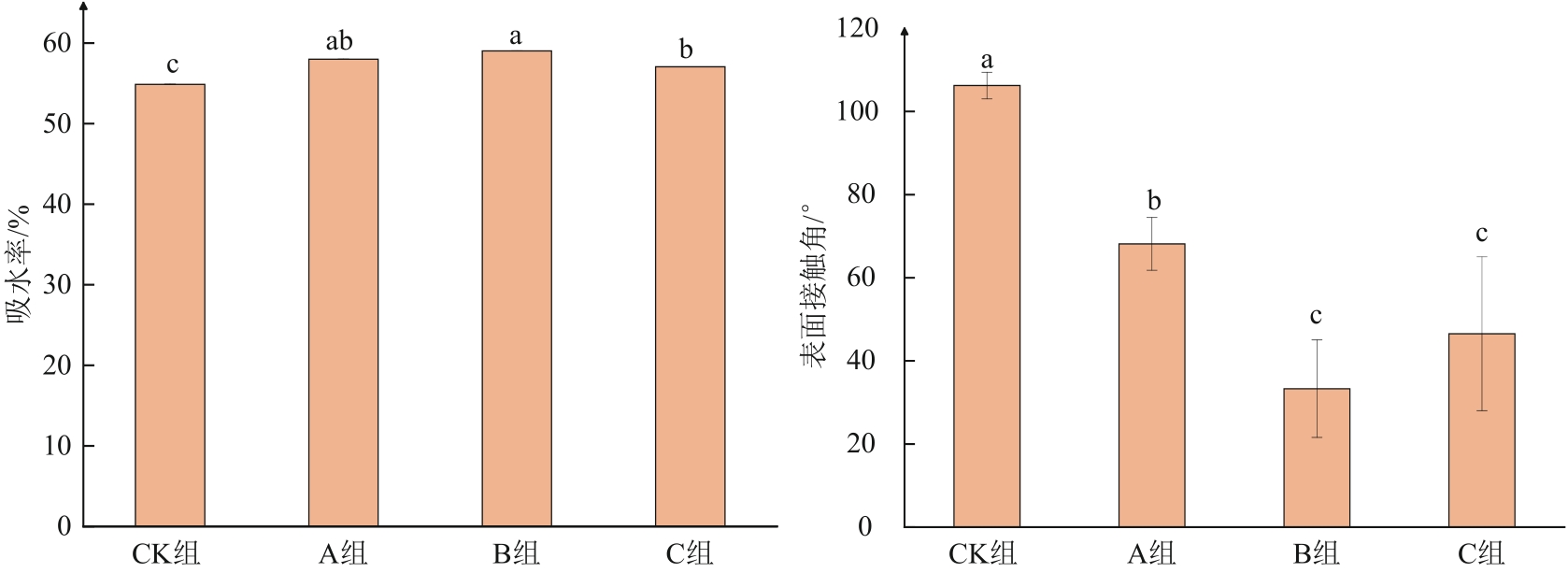
图2 冷等离子体处理对燕麦种子吸水率和亲水性的影响注:不同小写字母表示不同处理间在P<0.05水平上具有统计学意义。
Fig. 2 Effects of cold plasma treatment on water absorption and hydrophilicity of oat seeds
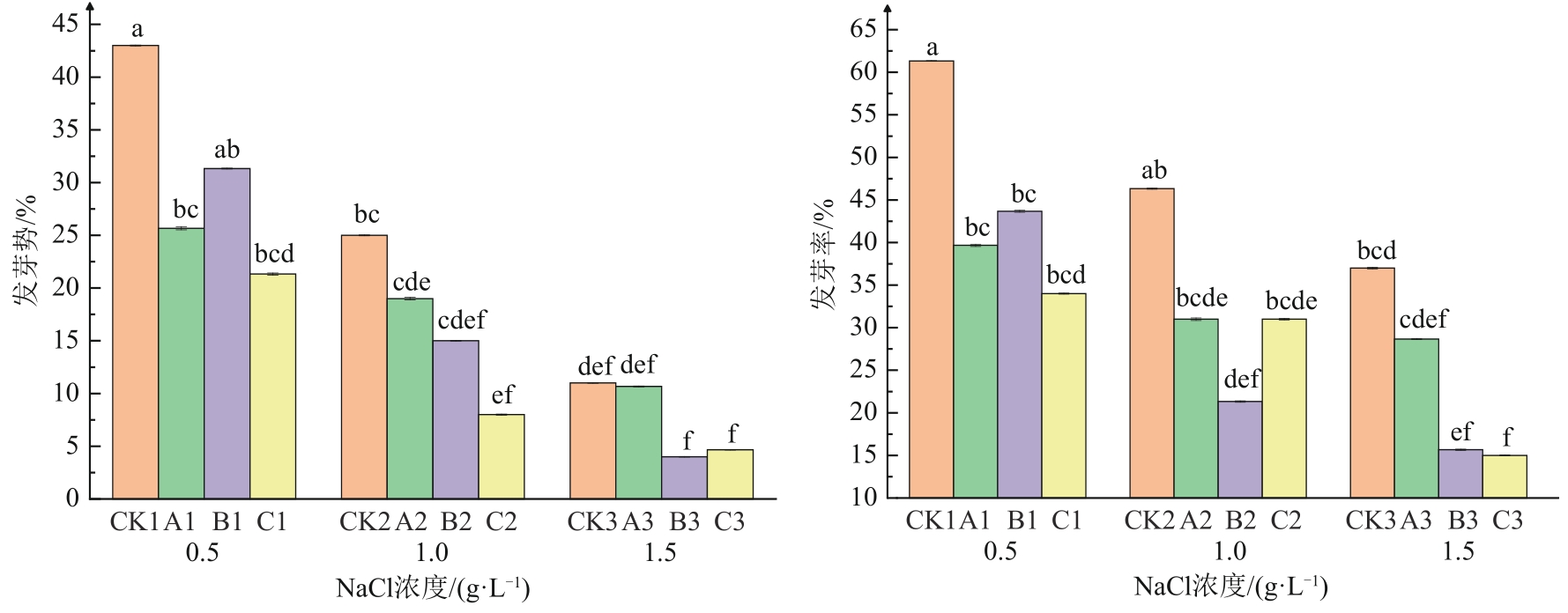
图3 冷等离子体处理对NaCl胁迫下燕麦种子发芽势和发芽率的影响注:不同小写字母表示不同处理间在P<0.05水平上具有统计学意义。
Fig. 3 Effects of cold plasma treatment on germination potential and germination rate of oat seeds under NaCl stress
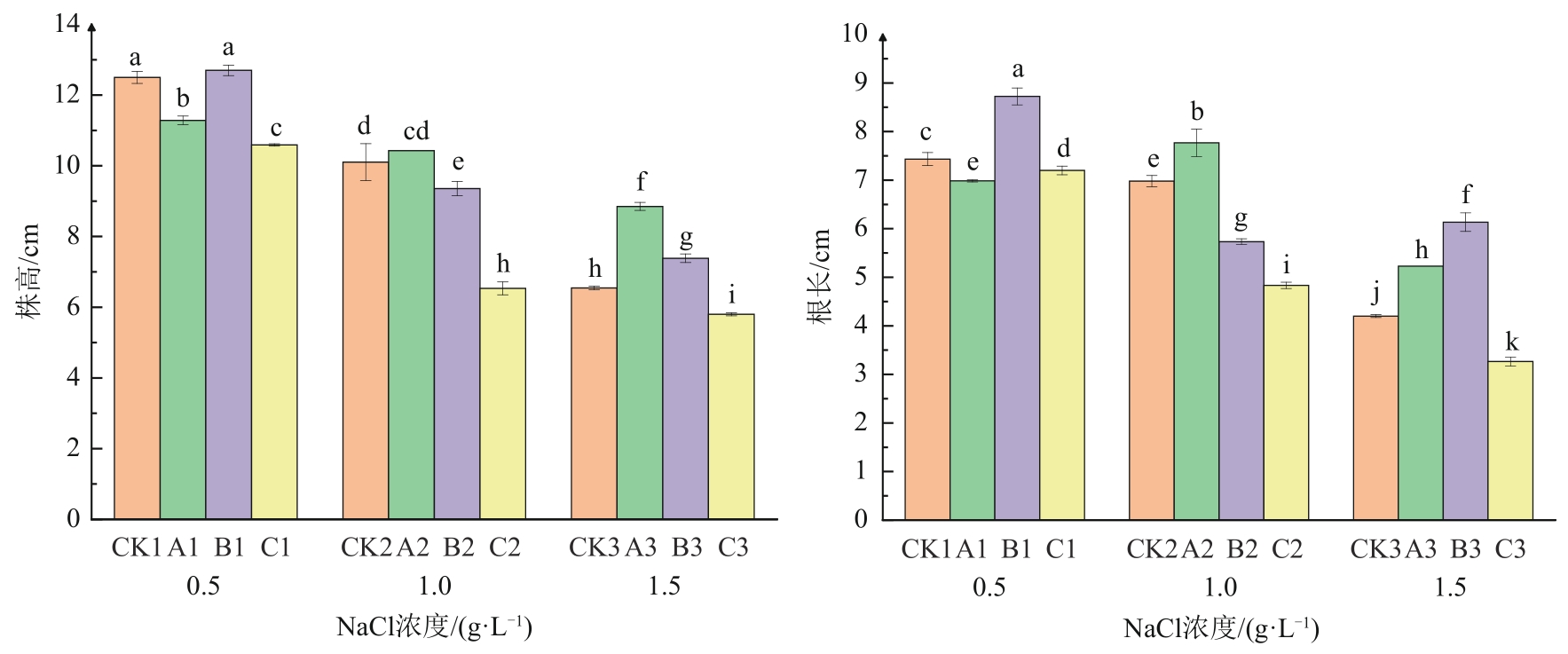
图4 冷等离子体处理对NaCl胁迫下燕麦株高和根长的影响注:不同小写字母表示不同处理间在P<0.05水平上具有统计学意义。
Fig. 4 Effects of cold plasma treatment on plant length and root length of oats under NaCl stress
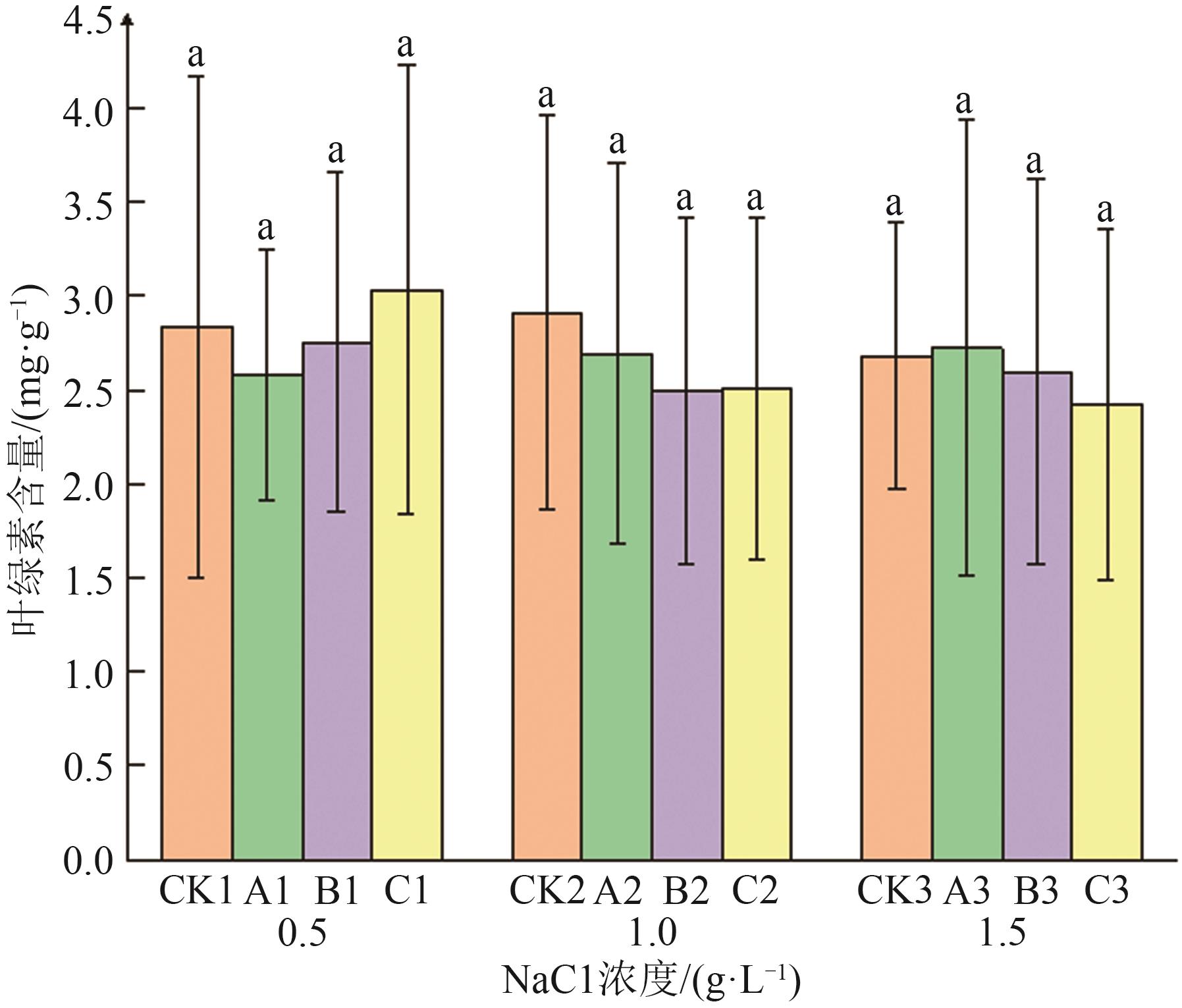
图5 冷等离子体处理对NaCl胁迫下燕麦幼苗叶绿素含量的影响注:不同小写字母表示不同处理间在P<0.05水平上具有统计学意义。
Fig. 5 Effects of cold plasma treatment on chlorophyll content of oat seedlings under NaCl stress
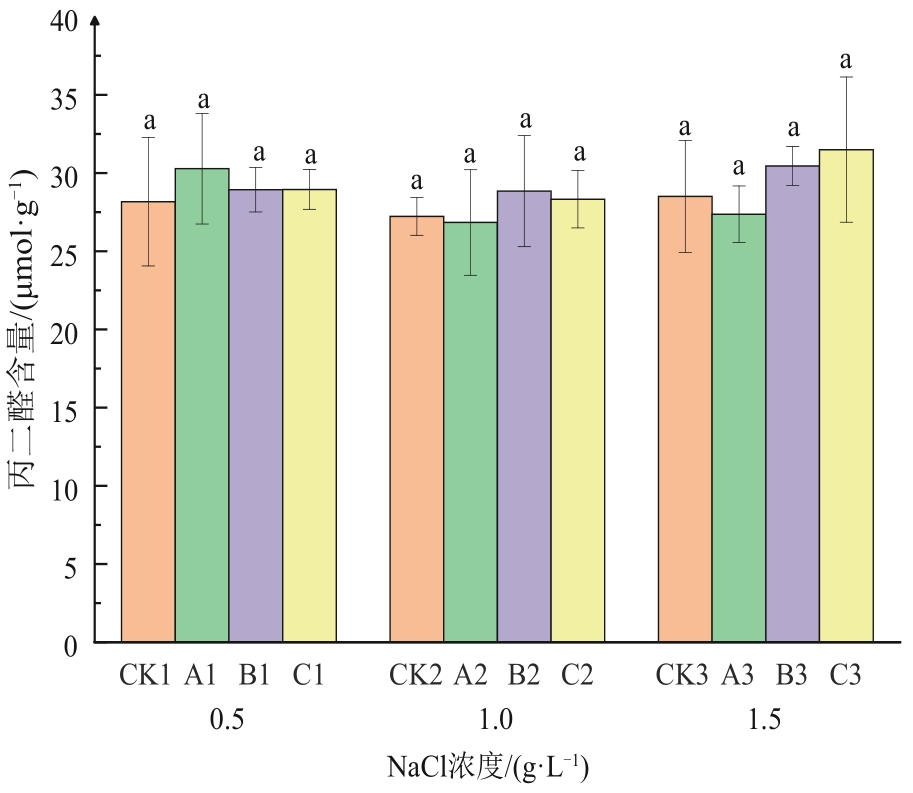
图6 冷等离子体处理对NaCl胁迫下燕麦幼苗丙二醛含量的影响注:不同小写字母表示不同处理间在P<0.05水平上具有统计学意义。
Fig. 6 Effects of cold plasma treatment on malondialdehyde content of oat seedlings under NaCl stress
| 指标 | 表面接触角 | 吸水率 | 发芽势 | 发芽率 | 株高 | 根长 | 叶绿素 | 丙二醛 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 表面接触角 | 1.000 | |||||||
| 吸水率 | -0.877** | 1.000 | ||||||
| 发芽势 | 0.411 | -0.296 | 1.000 | |||||
| 发芽率 | 0.626* | -0.532* | 0.922** | 1.000 | ||||
| 株高 | 0.139 | 0.066 | 0.909** | 0.741** | 1.000 | |||
| 根长 | 0.006 | 0.183 | 0.761** | 0.597* | 0.915** | 1.000 | ||
| 叶绿素 | 0.410 | -0.404 | 0.577* | 0.590* | 0.580* | 0.597* | 1.000 | |
| 丙二醛 | -0.479 | 0.299 | -0.318 | -0.471 | -0.327 | -0.360 | -0.503* | 1.000 |
表2 各指标相关性分析
Table 2 Correlation analysis of various indicators
| 指标 | 表面接触角 | 吸水率 | 发芽势 | 发芽率 | 株高 | 根长 | 叶绿素 | 丙二醛 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 表面接触角 | 1.000 | |||||||
| 吸水率 | -0.877** | 1.000 | ||||||
| 发芽势 | 0.411 | -0.296 | 1.000 | |||||
| 发芽率 | 0.626* | -0.532* | 0.922** | 1.000 | ||||
| 株高 | 0.139 | 0.066 | 0.909** | 0.741** | 1.000 | |||
| 根长 | 0.006 | 0.183 | 0.761** | 0.597* | 0.915** | 1.000 | ||
| 叶绿素 | 0.410 | -0.404 | 0.577* | 0.590* | 0.580* | 0.597* | 1.000 | |
| 丙二醛 | -0.479 | 0.299 | -0.318 | -0.471 | -0.327 | -0.360 | -0.503* | 1.000 |
| 组别 | 综合指标X1 | 综合指标X2 | 综合指标X3 | 隶属函数值μ1 | 隶属函数值μ2 | 隶属函数值μ3 | 综合评价F |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK1 | 1.791 2 | -0.539 7 | 1.313 6 | 1.000 0 | 0.377 6 | 0.931 1 | 0.820 2 |
| CK2 | 1.160 5 | -1.061 0 | -0.502 5 | 0.820 2 | 0.237 4 | 0.326 5 | 0.605 9 |
| CK3 | -0.146 7 | -1.944 2 | 0.082 0 | 0.447 6 | 0.000 0 | 0.521 1 | 0.331 4 |
| A1 | 0.174 7 | 0.665 8 | 1.520 4 | 0.539 2 | 0.701 6 | 1.000 0 | 0.633 5 |
| A2 | 0.370 6 | 0.427 0 | -1.483 0 | 0.595 1 | 0.637 4 | 0.000 0 | 0.543 1 |
| A3 | -0.222 0 | -0.250 2 | -1.434 1 | 0.426 1 | 0.455 4 | 0.016 3 | 0.390 4 |
| B1 | 0.729 1 | 1.775 6 | 0.323 9 | 0.697 2 | 1.000 0 | 0.601 6 | 0.770 9 |
| B2 | -0.655 9 | 0.787 3 | -0.147 4 | 0.302 4 | 0.734 3 | 0.444 7 | 0.437 3 |
| B3 | -1.190 8 | 0.708 4 | -0.066 9 | 0.150 0 | 0.713 1 | 0.471 5 | 0.340 4 |
| C1 | 0.499 5 | 0.507 1 | -0.491 9 | 0.631 8 | 0.659 0 | 0.330 0 | 0.607 0 |
| C2 | -0.793 4 | -0.490 0 | -0.474 3 | 0.263 2 | 0.390 9 | 0.335 9 | 0.306 4 |
| C3 | -1.716 8 | -0.586 0 | 1.360 1 | 0.000 0 | 0.365 1 | 0.946 6 | 0.202 5 |
表3 冷等离子体处理下燕麦抗盐性的综合评价结果
Table 3 Comprehensive evaluation results of salt resistance of oats under cold plasma treatment
| 组别 | 综合指标X1 | 综合指标X2 | 综合指标X3 | 隶属函数值μ1 | 隶属函数值μ2 | 隶属函数值μ3 | 综合评价F |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK1 | 1.791 2 | -0.539 7 | 1.313 6 | 1.000 0 | 0.377 6 | 0.931 1 | 0.820 2 |
| CK2 | 1.160 5 | -1.061 0 | -0.502 5 | 0.820 2 | 0.237 4 | 0.326 5 | 0.605 9 |
| CK3 | -0.146 7 | -1.944 2 | 0.082 0 | 0.447 6 | 0.000 0 | 0.521 1 | 0.331 4 |
| A1 | 0.174 7 | 0.665 8 | 1.520 4 | 0.539 2 | 0.701 6 | 1.000 0 | 0.633 5 |
| A2 | 0.370 6 | 0.427 0 | -1.483 0 | 0.595 1 | 0.637 4 | 0.000 0 | 0.543 1 |
| A3 | -0.222 0 | -0.250 2 | -1.434 1 | 0.426 1 | 0.455 4 | 0.016 3 | 0.390 4 |
| B1 | 0.729 1 | 1.775 6 | 0.323 9 | 0.697 2 | 1.000 0 | 0.601 6 | 0.770 9 |
| B2 | -0.655 9 | 0.787 3 | -0.147 4 | 0.302 4 | 0.734 3 | 0.444 7 | 0.437 3 |
| B3 | -1.190 8 | 0.708 4 | -0.066 9 | 0.150 0 | 0.713 1 | 0.471 5 | 0.340 4 |
| C1 | 0.499 5 | 0.507 1 | -0.491 9 | 0.631 8 | 0.659 0 | 0.330 0 | 0.607 0 |
| C2 | -0.793 4 | -0.490 0 | -0.474 3 | 0.263 2 | 0.390 9 | 0.335 9 | 0.306 4 |
| C3 | -1.716 8 | -0.586 0 | 1.360 1 | 0.000 0 | 0.365 1 | 0.946 6 | 0.202 5 |
| 1 | 都润,张思琦,张海文,等.逆境胁迫下向日葵的耐受机制[J].生物技术进展,2022,12(2):205-212. |
| DU R, ZHANG S Q, ZHANG H W, et al.. The tolerance mechanism of sunflower under abiotic stress[J]. Curr. Biotechnol., 2022, 12(2): 205-212. | |
| 2 | 祁旭升,王兴荣,许军,等.胡麻种质资源成株期抗旱性评价[J].中国农业科学,2010,43(15):3076-3087. |
| QI X S, WANG X R, XU J, et al.. Drought-resistance evaluation of flax germplasm at adult plant stage[J]. Sci. Agric. Sin., 2010, 43(15): 3076-3087. | |
| 3 | 赵东晓,杜建勋,陈传杰,等.桑树盐碱胁迫研究进展[J].山东农业科学,2015,47(5):132-135. |
| ZHAO D X, DU J X, CHEN C J, et al.. Research progress on saline alkali stress of mulberry[J]. Shandong Agric. Sci., 2015, 47(5): 132-135. | |
| 4 | 宋璟,岑慧芳,刘华玥,等.冷等离子体对作物种子处理效应的研究进展[J].作物杂志,2021(6):9-14. |
| SONG J, CEN H F, LIU H Y, et al.. Advances in cold plasma treatment effects on crop seeds[J]. Crops, 2021(6): 9-14. | |
| 5 | LI L, JIANG J, LI J, et al.. Effects of cold plasma treatment on seed germination and seedling growth of soybean[J/OL]. Sci. Rep., 2014, 4: 5859[2024-04-07]. . |
| 6 | JIANG J, HE X, LI L, et al.. Effect of cold plasma treatment on seed germination and growth of wheat[J]. Plasma Sci. Technol., 2014, 16(1): 54-58. |
| 7 | 周筑文,黄燕芬,杨思泽,等.大气压等离子体处理对番茄生长发育及产量与品质的影响[J].安徽农业科学,2010,38(2):1085-1088. |
| ZHOU Z W, HUANG Y F, YANG S Z, et al.. Effects of atmospheric pressure plasma on the growth, yield and quality of tomato[J]. J. Anhui Agric. Sci., 2010, 38(2): 1085-1088. | |
| 8 | 李怀智,庞金安.物理方法处理种子对黄瓜生长发育的影响研究进展[J].农业与技术,2003,23(2):47-49+57. |
| LI H Z, PANG J A. Progress of study on seed treatment of physical techniques in cucumber[J]. Agric. Technol., 2003, 23(2): 47-49+57. | |
| 9 | 骆美洁,赵衍鑫,宋伟,等.常压室温等离子体对玉米种子及花粉萌发的影响[J].分子植物育种,2016,14(5):1262-1267. |
| LUO M J, ZHAO Y X, SONG W, et al.. Effects on maize seed and pollen germination by atmospheric and room temperature plasma[J]. Mol. Plant Breed., 2016, 14(5): 1262-1267. | |
| 10 | 童家赟.空气等离子体预处理提高穿心莲种子活力的研究[D].广州:广州中医药大学,2012. |
| 11 | 邓敏,赵玲,滕应,等.冷等离子体种子处理对铜胁迫下小麦种子萌发与幼苗生长的影响[J].农业环境科学学报,2018,37(12):2669-2677. |
| DENG M, ZHAO L, TENG Y, et al.. The effects of cold plasma treatment on wheat seed germination and seedling growth under copper stress[J]. J. Agro-Environ. Sci., 2018, 37(12): 2669-2677. | |
| 12 | SHETEIWY A S M.引发和冷等离子体处理通过生理、分子及代谢调控提高水稻种子的抗逆性[D].杭州:浙江大学,2017. |
| 13 | ROY N C, HASAN M M, KABIR A H, et al.. Atmospheric pressure gliding arc discharge plasma treatments for improving germination, growth and yield of wheat[J/OL]. Plasma Sci. Technol., 2018, 20(11): 115501[2024-04-07]. . |
| 14 | 蔡庆生.植物生理学实验[M].北京:中国农业大学出版社,2013. |
| 15 | 陈建勋,王晓峰.植物生理学实验指导[M].广州:华南理工大学出版社,2015. |
| 16 | 任棚,吕晓桂,石磊.大气压冷等离子体持续和间隔处理对燕麦种子萌发的影响[J].中国农业科技导报,2023,25(7):215-221. |
| REN P, LYU X G, SHI L. Effects of atmospheric pressure cold plasma continuous and interval treatments on oat seed germination[J]. J. Agric. Sci. Technol., 2023, 25(7): 215-221. | |
| 17 | 罗礽兰,胡道武,王静静,等.基于主成分分析和隶属函数的棉花种子萌发期耐涝性鉴定评价[J].中国棉花,2023,50(3):1-5. |
| LUO R L, HU D W, WANG J J, et al.. Identification and evaluation of waterlogging tolerance of cotton seed at germination stage based on the principal component analysis and subordinate function[J]. China Cotton, 2023, 50(3): 1-5. | |
| 18 | WEITBRECHT K, MÜLLER K, LEUBNER-METZGER G. First off the mark: early seed germination[J]. J. Exp. Bot., 2011, 62(10): 3289-3309. |
| 19 | DUBINOV A E, KOZHAYEVA J P, ZUIMATCH E A. Changing germination rate of brown mustard seeds after treatment with plasmas of nanosecond electric discharges[J]. IEEE Trans. Plasma Sci., 2017, 45(2): 294-300. |
| 20 | 陈金萍,陈全家,郑凯,等.棉花萌发期抗旱指标筛选及种质资源抗旱性综合评价[J].生物技术进展,2023,13(4):556-564. |
| CHEN J P, CHEN Q J, ZHENG K, et al.. Cotton drought resistance index screening and comprehensive evaluation of drought resistance of germplasm resources during germination period[J]. Curr. Biotechnol., 2023, 13(4): 556-564. | |
| 21 | 王宝山,赵可夫.NaCl胁迫下玉米黄化苗质外体和共质体Na、Ca浓度的变化[J].作物学报,1997,23(1):27-33. |
| WANG B S, ZHAO K F. Changes in Na and Ca concentrations in the apoplast and symplast of the etiolated corn seedlings under NaCl stress[J]. Acta Agron. Sin., 1997, 23(1): 27-33. | |
| 22 | KALAJI H M, JAJOO A, OUKARROUM A, et al.. Chlorophyll a fluorescence as a tool to monitor physiological status of plants under abiotic stress conditions[J/OL]. Acta Physiol. Plant, 2016, 38(4): 102[2024-04-07]. . |
| 23 | GUO Q, WANG Y, ZHANG H, et al.. Alleviation of adverse effects of drought stress on wheat seed germination using atmospheric dielectric barrier discharge plasma treatment[J/OL]. Sci. Rep., 2017, 7(1): 16680[2024-04-07]. . |
| 24 | 李学孚,倪智敏,吴月燕,等. 盐胁迫对‘鄞红’葡萄光合特性及叶片细胞结构的影响[J]. 生态学报, 2015, 35(13): 4436-4444. |
| LI X F, NI Z M, WU Y Y, et al.. Effects of salt stress on photosynthetic characteristicsand leaf cell structure of‘Yinhong’ grape[J]. J. Ecol., 2015, 35 (13): 4436-4444. | |
| 25 | YANG J Y, ZHENG W, TIAN Y, et al.. Effects of various mixed salt-alkaline stresses on growth, photosynthesis, and photosynthetic pigment concentrations of Medicago ruthenica seedlings[J]. Photosynthetica, 2011, 49(2): 275-284. |
| 26 | 刘卫国,丁俊祥,邹杰,等.NaCl对齿肋赤藓叶肉细胞超微结构的影响[J].生态学报,2016,36(12):3556-3563. |
| LIU W G, DING J X, ZOU J, et al.. Ultrastructural responses of Syntrichia caninervis to a gradient of NaCl stress[J]. Acta Ecol. Sin., 2016, 36(12): 3556-3563. | |
| 27 | CHENG T, CHEN J, ZHANG J, et al.. Physiological and proteomic analyses of leaves from the halophyte Tangut Nitraria reveals diverse response pathways critical for high salinity tolerance[J/OL]. Front. Plant Sci., 2015, 6: 30[2024-04-07]. . |
| 28 | GRIEVE C M, LESCH S M, MAAS E V, et al.. Leaf and spikelet primordia initiation in salt-stressed wheat[J]. Crop Sci., 1993, 33(6): 1286-1294. |
| 29 | 王佺珍,刘倩,高娅妮,等.植物对盐碱胁迫的响应机制研究进展[J].生态学报,2017,37(16):5565-5577. |
| WANG Q Z, LIU Q, GAO Y N, et al.. Review on the mechanisms of the response to salinity-alkalinity stress in plants[J]. Acta Ecol. Sin., 2017, 37(16): 5565-5577. | |
| 30 | 史军辉,王新英,刘茂秀,等.NaCl胁迫对胡杨幼苗叶主要渗透调节物质的影响[J].西北林学院学报,2014,29(6):6-11. |
| SHI J H, WANG X Y, LIU M X, et al.. Effects of NaCl stress on main osmotic adjustment substances in the seedling leaves of Populus euphratica [J]. J. Northwest For. Univ., 2014, 29(6): 6-11. |
| [1] | 张香香,滕炎桐,陈涛. AtEXD参与植物盐胁迫的作用研究[J]. 生物技术进展, 2021, 11(1): 61-68. |
| [2] | 陈新兵,黄荣峰,王娟. 水稻矮杆突变体D814基因图位克隆与功能分析[J]. 生物技术进展, 2017, 7(6): 608-617. |
| [3] | 杨海峰,刘景辉,王俊英. 盐碱胁迫下不同燕麦品种钠、钾、钙流量测定分析[J]. 生物技术进展, 2014, 4(3): 192-196. |
| [4] | 葸玉琴,马春林,曹云涛,孔维宝,杨红. 自养和混养小球藻对NaCl胁迫的生理响应[J]. 生物技术进展, 2013, 3(3): 223-228. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
版权所有 © 2021《生物技术进展》编辑部