


生物技术进展 ›› 2024, Vol. 14 ›› Issue (6): 937-946.DOI: 10.19586/j.2095-2341.2024.0090
李昕阳1( ), 杨阳2,3(
), 杨阳2,3( ), 刘栋4,5, 刘宇光1, 刘俊泽1, 陈长宝1, 王欢1,3(
), 刘栋4,5, 刘宇光1, 刘俊泽1, 陈长宝1, 王欢1,3( ), 王淑敏1(
), 王淑敏1( )
)
收稿日期:2024-04-24
接受日期:2024-07-30
出版日期:2024-11-25
发布日期:2024-12-27
通讯作者:
王欢,王淑敏
作者简介:李昕阳E-mail: 17634093266@163.com基金资助:
Xinyang LI1( ), Yang YANG2,3(
), Yang YANG2,3( ), Dong LIU4,5, Yuguang LIU1, Junze LIU1, Changbao CHEN1, Huan WANG1,3(
), Dong LIU4,5, Yuguang LIU1, Junze LIU1, Changbao CHEN1, Huan WANG1,3( ), Shumin WANG1(
), Shumin WANG1( )
)
Received:2024-04-24
Accepted:2024-07-30
Online:2024-11-25
Published:2024-12-27
Contact:
Huan WANG,Shumin WANG
摘要:
真菌Simplicillium lanosoniveum已被报道具有多种生物学效应,往往被用作生物防治。然而,有关其液体发酵的研究却很少。通过形态学和系统发育分析,鉴定了1株从发网菌属中分离出的丝孢真菌SL001,即S. lanosoniveum。以菌丝生物量和胞外多糖产量为指标,通过单因素和正交实验优化发酵培养基的组成和比例,以阐明液体发酵S. lanosoniveum的最优培养条件。结果表明,在麦芽糖40 g·L-1、蛋白胨3 g·L-1和KH2PO4 1 g·L-1的营养条件下,S. lanosoniveum的菌丝生物量和胞外多糖产量最高,对S. lanosoniveum菌丝生物量的影响程度由大到小依次为麦芽糖>蛋白胨>KH2PO4。最后,根据营养需求对培养条件进一步优化。结果显示,最佳培养条件为麦芽糖40 g·L-1,蛋白胨3 g·L-1,KH2PO4 1 g·L-1,培养温度28 ℃,pH 5.5,转速150 r·min-1,装液量80 mL/250 mL,接种量6%。在最佳培养条件下,菌丝生物量和胞外多糖可达到最大值1.69 g·100 mL-1和3.968 mg·ml-1,与对照组相比有显著差异(P<0.01)。通过单因素和正交实验得到真菌S. lanosoniveum的最佳液体发酵条件,为进一步研究S. lanosoniveum的抗菌作用和工业化生产提供了理论依据。
中图分类号:
李昕阳, 杨阳, 刘栋, 刘宇光, 刘俊泽, 陈长宝, 王欢, 王淑敏. 基于菌丝生物量和胞外多糖产量的Simplicillium lanosoniveum液体发酵培养条件优化[J]. 生物技术进展, 2024, 14(6): 937-946.
Xinyang LI, Yang YANG, Dong LIU, Yuguang LIU, Junze LIU, Changbao CHEN, Huan WANG, Shumin WANG. Optimization of Liquid Fermentation Conditions for Mycelial Biomass and Exopolysaccharide Production of Simplicillium lanosoniveum[J]. Current Biotechnology, 2024, 14(6): 937-946.
| 物种名 | 菌株名 | 登录号 | 国家/地区 | 分离来源 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cordyceps pseudomilitaris | NHJ6 | AJ786589 | - | - |
| Lecanicillium lecanii | CBS 101247 | AJ292382 | 西印度群岛 | Coccus viridis |
| Simplicillium aogashimaense | JCM 18167 | AB604002 | 日本伊豆岛 | Asplenium antiquum下的土壤 |
| S. calcicola | LC5371 | KU746705 | 中国贵州省 | 岩石 |
| S. calcicola | LC5586 | KU746706 | 中国贵州省 | 岩石 |
| S. chinense | LC1345 | JQ410324 | 中国 | 木材 |
| S. cylindrosporum | JCM 18169 | AB603989 | 日本小笠原岛 | Cinnamomumpseudopedunculatum下的土壤 |
| S. lamellicola | CBS 116.25 | MH854806 | 英国 | - |
| S. lamellicola | CBS:596.71 | MH860281 | 英国 | - |
| S. lanosoniveum | Cs0701 | EU939525 | 中国台湾省 | Salvinia molesta |
| S. lanosoniveum | CHE-CNRCB 373 | KX686123 | 墨西哥 | Diaphorina citri |
| S. lanosoniveum | CBS 123.42 | MH856100 | 荷兰 | Cibotium schiedei |
| S. lanosoniveum | vecl_02 | KM035982 | 印度 | Elaeagnus latifolia |
| S. lanosoniveum | vecl_01 | KM035981 | 印度 | Elaeagnus latifolia |
| S. lanosoniveum | CBS 531.72 | MH860557 | 美国 | Salvinia rotundifolia |
| S. lanosoniveum | CBS 321.72 | MH860488 | 马来西亚 | - |
| S. lanosoniveum | SSBG2 | MG807436 | 俄罗斯 | Coccus hesperidum |
| S. lanosoniveum | CBS 962.72 | EF641862 | - | - |
| S. lanosoniveum | YLAC-5 | KY552635 | 中国 | Inula aconitum |
| S. lanosoniveum | Tr3 | MG026635 | 中国 | Salvia miltiorrhiza |
| S. lanosoniveum | 02502 | KT878334 | 中国 | 支气管肺泡灌洗液 |
| S. lanosoniveum | 43A | MN860012 | 中国吉林省 | Stemonitis splendens |
| S. lanosoniveum | 43B | MN860013 | 中国吉林省 | Stemonitis splendens |
| S. lanosoniveum | 44A | MN860014 | 中国吉林省 | Stemonitis splendens |
| S. lanosoniveum | 44B | MN860015 | 中国吉林省 | Stemonitis splendens |
| S. minatense | JCM 18178 | AB603993 | 日本港区 | Prunus yedoensis下的土壤 |
| S. minatense | JCM 18176 | AB603992 | 日本港区 | Prunus yedoensis下的土壤 |
| S. obclavatum | - | MH860859 | - | - |
| S. subtropicum | JCM 18180 | AB603990 | 日本小笠原岛 | Cinnamomumpseudopedunculatum下的土壤 |
| S. sympodiophorum | JCM 18184 | AB604003 | 日本伊豆岛 | Asplenium antiquum下的土壤 |
表1 本研究中用于系统发育分析的序列信息
Table 1 Sequences information used for phylogenetic analysis in this study
| 物种名 | 菌株名 | 登录号 | 国家/地区 | 分离来源 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cordyceps pseudomilitaris | NHJ6 | AJ786589 | - | - |
| Lecanicillium lecanii | CBS 101247 | AJ292382 | 西印度群岛 | Coccus viridis |
| Simplicillium aogashimaense | JCM 18167 | AB604002 | 日本伊豆岛 | Asplenium antiquum下的土壤 |
| S. calcicola | LC5371 | KU746705 | 中国贵州省 | 岩石 |
| S. calcicola | LC5586 | KU746706 | 中国贵州省 | 岩石 |
| S. chinense | LC1345 | JQ410324 | 中国 | 木材 |
| S. cylindrosporum | JCM 18169 | AB603989 | 日本小笠原岛 | Cinnamomumpseudopedunculatum下的土壤 |
| S. lamellicola | CBS 116.25 | MH854806 | 英国 | - |
| S. lamellicola | CBS:596.71 | MH860281 | 英国 | - |
| S. lanosoniveum | Cs0701 | EU939525 | 中国台湾省 | Salvinia molesta |
| S. lanosoniveum | CHE-CNRCB 373 | KX686123 | 墨西哥 | Diaphorina citri |
| S. lanosoniveum | CBS 123.42 | MH856100 | 荷兰 | Cibotium schiedei |
| S. lanosoniveum | vecl_02 | KM035982 | 印度 | Elaeagnus latifolia |
| S. lanosoniveum | vecl_01 | KM035981 | 印度 | Elaeagnus latifolia |
| S. lanosoniveum | CBS 531.72 | MH860557 | 美国 | Salvinia rotundifolia |
| S. lanosoniveum | CBS 321.72 | MH860488 | 马来西亚 | - |
| S. lanosoniveum | SSBG2 | MG807436 | 俄罗斯 | Coccus hesperidum |
| S. lanosoniveum | CBS 962.72 | EF641862 | - | - |
| S. lanosoniveum | YLAC-5 | KY552635 | 中国 | Inula aconitum |
| S. lanosoniveum | Tr3 | MG026635 | 中国 | Salvia miltiorrhiza |
| S. lanosoniveum | 02502 | KT878334 | 中国 | 支气管肺泡灌洗液 |
| S. lanosoniveum | 43A | MN860012 | 中国吉林省 | Stemonitis splendens |
| S. lanosoniveum | 43B | MN860013 | 中国吉林省 | Stemonitis splendens |
| S. lanosoniveum | 44A | MN860014 | 中国吉林省 | Stemonitis splendens |
| S. lanosoniveum | 44B | MN860015 | 中国吉林省 | Stemonitis splendens |
| S. minatense | JCM 18178 | AB603993 | 日本港区 | Prunus yedoensis下的土壤 |
| S. minatense | JCM 18176 | AB603992 | 日本港区 | Prunus yedoensis下的土壤 |
| S. obclavatum | - | MH860859 | - | - |
| S. subtropicum | JCM 18180 | AB603990 | 日本小笠原岛 | Cinnamomumpseudopedunculatum下的土壤 |
| S. sympodiophorum | JCM 18184 | AB604003 | 日本伊豆岛 | Asplenium antiquum下的土壤 |
| 水平 | 因素 | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| A:麦芽糖 | B:蛋白胨 | C:KH2PO4 | |
| 1 | 3% | 0.1% | 0.05% |
| 2 | 4% | 0.2% | 0.10% |
| 3 | 5% | 0.3% | 0.15% |
表2 发酵条件的因素和水平
Table 2 Factors and levels of fermentation condition
| 水平 | 因素 | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| A:麦芽糖 | B:蛋白胨 | C:KH2PO4 | |
| 1 | 3% | 0.1% | 0.05% |
| 2 | 4% | 0.2% | 0.10% |
| 3 | 5% | 0.3% | 0.15% |

图1 SL001在PDA培养基上培养14 d后的形态特征A:培养物的俯视图;B: 培养物的背面;C: 菌丝;D~G: 瓶梗和瓶梗顶端的分生孢子;H: 分生孢子。比例尺:C = 0.5 mm, D~F = 10 μm, G、 H = 5 μm;D、E、 G、 H用乳酸酚棉蓝溶液染色。
Fig. 1 Morphology of S. lanosoniveum on PDA medium after 14 days

图2 基于ITS序列构建的Simplicillium属系统发育树注:节点上标注了最大似然法自举值(>70%)和贝叶斯后验概率(≥95%)的支持度。该系统发育树以Lecanicillium lecanii 和Cordyceps pseudomilitaris为根序列。
Fig. 2 Phylogenetic relationships among the genus Simplicillium based on the ITS sequences data
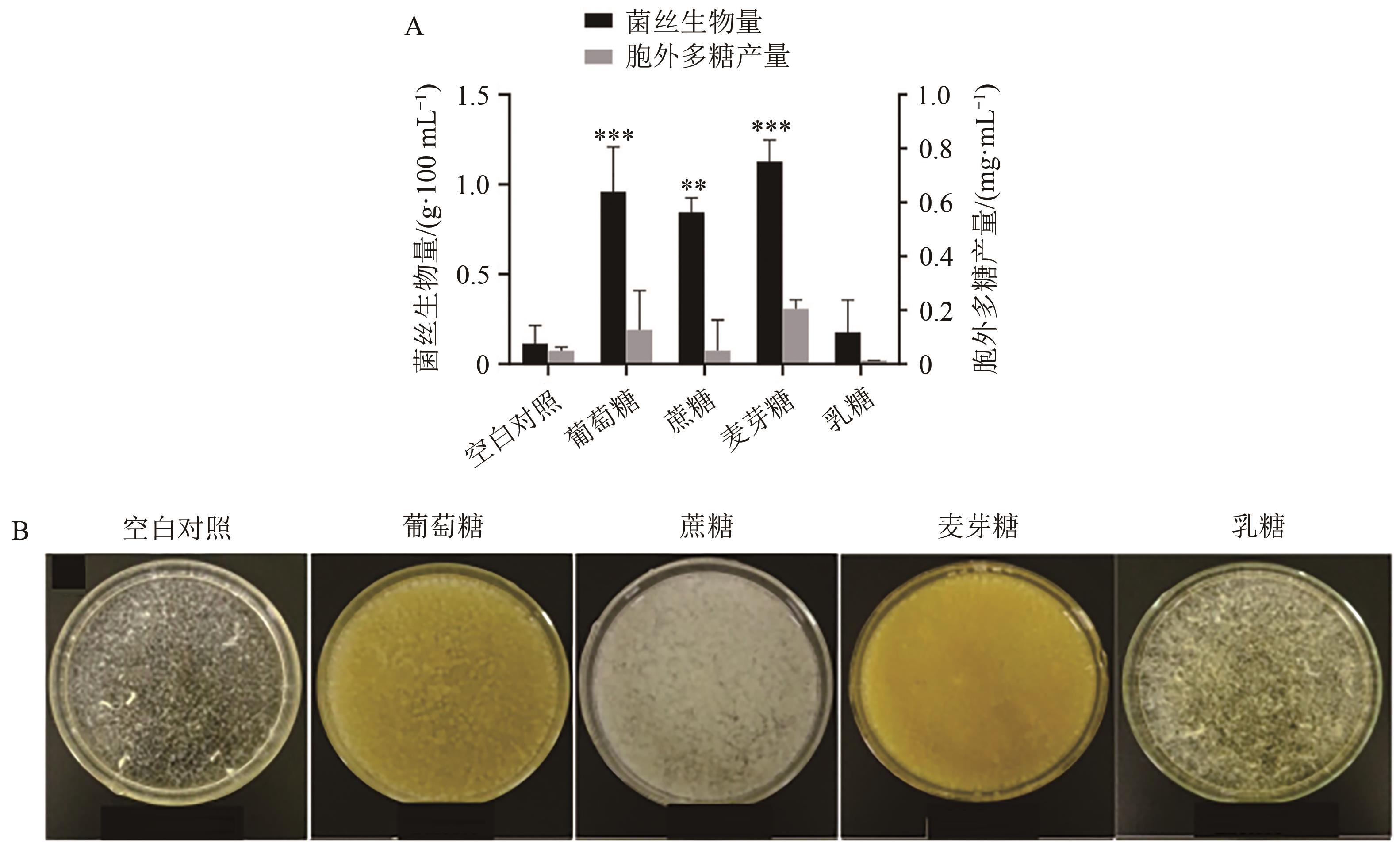
图3 不同碳源对菌丝生物量和胞外多糖产量的影响A:不同碳源对菌丝生物量和胞外多糖产量的影响;B:不同碳源菌丝生长情况。**与***分别表示与同参数下的空白对照比差异在P<0.01和P<0.001水平上具有统计学意义。
Fig. 3 Effect of different carbon source on mycelial biomass and exopolysaccharides yield
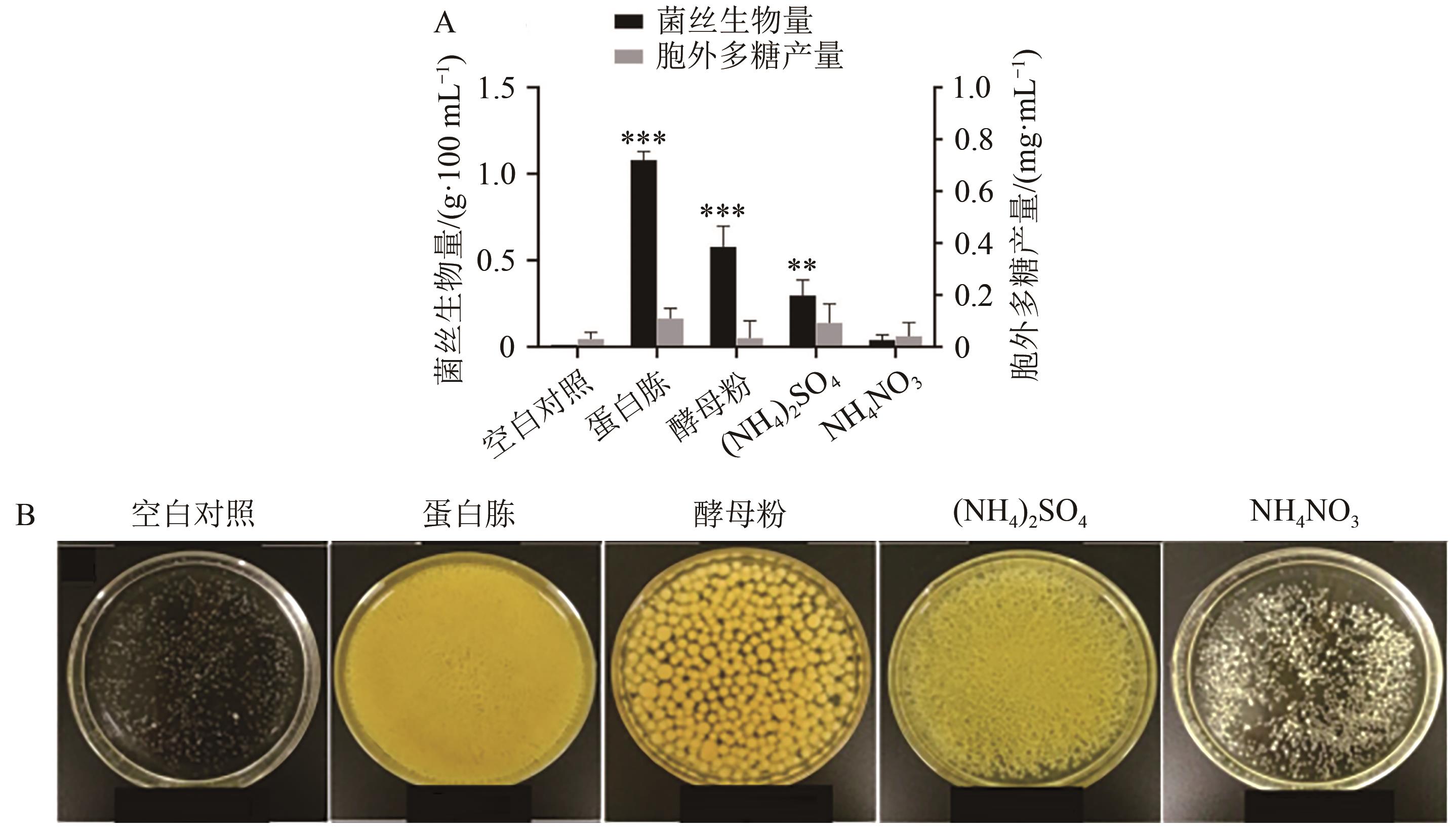
图4 不同氮源对菌丝生物量和胞外多糖产量的影响A:不同氮源对菌丝生物量和胞外多糖产量的影响;B:不同氮源菌丝生长情况。**与***分别表示与同参数下的空白对照比差异在P<0.01和P<0.001水平上具有统计学意义。
Fig. 4 Effect of different nitrogen source on mycelial biomass and exopolysaccharides yield
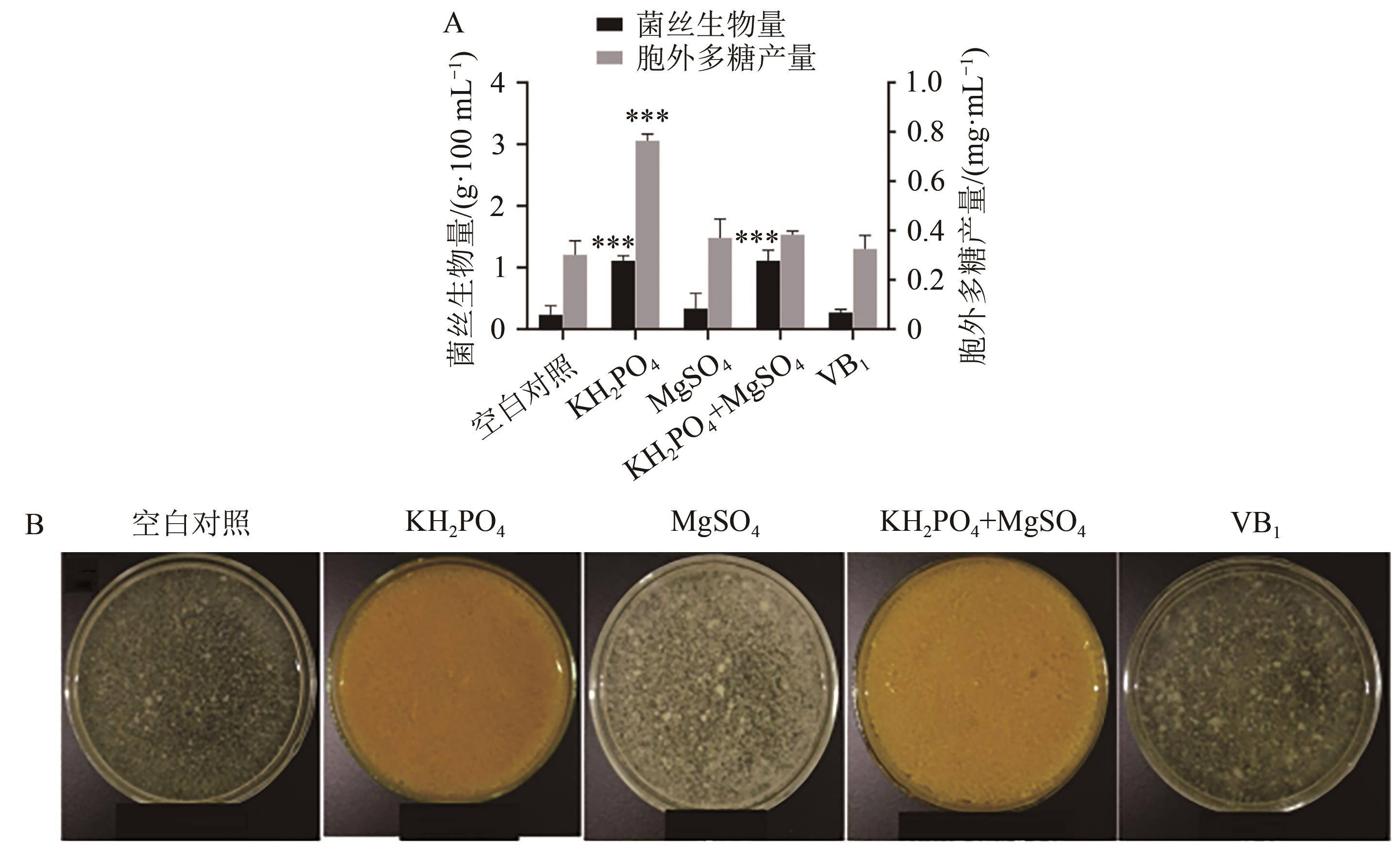
图5 不同微量元素对菌丝生物量和胞外多糖产量的影响A:不同微量元素对菌丝生物量和胞外多糖产量的影响;B:不同微量元素菌丝生长情况。**与***分别表示与同参数下的空白对照比差异在P<0.01和P<0.001水平上具有统计学意义。
Fig. 5 Effect of different microelement on mycelial biomass and exopolysaccharides yield
| 序号 | 因素水平 | 菌丝生物量(g·100 mL-1) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| A:麦芽糖 | B:蛋白胨 | C:KH2PO4 | ||
| 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0.70±0.18 |
| 2 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 0.70±0.09 |
| 3 | 1 | 3 | 3 | 0.81±0.26 |
| 4 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 0.97±0.21 |
| 5 | 2 | 2 | 3 | 1.11±0.10 |
| 6 | 2 | 3 | 1 | 1.33±0.11 |
| 7 | 3 | 1 | 3 | 0.88±0.05 |
| 8 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0.85±0.22 |
| 9 | 3 | 3 | 2 | 1.07±0.14 |
| k1 | 0.737 | 0.850 | 0.960 | — |
| k2 | 1.137 | 0.887 | 0.970 | — |
| k3 | 0.933 | 1.070 | 0.877 | — |
| r | 0.400 | 0.220 | 0.093 | — |
表5 S. lanosoniveum.最佳发酵条件的正交实验设计
Table 5 Orthogonal experiment design for optimal submerged fermentation condition of S. lanosoniveum
| 序号 | 因素水平 | 菌丝生物量(g·100 mL-1) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| A:麦芽糖 | B:蛋白胨 | C:KH2PO4 | ||
| 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0.70±0.18 |
| 2 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 0.70±0.09 |
| 3 | 1 | 3 | 3 | 0.81±0.26 |
| 4 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 0.97±0.21 |
| 5 | 2 | 2 | 3 | 1.11±0.10 |
| 6 | 2 | 3 | 1 | 1.33±0.11 |
| 7 | 3 | 1 | 3 | 0.88±0.05 |
| 8 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0.85±0.22 |
| 9 | 3 | 3 | 2 | 1.07±0.14 |
| k1 | 0.737 | 0.850 | 0.960 | — |
| k2 | 1.137 | 0.887 | 0.970 | — |
| k3 | 0.933 | 1.070 | 0.877 | — |
| r | 0.400 | 0.220 | 0.093 | — |
| 因素 | SS | Df | F | P |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 麦芽糖(A) | 0.240 | 2 | 80.000 | * |
| 蛋白胨(B) | 0.083 | 2 | 27.667 | * |
| KH2PO4(C) | 0.003 | 2 | 1.000 | |
| 误差 | 0.09 | 2 | ||
| 汇总 | 0.416 | 8 |
表6 方差分析
Table 6 Analysis of variance
| 因素 | SS | Df | F | P |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 麦芽糖(A) | 0.240 | 2 | 80.000 | * |
| 蛋白胨(B) | 0.083 | 2 | 27.667 | * |
| KH2PO4(C) | 0.003 | 2 | 1.000 | |
| 误差 | 0.09 | 2 | ||
| 汇总 | 0.416 | 8 |
| 1 | ZARE R, GAMS W.A revision of the Verticillium fungicola species complex and its affinity with the genus Lecanicillium [J].Mycol. Res., 2008, 112(7): 811-824. |
| 2 | SUNG G H, HYWEL-JONES N L, SUNG J M, et al.. Phylogenetic classification of Cordyceps and the clavicipitaceous fungi[J]. Stud. Mycol., 2007, 57: 5-59. |
| 3 | LIU F, CAI L. Morphological and molecular characterization of a novel species of Simplicillium from China[J]. Cryptogam. Mycol. 2012, 33(2): 137-144. |
| 4 | WEI D P, WANASINGHE D N, HYDE K D, et al.. The genus Simplicillium [J]. MycoKeys, 2019, 60: 69-92. |
| 5 | CHEN W H, LIU C, HAN Y F, et al.. Three novel insect-associated species of Simplicillium (Cordycipitaceae,Hypocreales) from Southwest China[J]. MycoKeys, 2019, 58: 83-102. |
| 6 | GOMES A, PINHO D B, CARDEAL Z, et al.. Simplicillium coffeanum, a new endophytic species from Brazilian coffee plants, emitting antimicrobial volatiles[J]. Phytotaxa, 2018, 333(2): 188-198. |
| 7 | GREENGARTEN P J, TUININGA A R, MORATH S U,et al.. Occurrence of soil- and tick-borne fungi and related virulence tests for pathogenicity to Ixodes scapularis (Acari:Ixodidae)[J]. J. Med. Entomol., 2011, 48(2): 337-344. |
| 8 | HUBNER-CAMPOS R F, LELES R N, RODRIGUES J, et al.. Efficacy of entomopathogenic hypocrealean fungi against Periplaneta americana [J]. Parasitol. int., 2013, 62(6): 517-521. |
| 9 | NONAKA K, KAIFUCHI S, ŌMURA S, et al.. Five new Simplicillium species (Cordycipitaceae) from soils in Tokyo, Japan[J]. Mycoscience, 2013, 54(1): 42-53. |
| 10 | WARD N A, SCHNEIDER R W, AIME M C. Colonization of soybean rust sori by Simplicillium lanosoniveum [J]. Fungal Ecol., 2011, 4(5): 303-308. |
| 11 | CHEN R S, HUANG C C, LI J C, et al.. First report of Simplicillium lanosoniveum causing brown spot on Salvinia auriculata and S. molesta in Taiwan[J]. Plant Dis., 2008, 92(11): 1589. |
| 12 | ZHANG Z F, ZHOU S Y, EURWILAICHITR L, et al.. Culturable mycobiota from Karst caves in China Ⅱ, with descriptions of 33 new species[J]. Fungal Divers., 2021, 106(1): 29-136. |
| 13 | 王妮,谢映平,樊金华.桑白盾蚧病原真菌Simplicillium ianosoniveum的致病性[J].菌物学报,2016,35(5):559-568. |
| WANG N, XIE Y P, FAN J H. Pathogenicity of Simplicillium ianosoniveum TYL001 isolated from Pseudaulacaspis pentagona [J]. Mycosystema, 2016, 35(5): 559-568. | |
| 14 | LIM S Y, LEE S, KONG H G, et al.. Entomopathogenicity of Simplicillium lanosoniveum isolated in Korea[J]. Mycobiology, 2014, 42(4): 317-321. |
| 15 | ISHII M, TAKESHITA J, ISHIYAMA M, et al.. Evaluation of the pathogenicity and infectivity of entomopathogenic hypocrealean fungi,isolated from wild mosquitoes in Japan and Burkina Faso, against female adult Anopheles stephensi mosquitoes[J]. Fungal Ecol., 2015, 15: 39-50. |
| 16 | SKAPTSOV M, SMIRNOV S, KUTSEV M, et al.. Pathogenicity of Simplicillium lanosoniveum to Coccus hesperidum [J]. Ukr. J. Ecol., 2017, 7(4): 689-691. |
| 17 | GAUTHIER N W, MARUTHACHALAM K, SUBBARAO K V, et al.. Mycoparasitism of Phakopsora pachyrhizi, the soybean rust pathogen, by Simplicillium lanosoniveum [J]. Biol. Contr., 2014, 76: 87-94. |
| 18 | FUKUDA T, SUDOH Y, TSUCHIYA Y, et al.. Isolation and biosynthesis of preussin B, a pyrrolidine alkaloid from Simplicillium lanosoniveum [J]. J. Nat. Prod., 2014, 77(4): 813-817. |
| 19 | YU Y T, HE S H, ZHAO Q M. Isolation and identifcation of matrine-producing fungal endophytes from Sophora alopecuroides in Ningxia[J]. Sci. Agric. Sini., 2013, 46: 2643-2654. |
| 20 | ASGHER M, UROOJ Y, AHMAD QAMAR S, et al.. Improved exopolysaccharide production from Bacillus licheniformis MS3:optimization and structural/functional characterization[J]. Int. J. Biol. Macromol., 2020, 151: 984-992. |
| 21 | ASGHER M, AHMAD Q S, IQBAL H M N. Microbial exopolysaccharide-based nano-carriers with unique multi-functionalities for biomedical sectors[J]. Biologia, 2021, 76(2): 673-685. |
| 22 | BILAL M, GUL I, BASHARAT A, et al.. Polysaccharides-based bio-nanostructures and their potential food applications[J]. Int. J. Biol. Macromol., 2021, 176: 540-557. |
| 23 | MA A, AR A, NK A, et al.. Bioconversion of sugarcane molasses waste to high-value exopolysaccharides by engineered Bacillus licheniformis [J/OL]. Case Stud. Chem. Environ. Engin., 2021, 3: 100084[2024-10-15]. . |
| 24 | JIANG H, LUAN Z, FAN Z, et al.. Antibacterial,antibiofilm,and antioxidant activity of polysaccharides obtained from fresh sarcotesta of Ginkgo biloba: bioactive polysaccharide that can be exploited as a novel biocontrol agent[J]. Evid. Based Complem. Altern. Med., 2021, 2021: 5518403. |
| 25 | MOUSSA S H, TAYEL A A, AL-TURKI A I. Evaluation of fungal chitosan as a biocontrol and antibacterial agent using fluorescence-labeling[J]. Int. J. Biol. Macromol., 2013, 54: 204-208. |
| 26 | FU R J, CHENG R, WANG S M, et al.. Succinoglycan Riclin reshaped the soil microbiota by accumulating plant probiotic species to improve the soil suppressiveness on Fusarium wilt of cucumber seedlings[J]. Int. J. Biol. Macromol., 2021, 182: 1883-1892. |
| 27 | COSTA T M, LENZI J, SILVA F H, et al.. Identification and antigiardial activity of biocompounds produced in the Ganoderma lipsiense Mycelium in submerged fermentation[J]. Nat. Prod. Res., 2021, 35(23): 5530-5534. |
| 28 | WANG X L, ZHANG L L, CHEN N, et al.. The effects of quorum sensing molecule farnesol on the yield and activity of extracellular polysaccharide from Grifola frondosa in liquid fermentation[J]. Int. J. Biol. Macromol., 2021, 191: 377-384. |
| 29 | AHMAD QAMAR S, ASGHER M, BILAL M. Sustainable production,optimization,and partial characterization of exopolysaccharides by Macrococcus brunensis [J]. Waste Biomass Valor., 2021, 12(12): 6847-6859. |
| 30 | FENG J, FENG N, TANG Q, et al.. Development and optimization of the triterpenoid and sterol production process with Lingzhi or reishi medicinal mushroom, Ganoderma lucidum strain G0017 (Agaricomycetes), in liquid submerged fermentation at large scale[J]. Int. J. Med. Mushrooms, 2021, 23(3): 43-53. |
| 31 | ROGERS S O, BENDICH A J. Extraction of total cellular DNA from plants, algae and fungi[J]. Plant Mol. Biol. Man., 1994(1): 183-190. |
| 32 | WHITE T J, BRUNS T, LEE S, et al.. Amplification and direct sequencing of fungal ribosomal RNA genes for phylogenetics[J]. PCR Protoc. Guide Methods Appl., 1990, 18(1): 315-322. |
| 33 | LIU D, GOFFINET B, ERTZ D, et al.. Circumscription and phylogeny of the Lepidostromatales (lichenized Basidiomycota) following discovery of new species from China and Africa[J]. Mycologia, 2017, 109(5): 730-748. |
| 34 | KUMAR S, STECHER G, TAMURA K. MEGA7: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 7.0 for bigger datasets[J]. Mitochondrial DNA Resour., 2016, 33(7): 1870-1874. |
| 35 | KATOH K, STANDLEY D M. A simple method to control over-alignment in the MAFFT multiple sequence alignment program[J]. Bioinformatics, 2016, 32(13): 1933-1942. |
| 36 | STAMATAKIS A. RAxML version 8: a tool for phylogenetic analysis and post-analysis of large phylogenies[J]. Bioinformatics, 2014, 30(9): 1312-1313. |
| 37 | HUELSENBECK J P, RONQUIST F. MRBAYES: Bayesian inference of phylogenetic trees[J]. Bioinformation, 2001, 17(8): 754-755. |
| 38 | POSADA D. jModelTest: phylogenetic model averaging[J]. Mol. Biol. Evol., 2008, 25(7): 1253-1256. |
| 39 | DUBOIS M, GILLES K A, HAMILTON J K, et al.. Colorimetric method for determination of sugars and related substances[J]. Anal. Chem., 1956, 28(3): 350-356. |
| 40 | KIM H O, YUN J W. A comparative study on the production of exopolysaccharides between two entomopathogenic fungi Cordyceps militaris and Cordyceps sinensis in submerged mycelial cultures[J]. J. Appl. Microbiol., 2005, 99(4): 728-738. |
| 41 | ENSHASY H A, ELSAYED E A, SUHAIMI N, et al.. Bioprocess optimization for pectinase production using Aspergillus niger in a submerged cultivation system[J/OL]. BMC Biotechnol., 2018, 18(1): 71[2024-10-15].. |
| 42 | SULEIMENOVA Z, AKHMETSADYKOV N, KALIEVA A, et al.. Effect of different cultural conditions for phytase production by Aspergillus niger in submerged fermentation [J]. Adv. Enzyme Res., 2016, 4(2): 62-67. |
| 43 | SINGH V, HAQUE S, NIWAS R, et al.. Strategies for fermentation medium optimization: an in-depth review[J/OL]. Front. Microbiol., 2016, 7: 2087[2024-10-15]. . |
| 44 | AMERI SHAH REZA M, VAHIDI H, KOBARFARD F. Optimization of growth conditions of Lentinus edodes Mycelium and polysaccharides on walnut shell by-products using response surface analysis[J]. Iran. J. Pharm. Res., 2018, 17(4): 1509-1522. |
| 45 | XIA Y, WANG Y, ZHANG B, et al.. Effect of cultural conditions on antrodin C production by basidiomycete Antrodia camphorata in solid-state fermentation[J]. Biotechnol. Appl. Biochem., 2014, 61(6): 724-732. |
| 46 | BAISWAR P, NGACHAN S V, RYMBAI H, et al.. Simplicillium lanosoniveum, a hyperparasite on Aecidium elaeagni-latifoliae in India[J/OL]. Australas. Plant Dis. Notes, 2014, 9(1): 144[2024-10-15]. . |
| 47 | DONG Q, DONG R, XING X, et al.. A new antibiotic produced by the Cyanobacterium-symbiotic fungus Simplicillium lanosoniveum [J]. Nat. Prod. Res., 2018, 32(11): 1348-1352. |
| 48 | WARD N A, ROBERTSON C L, CHANDA A K, et al.. Effects of Simplicillium lanosoniveum on Phakopsora pachyrhizi, the soybean rust pathogen, and its use as a biological control agent[J]. Phytopathology, 2012, 102(8): 749-760. |
| 49 | DE VUYST L, VANDERVEKEN F, VAN DE VEN S, et al.. Production by and isolation of exopolysaccharides from Streptococcus thermophilus grown in a milk medium and evidence for their growth-associated biosynthesis[J]. J. Appl. Microbiol., 1998, 84(6): 1059-1068. |
| 50 | LIU G Q, WANG X L. Optimization of critical medium components using response surface methodology for biomass and extracellular polysaccharide production by Agaricus blazei [J]. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol., 2007, 74(1): 78-83. |
| 51 | 杨莲芳.川牛膝枝枯病病原鉴定及生物学特性研究[D].雅安:四川农业大学,2009. |
| 52 | 张树强. 应用单孢分离技术选育鸡腿菇优良品种[D]. 塔里木大学, 2012. |
| 53 | SCHÉMAEZA B, SOMDA I, SEREME P, et al.. Effects of temperature and pH on Mycelium growth of Phoma sorghina (Sacc.) Boerema Dorenbosch and Van Kesteren in vitro [J]. Pak. J. Biol. Sci., 2013, 16(24): 2054-2057. |
| [1] | 赵彭年,杨德玉,王加友,丁一凡,安鹏,王远. 一株亚硝化细菌的分离鉴定及其发酵工艺优化[J]. 生物技术进展, 2019, 9(1): 69-77. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
版权所有 © 2021《生物技术进展》编辑部